
Solved Let A 1 2 3 4 5 And B 0 3 6 Find A B Chegg Solution for 24.4. let a = {1, 2} and b = {3, 4). write down all functions f : a → b. indicate which are one to one and which are onto b. Let a = {1, 2, 3, 4}. let f be the set of all functions from a to a. define a relation r on f as follows: for all f,g ∈ f, frg if and only if there exists x ∈ a so that f(x) ≤ g(x). (a) is r reflexive?.
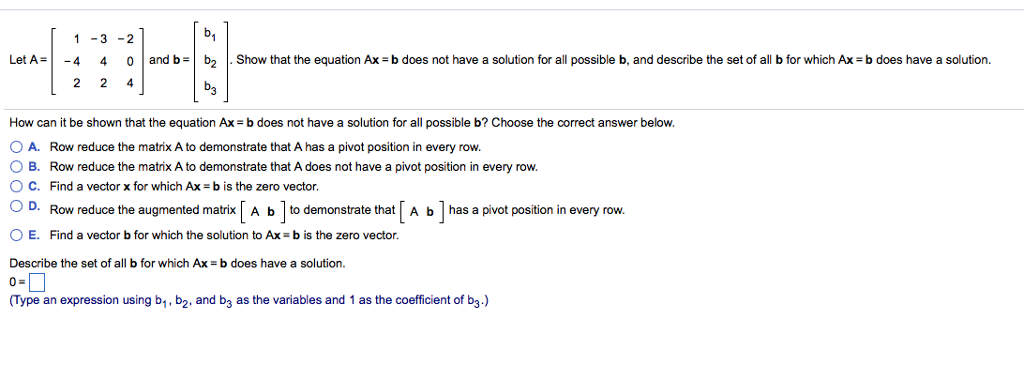
Solved Let A 1 3 2 4 4 0 2 2 4 And B B 1 B 2 Chegg Solution for let a = {1, 2, 3, 4], b = {a, b, c}, c = {x, y, z}. consider the relations r from a to b and s from b to c as follows: r = {(1, b), (3, a), (3,…. Let a = (1, 2, 3, 4), b = (1, 2, 3] and c = (2, 4). find all sets x satisfying each pair of following conditions : (i) x is the subset of b and x is not the subset of c . (ii) x is the subset of b,x is not equal to b and x is not the subset of c . find math textbook solutions? still have questions? 9. Let a = {1, 2}, b = {1, 2, 3, 4}, c = {5, 6} and d = {5, 6, 7, 8}. verify that a × c is a subset of b × d. if a and b are two set having 3 elements in common. if n (a) = 5, n (b) = 4, find n (a × b) and n [ (a × b) ∩ (b × a)]. state whether of the statement is true or false. if the statement is false, re write the given statement correctly:. Solution for let x = {1, 2, 3, 4}. determine whether each relation on x is a function from x into x. (a) f = {(2, 3), (1, 4), (2, 1), (3.2), (4, 4)} (b) g =….
