Binomial Expansion Binomial Theorem Ib Maths Aa Sl Hl

Ib Math Aa Sl Binomial Theorem Pdf Mathematical Analysis The binomial distribution is a special case of the poisson binomial distribution, which is the distribution of a sum of n independent non identical bernoulli trials b (pi). Important notes: the trials are independent, there are only two possible outcomes at each trial, the probability of "success" at each trial is constant quincunx have a play with the quincunx (then read quincunx explained) to see the binomial distribution in action.

Ib Mathematics Aa Sl Flashcards Binomial Theorem A polynomial equation with two terms usually joined by a plus or minus sign is called a binomial. binomials are used in algebraic mathematics. The binomial distribution evaluates the probability for an outcome to either succeed or fail. these are called mutually exclusive outcomes, which means you either have one or the other — but not both at the same time. Binomial is an algebraic expression that contains two different terms connected by addition or subtraction. in other words, we can say that two distinct monomials of different degrees connected by plus or minus signs form a binomial. Sometimes the number of combinations is known as a binomial coefficient, and sometimes the notation ncr is used. note that the number of permutations is r! times larger than the number of combinations.
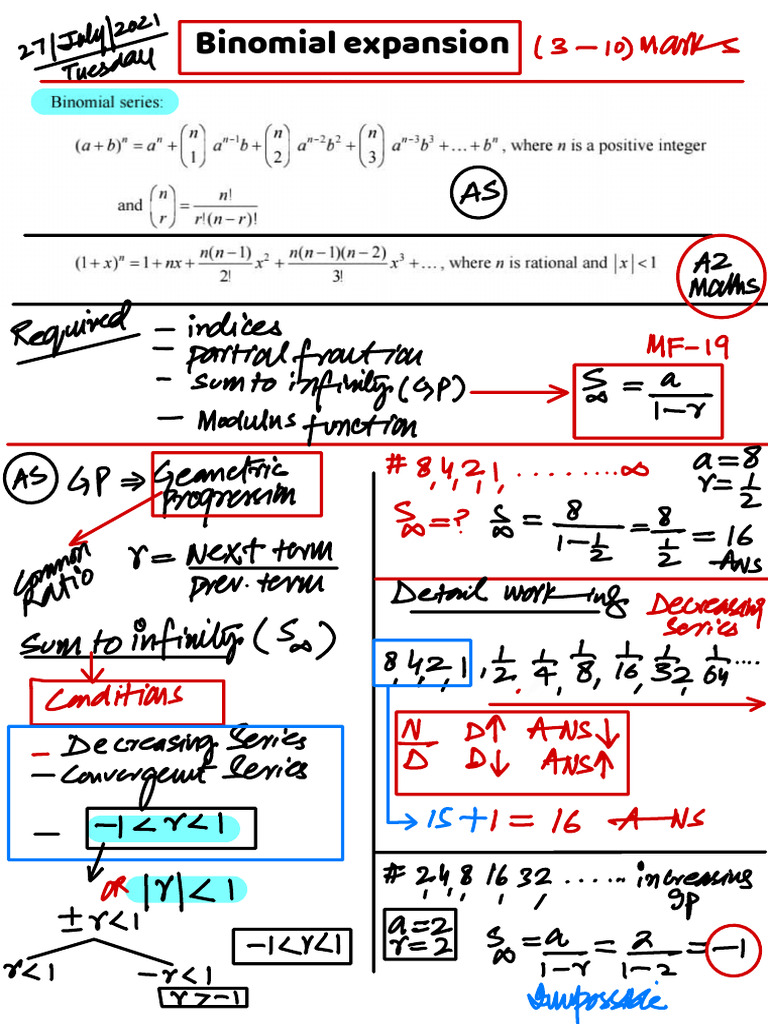
Maths A Level Binomial Expansion Pdf Arithmetic Division Binomial is an algebraic expression that contains two different terms connected by addition or subtraction. in other words, we can say that two distinct monomials of different degrees connected by plus or minus signs form a binomial. Sometimes the number of combinations is known as a binomial coefficient, and sometimes the notation ncr is used. note that the number of permutations is r! times larger than the number of combinations. The binomial distribution is, in essence, the probability distribution of the number of heads resulting from flipping a weighted coin multiple times. The binomial distribution is a probability distribution that describes the number of successes in a fixed number of independent trials, each with the same probability of success. Therefore, a binomial is a two term algebraic expression that contains variable, coefficient, exponents and constant. another example of a binomial polynomial is x2 4x. The binomial distribution is a discrete probability distribution that describes the probability of obtaining a certain number of successes in a sequence of independent trials, each of which has only two possible outcomes: success or failure.
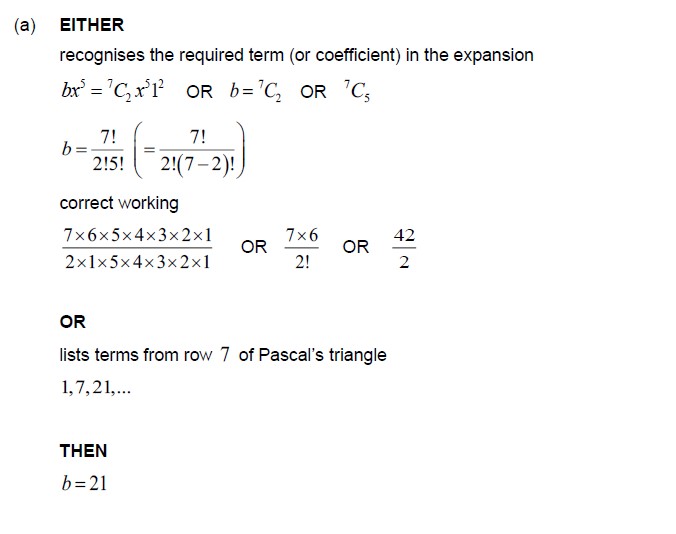
Ib Mathematics Aa Sl Binomial Theorem Study Notes The binomial distribution is, in essence, the probability distribution of the number of heads resulting from flipping a weighted coin multiple times. The binomial distribution is a probability distribution that describes the number of successes in a fixed number of independent trials, each with the same probability of success. Therefore, a binomial is a two term algebraic expression that contains variable, coefficient, exponents and constant. another example of a binomial polynomial is x2 4x. The binomial distribution is a discrete probability distribution that describes the probability of obtaining a certain number of successes in a sequence of independent trials, each of which has only two possible outcomes: success or failure.
Ibdp Maths Aa Sl Questions 1 4 Binomial Expansion Therefore, a binomial is a two term algebraic expression that contains variable, coefficient, exponents and constant. another example of a binomial polynomial is x2 4x. The binomial distribution is a discrete probability distribution that describes the probability of obtaining a certain number of successes in a sequence of independent trials, each of which has only two possible outcomes: success or failure.
Comments are closed.