
Psmod Topic 4 Numerical Descriptive Measures Nan Pdf Statistics Mean In a more strict sense, the skewness does not relate to the relationship between mean and median, particularly in the case of multimodal distributions and discrete distributions. this is a quick. Some numerical measure of how much confidence we have in such statements. in this chapter, we look at several statistical measures used to describe data and draw statistical inferences. 3.1 mean the most well known descriptive statistic is the mean, or average value, which is obtained.
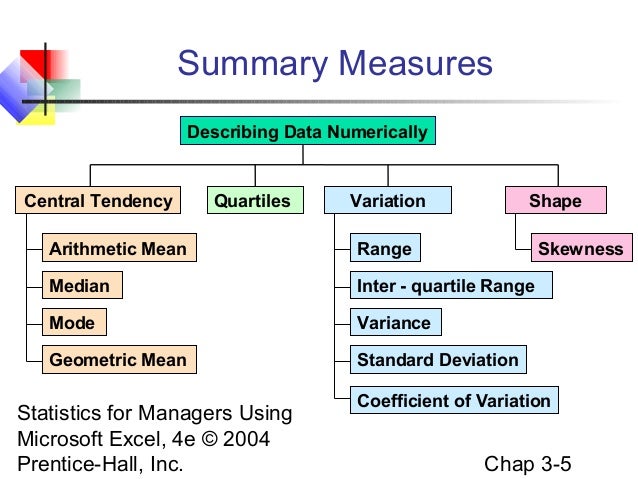
Chap03 Numerical Descriptive Measures Chapter 3: descriptive statistics: numerical measures learning objectives after studying this chapter and doing the exercises, you should be able to calculate and interpret the following statistical measures that help to describe the central location, variability and shape of data sets. 1. the mean, median and mode (measures of central location. We introduce numerical measures of location, dispersion, shape and association. if the measures are computed for data from a sample, they are called sample statistics . Numerical measures if the measures are computed for data from a sample, they are called sample statistics. if the measures are computed for data from a population, they are called ☆ descriptive population parameters. ☆ inferential data data. Descriptive statistics discussed previously described a sample, not the population. summary measures describing a population, called parameters, are denoted with greek letters. important population parameters are the population mean, variance, and standard deviation. which measure to choose?.

Ppt Chapter 3 Part A Descriptive Statistics Numerical Measures Numerical measures if the measures are computed for data from a sample, they are called sample statistics. if the measures are computed for data from a population, they are called ☆ descriptive population parameters. ☆ inferential data data. Descriptive statistics discussed previously described a sample, not the population. summary measures describing a population, called parameters, are denoted with greek letters. important population parameters are the population mean, variance, and standard deviation. which measure to choose?. Measure of location. identify the position of the mean, median, and mode for both symmetric and skewed distributions. compute and interpret the range, mean deviation, variance, and standard deviation. understand the characteristics, uses, advantages, and disadvantages of each measure of dispersion. (1) the covariance measures the strength of the linear relationship between two numerical variables (xand y). (2) the sample covariance is computed from the following equation:. Describing data: numerical measures true false 1. the arithmetic mean is the sum of the observations divided by the total number of observations. 2. for a set of data arranged or sorted in numerical order, the value of the observation in the center is called the weighted mean. 3. Chapter 3 descriptive statistics: numerical measures learning objectives 1. understand the purpose of measures of location. 2. be able to compute the mean, weighted mean, geometric mean, median, mode, quartiles, and various percentiles. 3. understand the purpose of measures of variability. 4.

Chapter 3 Numerical Descriptive Measures Chapter 3 Numerical Measure of location. identify the position of the mean, median, and mode for both symmetric and skewed distributions. compute and interpret the range, mean deviation, variance, and standard deviation. understand the characteristics, uses, advantages, and disadvantages of each measure of dispersion. (1) the covariance measures the strength of the linear relationship between two numerical variables (xand y). (2) the sample covariance is computed from the following equation:. Describing data: numerical measures true false 1. the arithmetic mean is the sum of the observations divided by the total number of observations. 2. for a set of data arranged or sorted in numerical order, the value of the observation in the center is called the weighted mean. 3. Chapter 3 descriptive statistics: numerical measures learning objectives 1. understand the purpose of measures of location. 2. be able to compute the mean, weighted mean, geometric mean, median, mode, quartiles, and various percentiles. 3. understand the purpose of measures of variability. 4.

Module 3 Descriptive Statistics Pdf Mode Statistics Mean Describing data: numerical measures true false 1. the arithmetic mean is the sum of the observations divided by the total number of observations. 2. for a set of data arranged or sorted in numerical order, the value of the observation in the center is called the weighted mean. 3. Chapter 3 descriptive statistics: numerical measures learning objectives 1. understand the purpose of measures of location. 2. be able to compute the mean, weighted mean, geometric mean, median, mode, quartiles, and various percentiles. 3. understand the purpose of measures of variability. 4.