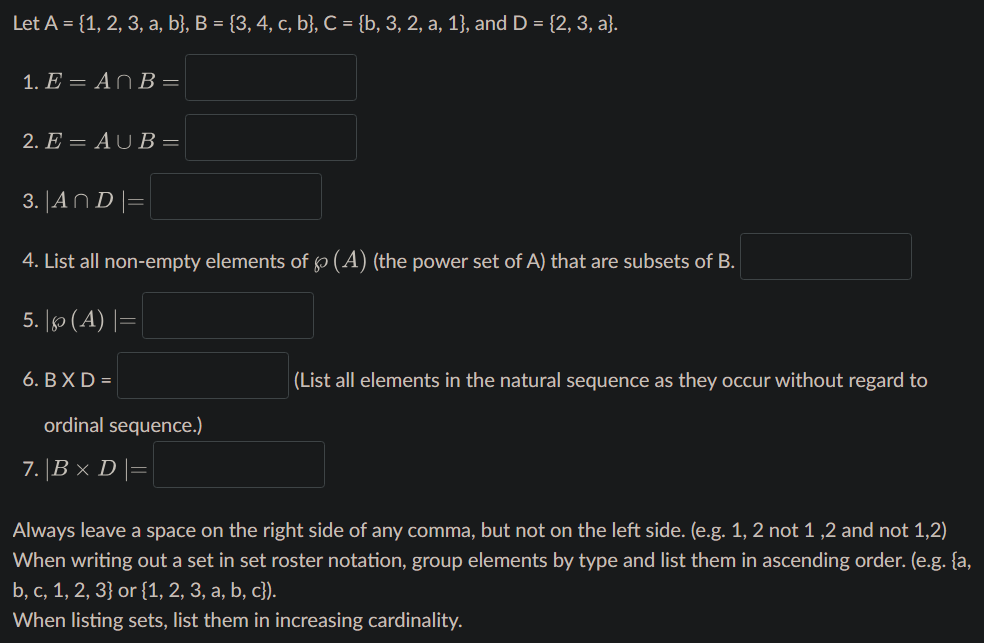
Solved Let A 1 2 3 A B B 3 4 C B C B 3 2 A 1 And Chegg Let a = {1, 2}, b = {1, 2, 3, 4}, c = {5, 6} and d = {5, 6, 7, 8}. verify that a × c is a subset of b × d. if a and b are two set having 3 elements in common. if n (a) = 5, n (b) = 4, find n (a × b) and n [ (a × b) ∩ (b × a)]. state whether of the statement is true or false. if the statement is false, re write the given statement correctly:. Solution for let x = {1, 2, 3, 4}. determine whether each relation on x is a function from x into x. (a) f = {(2, 3), (1, 4), (2, 1), (3.2), (4, 4)} (b) g =…. Let a = {1, 2}, b = {1, 2, 3, 4}, c = {5, 6} and d = {5, 6, 7, 8}. verify that a × (b ∩ c) = (a × b) ∩ (a × c) let a and b be two sets such that n (a) = 3 and n (b) = 2. if (x, 1), (y, 2), (z, 1) are in a × b, find a and b, where x, y and z are distinct elements. the cartesian product a × a has 9 elements among which are found (–1, 0) and (0, 1). Let a = {1, 2, 3}, b = {2, 3, 4}, then which of the following is a function from a to b? option : (c) a function is said to be defined from a to b if each element in set a has an unique image in set b. not all the elements in set b are the images of any element of set a. therefore, option c is correct. The union a∪b is {1, 2, 3, 4}. the set difference b\c is {3}. explanation: b∪c = {3, 4} (the union of b and c includes all the elements that are present in either set b or set c, or in both sets. since set b contains the element 3 and set c contains the element 4, the union of b and c is {3, 4}.) a∩b = ∅ (the intersection of a and b is. It is reflexive if this is a relation over the set $\{1,2,3,4\}$, and yes, the relation is symmetric. yes, if we remove $(1,2)$ or $(2,1)$ then it is anti symmetric. the relation is transitive, we do not need $(2,3)$ and $(3,4)$ to be in the set.
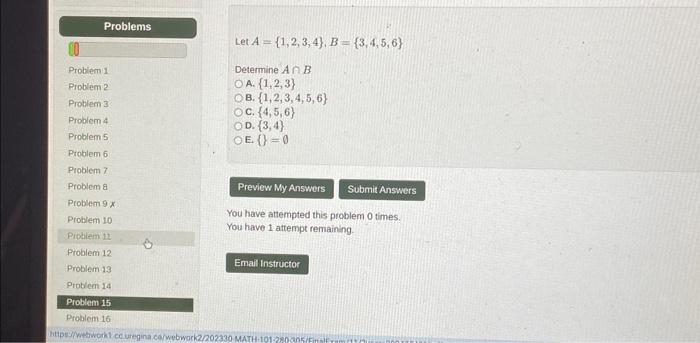
Solved Let A 1 2 3 4 B 3 4 5 6 Determine Aв B A 1 2 3 Chegg Let a = {1, 2}, b = {1, 2, 3, 4}, c = {5, 6} and d = {5, 6, 7, 8}. verify that a × (b ∩ c) = (a × b) ∩ (a × c) let a and b be two sets such that n (a) = 3 and n (b) = 2. if (x, 1), (y, 2), (z, 1) are in a × b, find a and b, where x, y and z are distinct elements. the cartesian product a × a has 9 elements among which are found (–1, 0) and (0, 1). Let a = {1, 2, 3}, b = {2, 3, 4}, then which of the following is a function from a to b? option : (c) a function is said to be defined from a to b if each element in set a has an unique image in set b. not all the elements in set b are the images of any element of set a. therefore, option c is correct. The union a∪b is {1, 2, 3, 4}. the set difference b\c is {3}. explanation: b∪c = {3, 4} (the union of b and c includes all the elements that are present in either set b or set c, or in both sets. since set b contains the element 3 and set c contains the element 4, the union of b and c is {3, 4}.) a∩b = ∅ (the intersection of a and b is. It is reflexive if this is a relation over the set $\{1,2,3,4\}$, and yes, the relation is symmetric. yes, if we remove $(1,2)$ or $(2,1)$ then it is anti symmetric. the relation is transitive, we do not need $(2,3)$ and $(3,4)$ to be in the set.
