
Solved A Hammer Thrower Accelerates The Hammer Mass 7 30 Kg From A hammer thrower accelerates the hammer (mass = 7.30 kg) from rest within four full turns (revolutions) and releases it at a speed of 26.5 m s. assuming a uniform rate of increase in angular velocity and a horizontal circular path of radius 1.20 m, calculate. (10 53) a hammer thrower accelerates the hammer (mass = 7.30 kg) from rest within four full turns (revolutions) and releases it at a speed of 26.5 m s. assuming a.
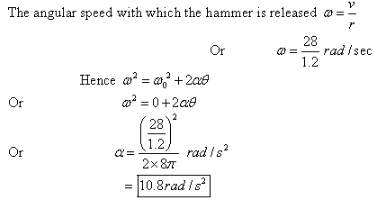
Solved A Hammer Thrower Accelerates The Hammer Mass 7 30 Kg From In a track and field event, a hammer thrower accelerates the hammer (mass = 7.30 kg) from rest within four full turns (revolutions) and releases it at a speed of 22.0 m s. assuming a uniform rate of increase in angular velocity and a radius of 1.30 m, calculate the angular acceleration. A hammer thrower accelerates the hammer (mass = 7.30 kg) from rest within four full turns (revolutions) and releases it at a speed of 27.1 m s . a) assuming a uniform rate of increase in angular velocity and a horizontal circular path of radius 1.26 m , calculate the angular acceleration. α α = nothing rad s2 b) calculate the (linear. A hammer thrower accelerates the hammer (mass \(=7.30 \mathrm{~kg}\) ) from rest within four full turns (revolutions) and releases it at a speed of \(26.5 \mathrm{~m} \mathrm{s}\). A hammer thrower accelerates the hammer (mass $=7.30 \mathrm{~kg}$ ) from rest within four full turns (revolutions) and releases it at a speed of $26….

Solved A Hammer Thrower Accelerates The Hammer Mass 7 30 Kg From A hammer thrower accelerates the hammer (mass \(=7.30 \mathrm{~kg}\) ) from rest within four full turns (revolutions) and releases it at a speed of \(26.5 \mathrm{~m} \mathrm{s}\). A hammer thrower accelerates the hammer (mass $=7.30 \mathrm{~kg}$ ) from rest within four full turns (revolutions) and releases it at a speed of $26…. A hammer thrower accelerates the hammer (mass = 7.30 kg) from rest within four full turns (revolutions) and releases it at a speed of 28.4 m s . a) assuming a uniform rate of increase in angular velocity and a horizontal circular path of radius 1.27 m , calculate the angular acceleration. A hammer thrower accelerates the hammer (mass = 7.30 kg) from rest within four full turns (revolutions) and releases it at a speed of 28.0 m s. assuming a uniform rate of increase in angular velocity and a horizontal circular path of radius 1.20 m, calculate the angular acceleration. A hammer thrower accelerates the hammer (mass = 7.30 kg) from rest within four full turns (revolutions) and releases it at a speed of 27.7 m s. a.) assuming a uniform rate of increase in angular velocity and a horizontal circular path of radius 1.30 m , calculate the angular acceleration. b.) calculate the (linear) tangential acceleration. Assuming a uniform rate of increase in angular velocity and a horizontal circular path of radius 1.20 m, calculate (a) the angular acceleration, (b) the (linear) tangential acceleration, (c) the centripetal acceleration just before release, (d) the net force being exerted on the hammer by the athlete just before release, and (e) the angle of thi.
Solved Iii A Hammer Thrower Accelerates The Hammer Mass 7 30 Kg A hammer thrower accelerates the hammer (mass = 7.30 kg) from rest within four full turns (revolutions) and releases it at a speed of 28.4 m s . a) assuming a uniform rate of increase in angular velocity and a horizontal circular path of radius 1.27 m , calculate the angular acceleration. A hammer thrower accelerates the hammer (mass = 7.30 kg) from rest within four full turns (revolutions) and releases it at a speed of 28.0 m s. assuming a uniform rate of increase in angular velocity and a horizontal circular path of radius 1.20 m, calculate the angular acceleration. A hammer thrower accelerates the hammer (mass = 7.30 kg) from rest within four full turns (revolutions) and releases it at a speed of 27.7 m s. a.) assuming a uniform rate of increase in angular velocity and a horizontal circular path of radius 1.30 m , calculate the angular acceleration. b.) calculate the (linear) tangential acceleration. Assuming a uniform rate of increase in angular velocity and a horizontal circular path of radius 1.20 m, calculate (a) the angular acceleration, (b) the (linear) tangential acceleration, (c) the centripetal acceleration just before release, (d) the net force being exerted on the hammer by the athlete just before release, and (e) the angle of thi.
