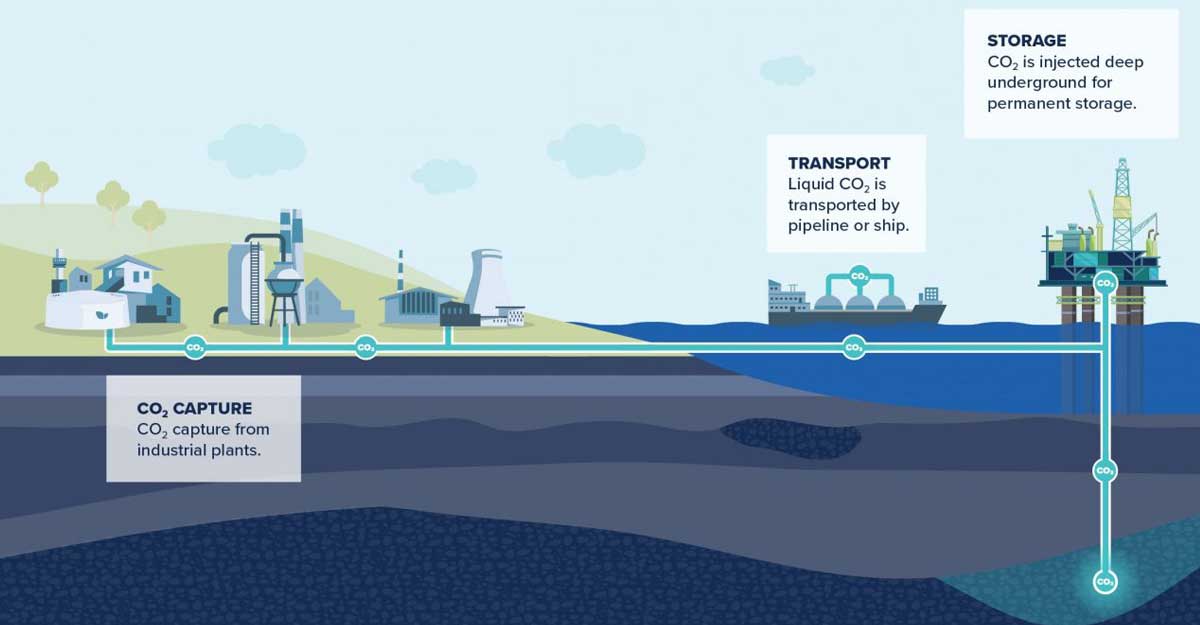
Ccs Key To Net Zero Capture Storage Explained Carbon capture and storage (ccs) is essential for net zero emissions to be achieved in any economy using fossil fuels or releasing carbon in any other ways. improving efficiency and decreased emissions represent a first priority. however, for hard to decarbonise areas such as heavy industry, ccs may represent the last line of defence against. Carbon capture and storage (ccs) is a way of reducing carbon dioxide (co 2) emissions, which could be key to helping to tackle global warming. it’s a three step process, involving: capturing the co 2 produced by power generation or industrial activity, such as hydrogen production, steel or cement making; transporting it; and then permanently.

Why Carbon Capture And Storage Ccs Energy Factor We identify ccs as a key for achieving net zero ghg emissions: first, ccs is required as a net carbon dioxide sink to compensate residual emissions from lulucf and sectors that are not part of the energy system. second, the electricity demand for decarbonizing the heating and mobility sectors exceeds the availability of renewable electricity. Public private partnerships are going to be the key to unlocking carbon capture. faced with the immediate and serious challenge of climate change, carbon capture and storage (ccs) technology has emerged as a robust and innovative tool to reduce carbon emissions and make progress towards net zero goals. Today, ccs is recognised as a key technology in achieving net zero emissions and preventing the most severe impacts of climate change. ccs consists of three primary steps: 1. capture: co₂ is separated from industrial emissions using techniques such as pre combustion, post combustion, and oxy fuel combustion. What is the role of ccs in achieving net zero? co 2 capture, transport, and storage (ccs) describes the process of capturing carbon dioxide (co 2) emissions from point sources such as power plants or industrial sites, transporting it by ships, trucks or pipelines to a storage site, and injecting it in deep underground geological formations to.
Ccs Key To Net Zero Capture Storage Explained Today, ccs is recognised as a key technology in achieving net zero emissions and preventing the most severe impacts of climate change. ccs consists of three primary steps: 1. capture: co₂ is separated from industrial emissions using techniques such as pre combustion, post combustion, and oxy fuel combustion. What is the role of ccs in achieving net zero? co 2 capture, transport, and storage (ccs) describes the process of capturing carbon dioxide (co 2) emissions from point sources such as power plants or industrial sites, transporting it by ships, trucks or pipelines to a storage site, and injecting it in deep underground geological formations to. Relying on carbon capture and storage (ccs) to reach net zero would cost governments around the world at least $30 trillion more than a route based on renewable energy, energy efficiency and electrification, according to research from the university of oxford. that crazy figure is roughly twice what it would cost to decarbonise china. The three step process of ccs. ccs works through a three step process: capture, transport, and storage. capture: co 2 is captured from industrial processes before or after combustion. pre combustion capture removes co 2 before combustion during hydrocarbon processing, while post combustion capture removes co 2 from exhaust gases after fossil fuels are burned. Carbon capture and storage (ccs) is a crucial technology in the fight against climate change. ccs involves capturing co2 emissions from sources such as power plants and industrial facilities, pressurizing it into a liquid like form sometimes referred to as “supercritical co2”, and then transporting and permanently storing carbon safely and.
