
A Neutrino Diffuse Signal From The Milky Way Detected By Icecube Antares We show that the γ rays accompanying the high energy neutrinos recently observed by the icecube observatory from the galactic plane have a flux that is consistent with the gde γ observed by the {\it fermi} lat and tibet as γ experiments around 1 tev and 0.5 pev, respectively. A neutrino diffuse signal from the milky way detected by icecube 29 june 2023 the galactic ridge is a region of the inner galaxy coincident with the galactic plane of the milky way.

A Neutrino Diffuse Signal From The Milky Way Detected By Icecube Antares High energy neutrinos have been observed from the milky way by the icecube observatory between 0.5 tev and multi petaelectronvolts 1, 2. the galactic diffuse emission (gde) in neutrinos. The high energy neutrinos, with energies millions to billions of times higher than those produced by the fusion reactions that power stars, were detected by the icecube neutrino observatory, a gigaton detector operating at the amundsen scott south pole station. Today on june 29th, the icecube collaboration has announced a highly significant evidence for neutrinos coming from the galactic ridge using data collected with the icecube neutrino telescope located at the south pole. The icecube collaboration searched for neutrino emission from within the milky way (see the perspective by fusco) and found evidence of extra neutrinos emitted along the plane of the galaxy, which is consistent with the distribution of gamma ray emission.
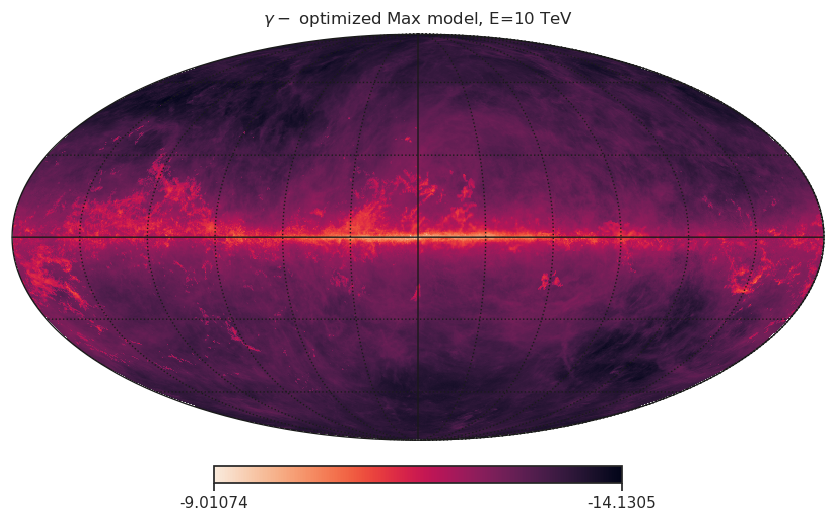
A Neutrino Diffuse Signal From The Milky Way Detected By Icecube Antares Today on june 29th, the icecube collaboration has announced a highly significant evidence for neutrinos coming from the galactic ridge using data collected with the icecube neutrino telescope located at the south pole. The icecube collaboration searched for neutrino emission from within the milky way (see the perspective by fusco) and found evidence of extra neutrinos emitted along the plane of the galaxy, which is consistent with the distribution of gamma ray emission. To detect cosmic neutrinos, very large volume neutrino observatories monitor natural bodies of water or ice for the cherenkov light induced by the passage of the charged particles that. Scientists detected a high energy neutrino emission from within the milky way for the very first time using the icecube neutrino observatory, a press statement reveals. Search for neutrino emission using machine learning techniques applied to ten years of data from the icecube neutrino observatory. we identify neutrino emission from the galactic plane at the 4.5σlevel of significance, by compar ing diffuse emission models to a background only hypothesis. the signal is. Once a neutrino interacts with the medium in which the detector is situated (the antarctic ice, for example), it will produce relativistic, subatomic, charged particles. if the medium is transparent to light, the cherenkov radiation emitted in the process can be detected.

A Neutrino Diffuse Signal From The Milky Way Detected By Icecube Antares To detect cosmic neutrinos, very large volume neutrino observatories monitor natural bodies of water or ice for the cherenkov light induced by the passage of the charged particles that. Scientists detected a high energy neutrino emission from within the milky way for the very first time using the icecube neutrino observatory, a press statement reveals. Search for neutrino emission using machine learning techniques applied to ten years of data from the icecube neutrino observatory. we identify neutrino emission from the galactic plane at the 4.5σlevel of significance, by compar ing diffuse emission models to a background only hypothesis. the signal is. Once a neutrino interacts with the medium in which the detector is situated (the antarctic ice, for example), it will produce relativistic, subatomic, charged particles. if the medium is transparent to light, the cherenkov radiation emitted in the process can be detected.

A Neutrino Diffuse Signal From The Milky Way Detected By Icecube Antares Search for neutrino emission using machine learning techniques applied to ten years of data from the icecube neutrino observatory. we identify neutrino emission from the galactic plane at the 4.5σlevel of significance, by compar ing diffuse emission models to a background only hypothesis. the signal is. Once a neutrino interacts with the medium in which the detector is situated (the antarctic ice, for example), it will produce relativistic, subatomic, charged particles. if the medium is transparent to light, the cherenkov radiation emitted in the process can be detected.
