
Chemistry Quantum Numbers Pdf Atomic Orbital Physical Chemistry Chad provides a comprehensive lesson on the atomic orbitals and quantum numbers. he describes the characteristics and shapes of the s, p, d, and f orbitals and then explains how the four. The principal quantum number is one of three quantum numbers used to characterize an orbital. an atomic orbital , which is distinct from an orbit , is a general region in an atom within which an electron is most probable to reside.
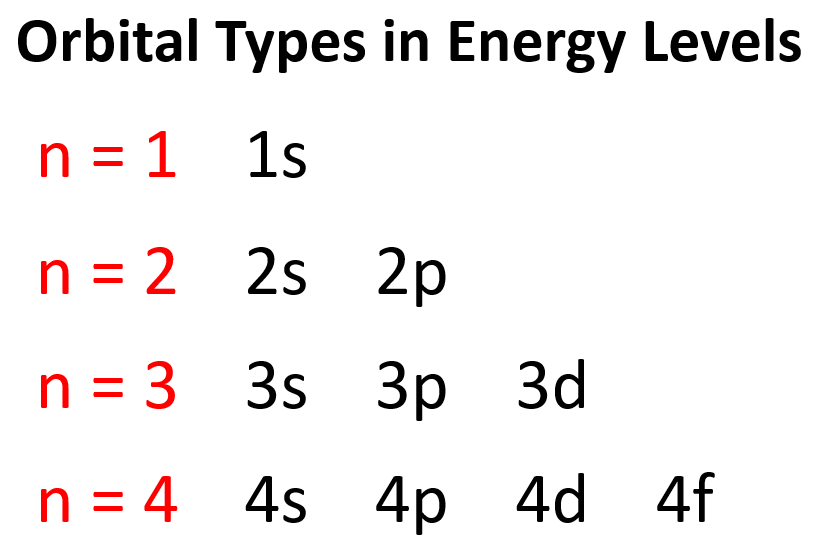
Quantum Numbers Chemistry Steps Describe the properties of an electron associated with each of the following four quantum numbers: n, l, ml, and ms. identify the subshell in which electrons with the following quantum numbers are found: consider the orbitals shown here in outline. what is the maximum number of electrons contained in an orbital of type (x)? of type (y)?. The principal quantum number, n, gives the electronic shell in which an electron resides and can have values from 1 to ∞. for an electron in the 1s orbital n=1. for an electron in a 2s or 2p orbital n=2. In atoms, there are a total of four quantum numbers: the principal quantum number (n), the orbital angular momentum quantum number (l), the magnetic quantum number (ml), and the electron spin quantum number (ms). the principal quantum number, n n, describes the energy of an electron and the most probable distance of the electron from the nucleus. There are four types of atomic orbitals – s, p, d, and f. each orbital has a characteristic shape shown below: s orbitals have a spherical shape, p orbitals are dumbbell shaped, d orbitals are shaped like a cloverleaf, and f orbitals are characterized by more complex shapes.
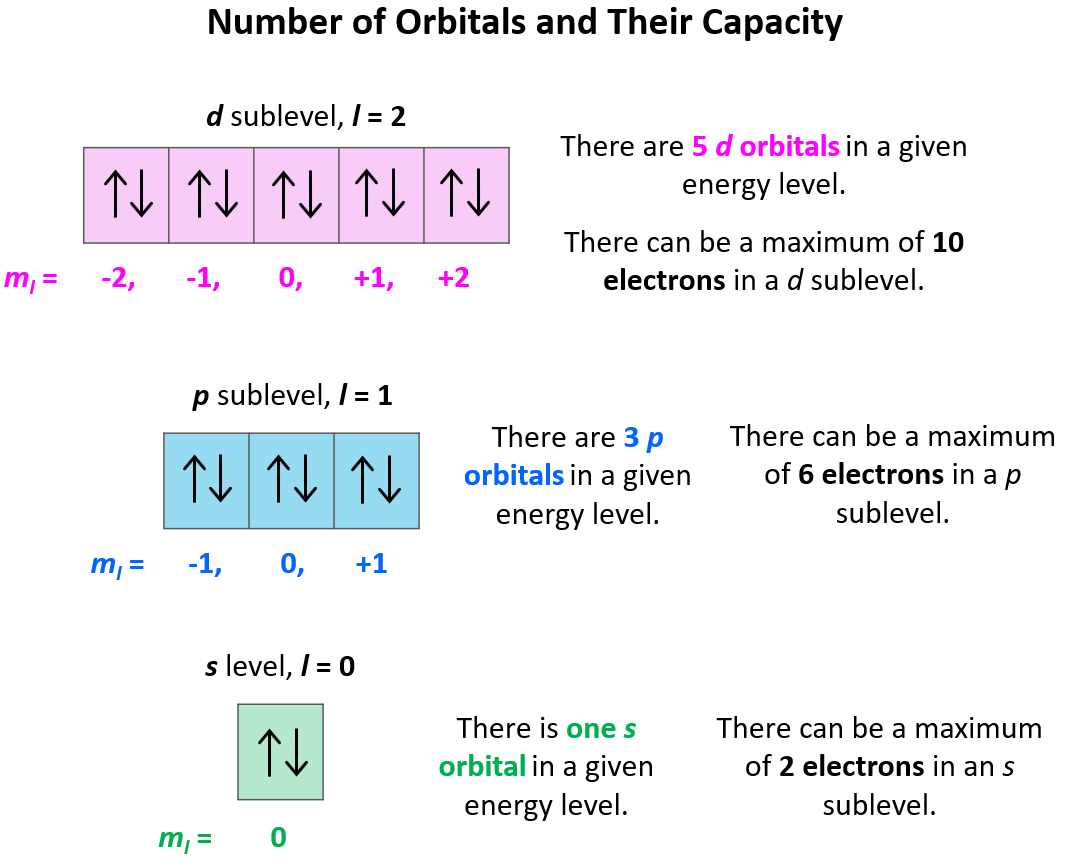
Quantum Numbers Chemistry Steps In atoms, there are a total of four quantum numbers: the principal quantum number (n), the orbital angular momentum quantum number (l), the magnetic quantum number (ml), and the electron spin quantum number (ms). the principal quantum number, n n, describes the energy of an electron and the most probable distance of the electron from the nucleus. There are four types of atomic orbitals – s, p, d, and f. each orbital has a characteristic shape shown below: s orbitals have a spherical shape, p orbitals are dumbbell shaped, d orbitals are shaped like a cloverleaf, and f orbitals are characterized by more complex shapes. Thus, it takes