A Atrial Flutter With Variable And 1 1 Av Conduction The Second And

A Atrial Flutter With Variable And 1 1 Av Conduction The Second And While atrial flutter with varying degrees of a v block is usually diagnosed readily with the aid of the electrocardiogram, 1:1 a v conduction has been confused with paroxysmal atrial, nodal and ventricular tachycardias and ventricular flutter. Abstract atrial flutter usually occurs with some degree of a v block; however, uncommonly it occurs without a v block, i. e., with 1: 1 a v conduction. this is an infrequent arrhythmia and is regarded as the most rapid form of tachycardia known to occur in the adult. 2 it is a prostrating event because of the extreme rapidity of the heart beat.
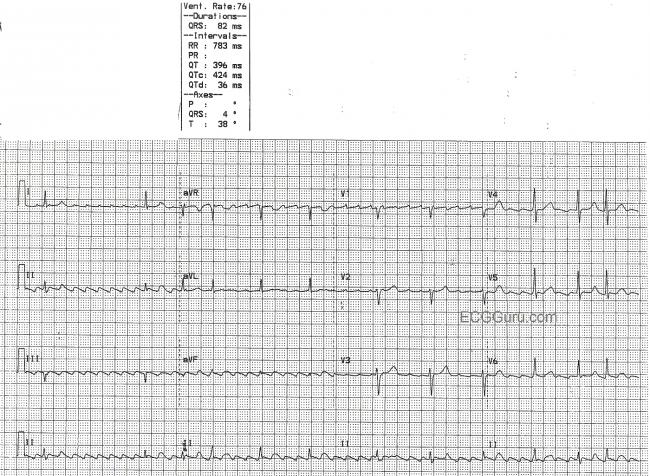
Atrial Flutter With Variable Conduction Ecg Guru Instructor Resources After receiving a bolus of amiodarone, an interval ecg showed afl with variable block and a flutter rate of 94 beats per minute, consistent with 1:1 afl under flecainide use (figure 2). The presence of electrical (or qrs) and t wave alternans is more suggestive that this is a supraventricular tachyarrhythmia, and likely flutter with 1:1 av conduction. although it has been reported that electrical alternans may occur in ventricular tachycardia, this is very unusual. (a) atrial flutter with variable and 1:1 av conduction. the second and fifth qrs complexes are pre excited (short arrows) with evidence of antegrade conduction down a left. The p waves, also called flutter waves, march out regularly at a rate of around 300 minute, which is typical of atrial flutter. the conduction ratio is variable, and the intervals between the conducted p waves and the qrs complexes vary, as well, reflecting changing refractoriness of the av node.

Atrial Flutter With Variable Conduction Download Scientific Diagram (a) atrial flutter with variable and 1:1 av conduction. the second and fifth qrs complexes are pre excited (short arrows) with evidence of antegrade conduction down a left. The p waves, also called flutter waves, march out regularly at a rate of around 300 minute, which is typical of atrial flutter. the conduction ratio is variable, and the intervals between the conducted p waves and the qrs complexes vary, as well, reflecting changing refractoriness of the av node. Two ecgs at one hour interval showed atrial flutter with 1:1 and 2:1 av conduction (ecg 3 and ecg 4), respectively. she was initially treated with rate control strategy, and while waiting for dc cardioversion as an outpatient she reverted to sinus rhythm. Interpreting an atrial flutter ecg involves identifying its unique waveforms and conduction ratios. the primary hallmark is the presence of continuous flutter waves in leads ii, iii, and avf, without distinct p waves. these waves occur at regular intervals, often producing a "sawtooth" pattern. Ecg with atrial flutter and constant 5:1 atrioventricular (av) conduction. the lead ii rhythm strip at the bottom shows a fixed flutter wave to qrs interval, indicating the presence of atrioventricular conduction. We present a unique case of atrial flutter with 1:1 av conduction with no known trigger. case presentation: a 70 year old male with a history of hypertension, hyperlipidemia, sleep apnea and diabetes presented for evaluation of mild lightheadedness that began several days prior to presentation.

Atrial Flutter With Variable Conduction Royalty Free Stock Photography Two ecgs at one hour interval showed atrial flutter with 1:1 and 2:1 av conduction (ecg 3 and ecg 4), respectively. she was initially treated with rate control strategy, and while waiting for dc cardioversion as an outpatient she reverted to sinus rhythm. Interpreting an atrial flutter ecg involves identifying its unique waveforms and conduction ratios. the primary hallmark is the presence of continuous flutter waves in leads ii, iii, and avf, without distinct p waves. these waves occur at regular intervals, often producing a "sawtooth" pattern. Ecg with atrial flutter and constant 5:1 atrioventricular (av) conduction. the lead ii rhythm strip at the bottom shows a fixed flutter wave to qrs interval, indicating the presence of atrioventricular conduction. We present a unique case of atrial flutter with 1:1 av conduction with no known trigger. case presentation: a 70 year old male with a history of hypertension, hyperlipidemia, sleep apnea and diabetes presented for evaluation of mild lightheadedness that began several days prior to presentation.

Atrial Flutter With Variable Conduction Royalty Free Stock Photography Ecg with atrial flutter and constant 5:1 atrioventricular (av) conduction. the lead ii rhythm strip at the bottom shows a fixed flutter wave to qrs interval, indicating the presence of atrioventricular conduction. We present a unique case of atrial flutter with 1:1 av conduction with no known trigger. case presentation: a 70 year old male with a history of hypertension, hyperlipidemia, sleep apnea and diabetes presented for evaluation of mild lightheadedness that began several days prior to presentation.
Comments are closed.