1 25m Grant To Advance Control Of 2d Materials Cornell Engineering Berman: “toward macroscale superlubricity with 2d materials“. prof. marian: "2d mxenes to tailor friction and wear from machine elements and biomedical applications to energy harvesting". In this review, we outline basic mechanisms for frictional energy dissipation during sliding of two surfaces against each other, and the procedures for manipulating friction and wear by introducing 2d materials at the tribological interface.

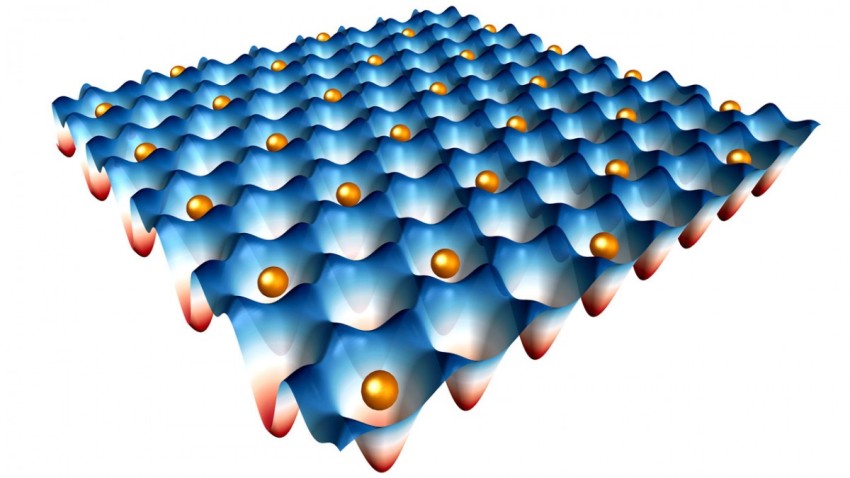
2d Materials Alchetron The Free Social Encyclopedia Two dimensional (2d) materials have demonstrated unique friction and antiwear properties unmatched by their bulk (3d) counterparts. a relatively new, large and quickly growing family of two dimensional early transition metal carbides and nitrides (mxenes) present a great potential in different applications. Firstly, superlubricious state for heterogeneous interface between 2d materials with large lattice mismatch has been predicted. the superlubricity has been attributed to the negligible interfacial charge density fluctuation during sliding, and has been realized at both nanoscale and microscale. The results reveal that macroscale structural superlubricity of 2d materials is highly dependent on the dynamic evolution of tribolayers nanostructures, as well as the adsorption and tribochemical behaviors governed by extreme pressure. In this review, we summarize the beneficial properties of layered 2d materials that enable the control of their tribological behavior and make them excellent candidates for efficient friction and wear reduction in dry running and boundary lubricated machine components.

Pdf 2d Materials The results reveal that macroscale structural superlubricity of 2d materials is highly dependent on the dynamic evolution of tribolayers nanostructures, as well as the adsorption and tribochemical behaviors governed by extreme pressure. In this review, we summarize the beneficial properties of layered 2d materials that enable the control of their tribological behavior and make them excellent candidates for efficient friction and wear reduction in dry running and boundary lubricated machine components. In this paper, we will provide an overview of recent progress in superlubricity research involving solid, liquid, and gaseous media and discuss the prospects for achieving superlubricity in engineering applications leading to greater efciency, durability, environmental fi quality, and hence global sustainability. In terms of materials, graphite, diamond like carbon, and various 2d materials have emerged as prominent superlubric materials. their unique atomic structures and properties allow for reduced friction and wear. In this review, we outline basic mechanisms for frictional energy dissipation during sliding of two surfaces against each other, and the procedures for manipulating friction and wear by. Interested in #tribology, #superlubricity, #2dmaterials, or #mxenes? check out the recording of the latest #2dmat session with prof. dr. diana berman (“toward….
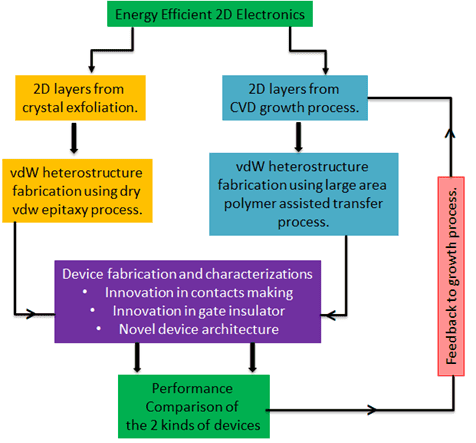
2d Materials In this paper, we will provide an overview of recent progress in superlubricity research involving solid, liquid, and gaseous media and discuss the prospects for achieving superlubricity in engineering applications leading to greater efciency, durability, environmental fi quality, and hence global sustainability. In terms of materials, graphite, diamond like carbon, and various 2d materials have emerged as prominent superlubric materials. their unique atomic structures and properties allow for reduced friction and wear. In this review, we outline basic mechanisms for frictional energy dissipation during sliding of two surfaces against each other, and the procedures for manipulating friction and wear by. Interested in #tribology, #superlubricity, #2dmaterials, or #mxenes? check out the recording of the latest #2dmat session with prof. dr. diana berman (“toward….
