Autotrophic Nutrition Definition Types And Examples Geeksforgeeks Autotrophs play a vital role in the carbon cycle, producing oxygen as a byproduct of photosynthesis and serving as primary producers in food chains. in this article, we will study autotrophs, their types, examples and functions in the ecosystem. Nutrition can be divided into two main types: the autotrophic mode of nutrition, where organisms produce their own food, and the heterotrophic mode of nutrition, where organisms consume other living organisms or organic matter for nutrients.
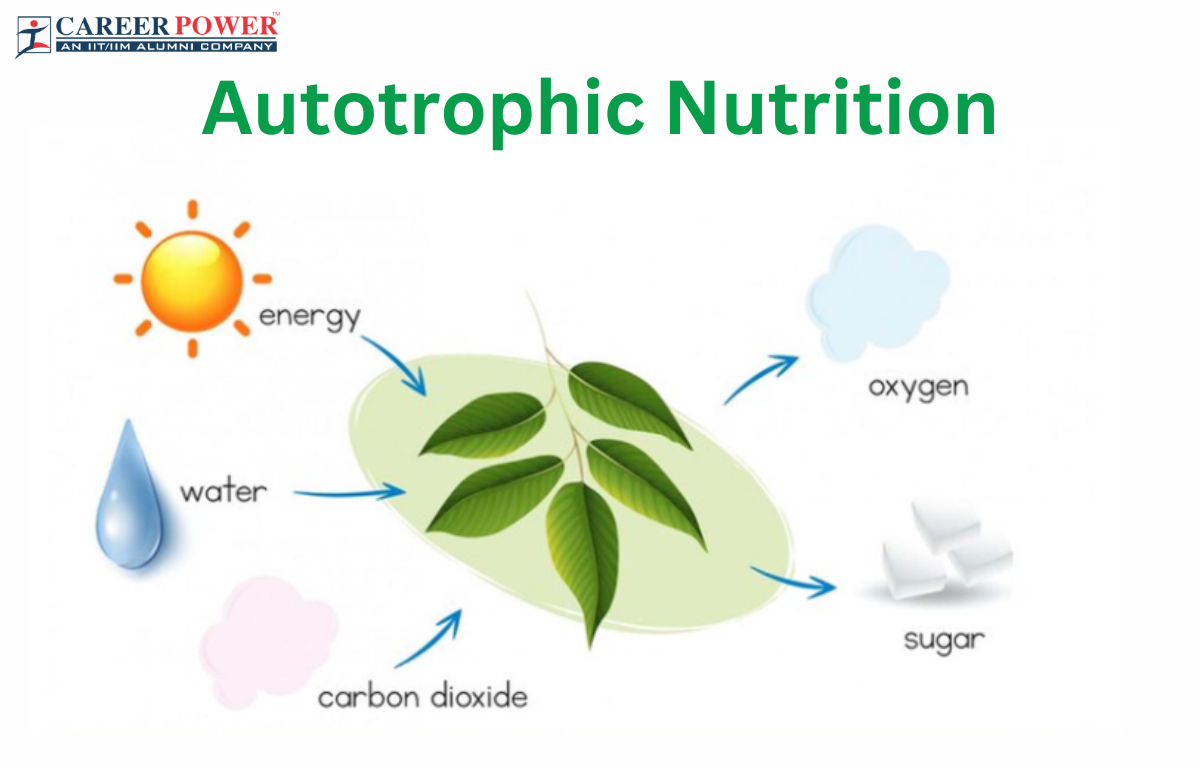
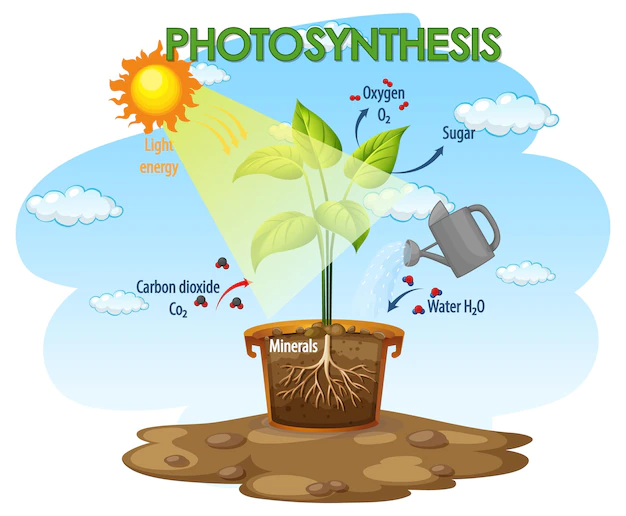
What Is Autotrophic Nutrition Types And Examples Of A Vrogue Co Discover how plants and certain microbes produce their own food through autotrophic nutrition. learn about photosynthesis, key examples, and the difference between autotrophic nutrition and heterotrophic nutrition. “autotrophic nutrition is a process where an organism prepares its own food from a simple inorganic material like water, mineral salts and carbon dioxide in the presence of sunlight.”. Autotrophic nutrition is a process where organisms synthesize their organic compounds from inorganic substances found in their environment. in simpler terms, these organisms are capable of converting simple inorganic compounds into complex organic molecules that serve as their source of sustenance. What is autotrophic nutrition? autotrophic nutrition is a biological process in which organisms produce their own organic compounds, such as carbohydrates, using simple inorganic substances like carbon dioxide and water.

