
Hibbeler Chapter5 Engineering mechanics statics, 13th edition, r. c. hibbeler chapter 5: equilibrium of a rigid body problem: 5–16 *5–16. determine the components of reaction at the supports a and b on. Subscribe my channel for more problem solutions!kindly like, share and comment, this will help to promote my channel!!equilibrium of a rigid body (2d equilib.

Solution Statics And Mechanics Of Materials 5th Edition Hibbeler "in this section we will develop both the necessary and sufficient conditions required for equilibrium of a rigid body. to do this, consider the rigid body in fig. 5 1a, which is fixed in the x, y, z reference and is either at rest or moves with the reference at constant velocity. Chapter 5: equilibrium of rigid bodies academic year: 2022 textbook: engineering mechanics, statics 14th edition”, by r. c. hibbeler, 2016. united arab emirates university detailed solution with steps and explanation to the following selected problems from textbook:. Assuming that the foundation exerts a linearly varying load distribution on its bottom, determine the load intensities w 1 and w 2 for equilibrium in terms of the parameters shown. Solving these two equations, we get cx = 30656 n or 30.7 kn and cy = 3372 n or 33.7 kn. engineering mechanics: statics, twelfth edition russell c. hibbeler.

Solution Engineering Mechanics Statics Of Rigid Bodies Chapter 5 Assuming that the foundation exerts a linearly varying load distribution on its bottom, determine the load intensities w 1 and w 2 for equilibrium in terms of the parameters shown. Solving these two equations, we get cx = 30656 n or 30.7 kn and cy = 3372 n or 33.7 kn. engineering mechanics: statics, twelfth edition russell c. hibbeler. This chapter focuses on the equilibrium of rigid bodies, providing detailed free body diagrams for various mechanical systems such as dumpsters, winches, and trusses. each problem includes the determination of reactions and tension forces, illustrating the application of fundamental principles in static equilibrium. Engineering mechanics statics, 13th edition, r. c. hibbeler chapter 5: equilibrium of a rigid body problem: f5–1 f5–1. determine the horizontal and vertical components of. Chp # 5 equilibrium of a rigid body free download as pdf file (.pdf), text file (.txt) or view presentation slides online. here is the chapter 5 from rc hibbler's 14th edition from engineering mechanics. Equilibrium of a rigid body this subject is of central importance in statics. we regard a rigid body as a collection of particles. = resultant external force on particle i = internal force on particle i by particle j = internal force on particle j by particle i.

Statics And Mechanics Of Materials 5th Edition Hibbeler Solutions This chapter focuses on the equilibrium of rigid bodies, providing detailed free body diagrams for various mechanical systems such as dumpsters, winches, and trusses. each problem includes the determination of reactions and tension forces, illustrating the application of fundamental principles in static equilibrium. Engineering mechanics statics, 13th edition, r. c. hibbeler chapter 5: equilibrium of a rigid body problem: f5–1 f5–1. determine the horizontal and vertical components of. Chp # 5 equilibrium of a rigid body free download as pdf file (.pdf), text file (.txt) or view presentation slides online. here is the chapter 5 from rc hibbler's 14th edition from engineering mechanics. Equilibrium of a rigid body this subject is of central importance in statics. we regard a rigid body as a collection of particles. = resultant external force on particle i = internal force on particle i by particle j = internal force on particle j by particle i.

Hibbeler Chapter5 Chp # 5 equilibrium of a rigid body free download as pdf file (.pdf), text file (.txt) or view presentation slides online. here is the chapter 5 from rc hibbler's 14th edition from engineering mechanics. Equilibrium of a rigid body this subject is of central importance in statics. we regard a rigid body as a collection of particles. = resultant external force on particle i = internal force on particle i by particle j = internal force on particle j by particle i.
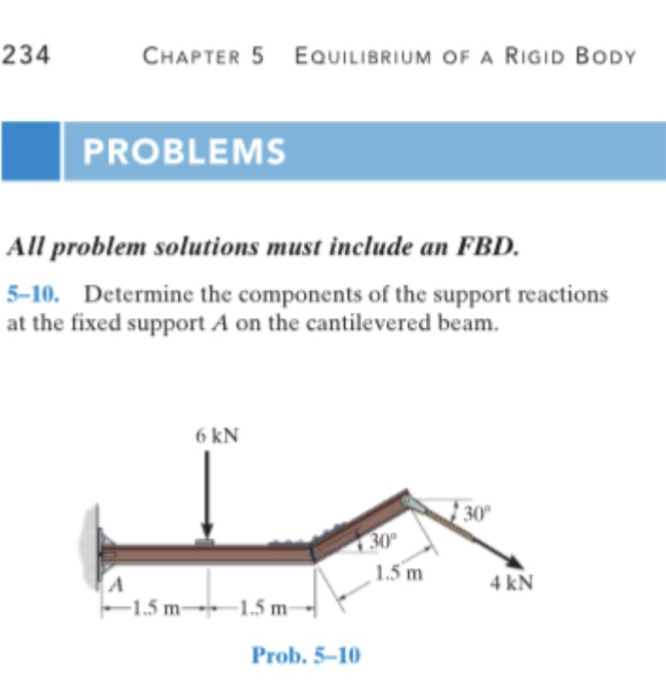
Solved 234 Chapter 5 Equilibrium Of A Rigid Body Problems Chegg
