Atomic Structure Atomic Number Mass Number And Electron

Atoms Elements Atomic Number And Atomic Mass Number 1 Pdf Atoms The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom is its atomic number (\ (z\)). this is the defining trait of an element: its value determines the identity of the atom. for example, any atom that contains six protons is the element carbon and has the atomic number 6, regardless of how many neutrons or electrons it may have. a neutral atom must contain the same number of positive and negative. Because each proton and each neutron contribute approximately one amu to the mass of an atom, and each electron contributes far less, the atomic mass of a single atom is approximately equal to its mass number (a whole number).
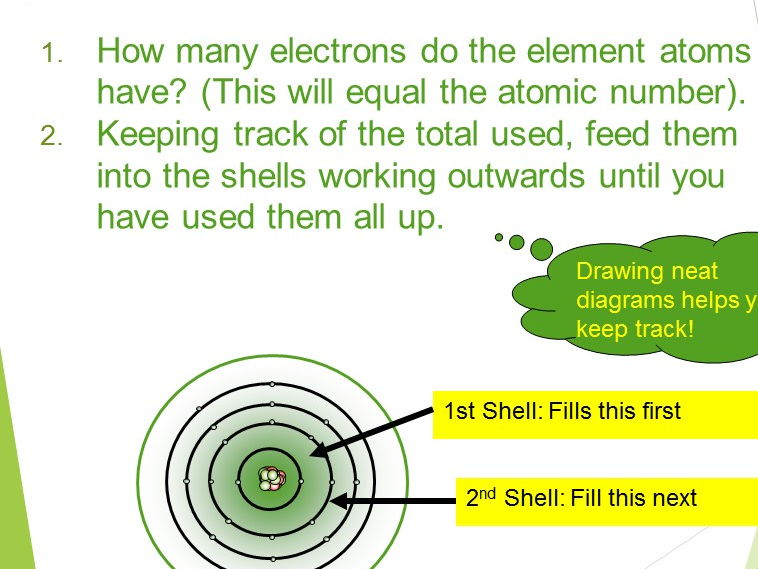
Atomic Structure Atomic Number Mass Number And Electron Learn about and revise atomic structure with this bbc bitesize gcse chemistry (aqa) study guide. Atomic number and mass number are always whole numbers because they are obtained by counting whole objects (protons, neutrons, and electrons). the sum of the mass number and the atomic number for an atom (a z) corresponds to the total number of subatomic particles present in the atom. The nucleus (or center) of an atom is made up of protons and neutrons. the number of protons in the nucleus, known as the "atomic number," primarily determines where that atom fits on the periodic table. the number of protons in the nucleus also defines in large part the characteristics of an atom—is it a gas or a metal, for example. Based on these, we can define and understand some important concepts related to atoms, such as valency, atomic number, mass number, and isotopes. the electrons in the outermost shell of an atom are called valence electrons. these electrons are involved in chemical bonding.

Atomic Structure Atomic Number Mass Number And Electron The nucleus (or center) of an atom is made up of protons and neutrons. the number of protons in the nucleus, known as the "atomic number," primarily determines where that atom fits on the periodic table. the number of protons in the nucleus also defines in large part the characteristics of an atom—is it a gas or a metal, for example. Based on these, we can define and understand some important concepts related to atoms, such as valency, atomic number, mass number, and isotopes. the electrons in the outermost shell of an atom are called valence electrons. these electrons are involved in chemical bonding. Electrons have a negligible mass, so we don’t usually count it when working out the mass of an atom. it is useful to know what the nuclear symbols are: we can perform calculations to determine the number of subatomic particles. ions are formed from atoms when electrons are transferred between them:. Protons, neutrons and electrons have charges and masses. the masses and charges are too small to be much use in chemistry. for example, the mass of a single electron is 9.109 × 10 −31 kilograms. we, therefore, use relative values for the masses and charges of the subatomic particles, shown below. Determine the number of protons, neutrons, and electrons in an atom. identify the charge and relative mass of subatomic particles. label the location of subatomic particles in the atom. determine the mass of an atom based on its subatomic particles. write a z and symbol mass format for an atom. Atomic structure underpins the behaviour of elements, their interactions, and the formation of molecules. these are fundamental to chemistry, physics, and many applied sciences. this resource explains the structure of atoms, atomic numbers and mass numbers, and isotopes and atomic masses.
Comments are closed.