
Bushfire Hub Presentation How Does Bushfire Affect Biodiversity And Learn how the bushfire hub is delivering world leading, cost effective research that will drive positive transformation in how bushfire is managed in australia. The unusually severe 2019–2020 australian bushfire season has been linked to climate change and the impacts on wildlife and ecosystems are still being studied. we use remotely sensed thermal data to assess the differences between annual fire seasons from 2012 to 2019 in eastern australia to understand the unique characteristics of the 2019.
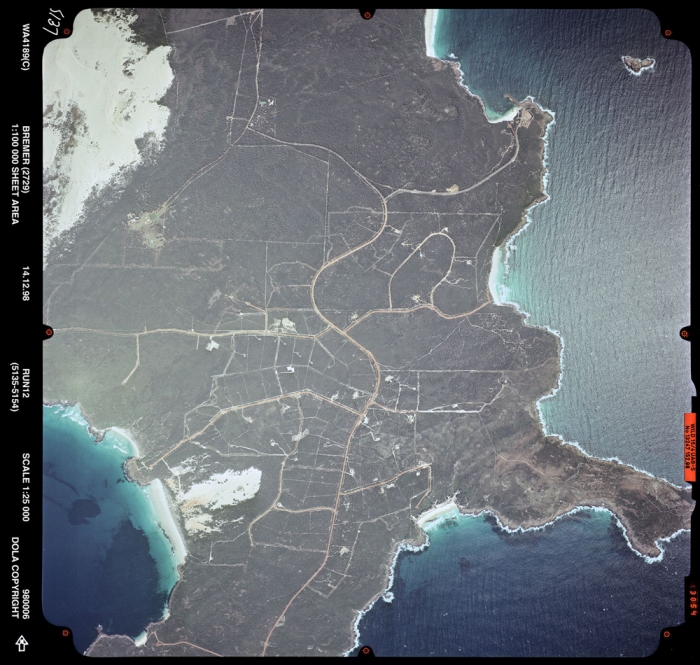

Bushfire And Biodiversity Ian Weir Architect In this project the firescape landscape fire regime simulator was used to explore: the quantitative nature of bushfire risk to people, property, biodiversity and catchment values. firescape captures the key processes that determine the incidence and spread of fires (weather, terrain and fuels). The 2019–2020 bushfire season demonstrated just how integral effective fire management within the bmnp is for the ongoing conservation of its biodiversity, after 64% of the park was impacted by predominantly moderate to extreme severity bushfires (smith, 2020). Many species of native plant have seed that is stimulated to germinate by fire while others have adapted to reshoot vigorously from roots or stems. intense fire can alter wildlife habitat in the short to medium term by removing old, hollow bearing trees, leaf litter, plant cover and some food sources. We focussed on two key concerns: (1) the threat of bushfires occurring close to residential areas; and (2) the need for effective conservation measures to maintain important and unique biodiversity in these same locations.
Bushfire And Biodiversity Ian Weir Architect Many species of native plant have seed that is stimulated to germinate by fire while others have adapted to reshoot vigorously from roots or stems. intense fire can alter wildlife habitat in the short to medium term by removing old, hollow bearing trees, leaf litter, plant cover and some food sources. We focussed on two key concerns: (1) the threat of bushfires occurring close to residential areas; and (2) the need for effective conservation measures to maintain important and unique biodiversity in these same locations. Wildfires have complex impacts on forests, including changes in vegetation, threats to biodiversity, and emissions of greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide, which exacerbate climate change. the influence of wildfires on animal habitats is particularly noteworthy, as they can lead to significant changes in native environments. And so it’s key that we consider biodiversity loss due to wildfires in terms of entire networks of interacting organisms, including humans, rather than simply one or two charismatic animals. Preparation and responses to wildfires have improved for human life and property, but there has been far less progress in protecting threatened species and ecological communities before, during and after wildfire. our project aimed to identify what is required to improve conservation outcomes during large fire events.
