
Bone Cells Diagram Quizlet These are the main features of a bone cell. 3. cell functions. 4. these are the shapes that bone cells can be. it helps that there are two shapes that they can be so that more bone can fit in a body. 5. what organ is your cell found in? my cell can be found all over the body since bones are rigid organs. 6. Bone is a mineralized connective tissue that exhibits four types of cells: osteoblasts, bone lining cells, osteocytes, and osteoclasts [1, 2]. bone exerts important functions in the body, such as locomotion, support and protection of soft tissues, calcium and phosphate storage, and harboring of bone marrow [3, 4].
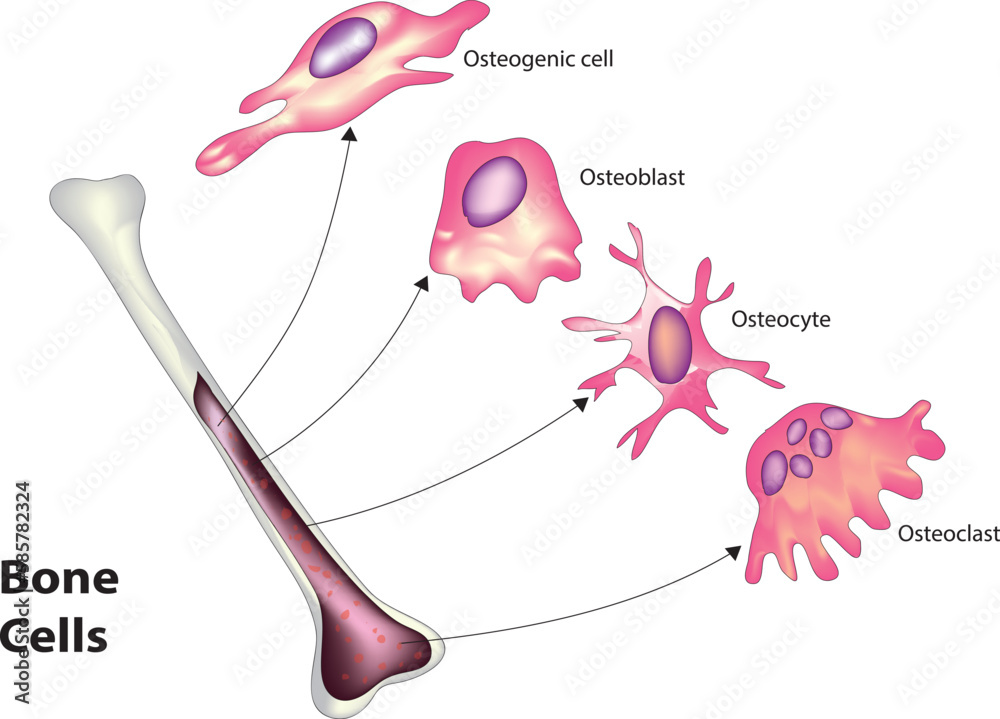
Bone Cells Stock Vector Adobe Stock Ambrosi and colleagues profile human skeletal stem cells (hsscs) across ten fetal skeletal sites and from patients throughout adulthood, identifying, mapping, and functionally testing four distinct hssc subtypes. skeletal aging and disease are characterized by a dominant fibrogenic hssc variant, but targeting defined gene regulatory networks reinstates functional hssc diversity. With the advancement of molecular and genetic tools, our comprehension of the intracellular signals activated in bone cells has evolved significantly, from early suggestions that osteoblasts and osteoclasts have common precursors and that osteocytes are inert cells in the bone matrix, to the very sophisticated understanding of a network of. Bone is composed of four different cell types; osteoblasts, osteocytes, osteoclasts and bone lining cells. osteoblasts, bone lining cells and osteoclasts are present on bone surfaces and are derived from local mesenchymal cells called progenitor cells. osteocytes permeate the interior of the bone and are produced from the fusion of mononuclear. Bone development and the adaptation of the adult skeleton to mechanical needs and hormonal changes depend on the ability of bone cells to resorb and form bone in the right places and at the right time. bone growth, modeling, or remodeling are defined by the spatial and temporal relationship between bone resorption and bone formation.

Bone Cells By Mia Sassenrath Bone is composed of four different cell types; osteoblasts, osteocytes, osteoclasts and bone lining cells. osteoblasts, bone lining cells and osteoclasts are present on bone surfaces and are derived from local mesenchymal cells called progenitor cells. osteocytes permeate the interior of the bone and are produced from the fusion of mononuclear. Bone development and the adaptation of the adult skeleton to mechanical needs and hormonal changes depend on the ability of bone cells to resorb and form bone in the right places and at the right time. bone growth, modeling, or remodeling are defined by the spatial and temporal relationship between bone resorption and bone formation. Bone cells are the cells that make up bone tissue. bone is a highly specialized connective tissue with three main functions; to protect the internal organs, to create a rigid frame for muscular movement, and to store minerals such as calcium and phosphorous. bone tissue may be classified as compact or spongy, depending on its density and function. With the advancement of molecular and genetic tools, our comprehension of the intracellular signals activated in bone cells has evolved significantly, from early suggestions that osteoblasts and osteoclasts have common precursors and that osteocytes are inert cells in the bone matrix, to the very sophisticated understanding of a network of. Skeletal homeostasis is fulfilled by specialized bone cells in association with systemic and local regulators. herein i review landmark discoveries that shed light on the intricate mesh connecting bone cells among themselves and with other systems, thus representing the cellular basis of normal and abnormal bone development and homeostasis. This review focuses on understanding the macroscopic and microscopic characteristics of bone tissue and reviews current knowledge of its physiology. it explores how these features intricately collaborate to maintain the balance between osteoblast mediated bone formation and osteoclast mediated bone ….

Bone Cells By Mia Sassenrath Bone cells are the cells that make up bone tissue. bone is a highly specialized connective tissue with three main functions; to protect the internal organs, to create a rigid frame for muscular movement, and to store minerals such as calcium and phosphorous. bone tissue may be classified as compact or spongy, depending on its density and function. With the advancement of molecular and genetic tools, our comprehension of the intracellular signals activated in bone cells has evolved significantly, from early suggestions that osteoblasts and osteoclasts have common precursors and that osteocytes are inert cells in the bone matrix, to the very sophisticated understanding of a network of. Skeletal homeostasis is fulfilled by specialized bone cells in association with systemic and local regulators. herein i review landmark discoveries that shed light on the intricate mesh connecting bone cells among themselves and with other systems, thus representing the cellular basis of normal and abnormal bone development and homeostasis. This review focuses on understanding the macroscopic and microscopic characteristics of bone tissue and reviews current knowledge of its physiology. it explores how these features intricately collaborate to maintain the balance between osteoblast mediated bone formation and osteoclast mediated bone ….

Bone Cells By Mia Sassenrath Skeletal homeostasis is fulfilled by specialized bone cells in association with systemic and local regulators. herein i review landmark discoveries that shed light on the intricate mesh connecting bone cells among themselves and with other systems, thus representing the cellular basis of normal and abnormal bone development and homeostasis. This review focuses on understanding the macroscopic and microscopic characteristics of bone tissue and reviews current knowledge of its physiology. it explores how these features intricately collaborate to maintain the balance between osteoblast mediated bone formation and osteoclast mediated bone ….