three quantum numbers to define an orbital but four quantum numbers to identify one of the electrons that can occupy the orbital. the allowed combinations of n, l, and m quantum numbers for the first four shells are given in the table below. Having introduced the basics of atomic structure and quantum mechanics, we can use our understanding of quantum numbers to determine how atomic orbitals relate to one another. this allows us to determine which orbitals are occupied by electrons in each atom. We can describe the electron in the hydrogen atom with four quantum numbers — n, l, m l, and m s. below are the descriptions of each quantum number. 1. principle quantum number, n. describes the energy of an oribal a well as the relative size of an orbital. the principle quantum number, n, is a positive integer; n = 1, 2, 3, ….∞. Quantum numbers and atomic orbitals each electron in an atom is described by four different quantum numbers (n, l, m l, & m s) 1.principal quantum number (n): specifies the energy of an electron and the size of the orbital. all orbitals that have the same value of n are said to be in the same shell (level). n takes the values of 1, 2, 3, …, ∞.
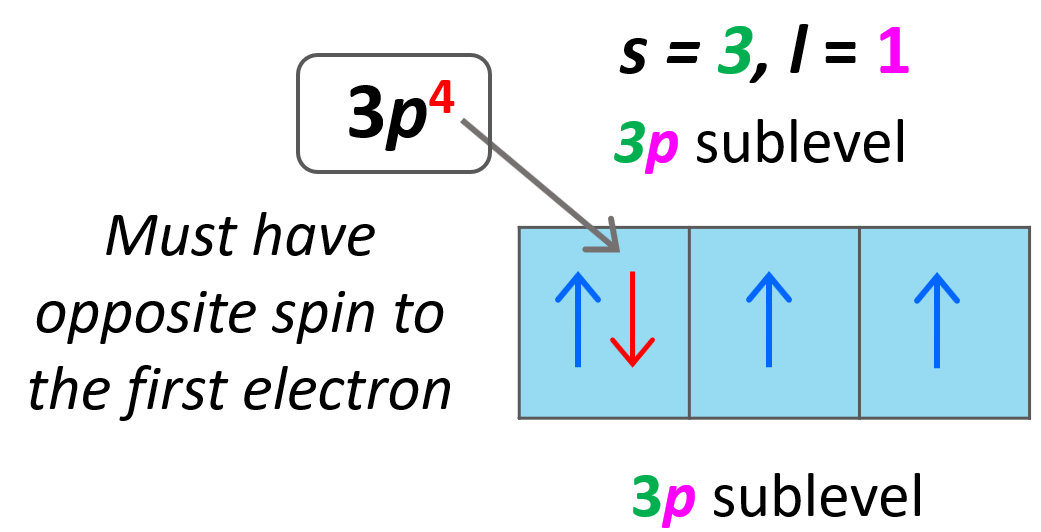
Quantum Numbers Chemistry Steps Thus, it takes three quantum numbers to define an orbital but four quantum numbers to identify one of the electrons that can occupy the orbital. the allowed combinations of n, l, and m quantum numbers for the first four shells are given in the table below. Having introduced the basics of atomic structure and quantum mechanics, we can use our understanding of quantum numbers to determine how atomic orbitals relate to one another. this allows us to determine which orbitals are occupied by electrons in each atom. We can describe the electron in the hydrogen atom with four quantum numbers — n, l, m l, and m s. below are the descriptions of each quantum number. 1. principle quantum number, n. describes the energy of an oribal a well as the relative size of an orbital. the principle quantum number, n, is a positive integer; n = 1, 2, 3, ….∞. Quantum numbers and atomic orbitals each electron in an atom is described by four different quantum numbers (n, l, m l, & m s) 1.principal quantum number (n): specifies the energy of an electron and the size of the orbital. all orbitals that have the same value of n are said to be in the same shell (level). n takes the values of 1, 2, 3, …, ∞.