Autotrophic Nutrition Definition Types Examples Protonstalk Autotrophic nutrition is a process where organisms synthesize their organic compounds from inorganic substances found in their environment. in simpler terms, these organisms are capable of converting simple inorganic compounds into complex organic molecules that serve as their source of sustenance. What is autotrophic nutrition? autotrophic nutrition is a biological process in which organisms produce their own organic compounds, such as carbohydrates, using simple inorganic substances like carbon dioxide and water. Autotrophic nutrition, derived from the greek words “auto” meaning “self” and “trophe” meaning “nutrition,” refers to the mode of nutrition in which organisms produce their own food. they accomplish this by synthesising complex organic compounds from simple inorganic substances, such as carbon dioxide and water, in the presence of sunlight. ‘auto’ means ‘self’ and ‘troph’ means ‘nutrition’. therefore, the organisms which make their own food from simple inorganic sources like carbon dioxide and water are known as autotrophs. the end product is an organic product like glucose . all green plants are autotrophs. some bacteria are also autotrophic. The literal meaning of autotrophic nutrition is self nutrition. therefore, in the process of autotrophic nutrition, organisms make their own sustenance from straightforward inorganic components including water, mineral salts and carbon dioxide.

Autotrophic Nutrition Definition Types Examples Protonstalk Autotrophic nutrition, derived from the greek words “auto” meaning “self” and “trophe” meaning “nutrition,” refers to the mode of nutrition in which organisms produce their own food. they accomplish this by synthesising complex organic compounds from simple inorganic substances, such as carbon dioxide and water, in the presence of sunlight. ‘auto’ means ‘self’ and ‘troph’ means ‘nutrition’. therefore, the organisms which make their own food from simple inorganic sources like carbon dioxide and water are known as autotrophs. the end product is an organic product like glucose . all green plants are autotrophs. some bacteria are also autotrophic. The literal meaning of autotrophic nutrition is self nutrition. therefore, in the process of autotrophic nutrition, organisms make their own sustenance from straightforward inorganic components including water, mineral salts and carbon dioxide.

What Is Autotrophic Nutrition Types And Examples Of A Vrogue Co The literal meaning of autotrophic nutrition is self nutrition. therefore, in the process of autotrophic nutrition, organisms make their own sustenance from straightforward inorganic components including water, mineral salts and carbon dioxide.