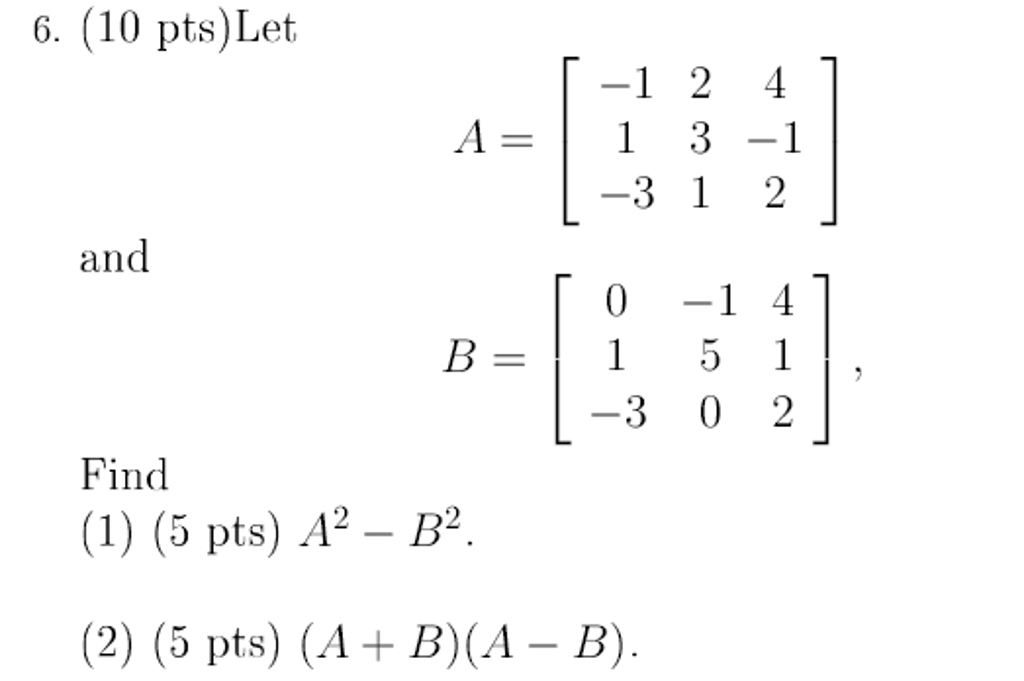
Solved Let A 1 1 3 2 3 1 4 1 2 And B 0 1 3 1 Chegg The union a∪b is {1, 2, 3, 4}. the set difference b\c is {3}. explanation: b∪c = {3, 4} (the union of b and c includes all the elements that are present in either set b or set c, or in both sets. since set b contains the element 3 and set c contains the element 4, the union of b and c is {3, 4}.) a∩b = ∅ (the intersection of a and b is. It is reflexive if this is a relation over the set $\{1,2,3,4\}$, and yes, the relation is symmetric. yes, if we remove $(1,2)$ or $(2,1)$ then it is anti symmetric. the relation is transitive, we do not need $(2,3)$ and $(3,4)$ to be in the set.
