Class I Malocclusion With Crowding Intra Arch Problems Dr Paridhi Agrawal

Intra Arch Problems Dental Classification Dentist Beginning with the corrective orthodontics. this is the first topic crowding and its correction. this video covers all in all crowding. .more. Treatment objectives were to correct the maxillary and mandibular crowding, the deep bite, and the midline shifting on the lower arch, and to achieve a class i relationship with an ideal arch form, overjet, and overbite.
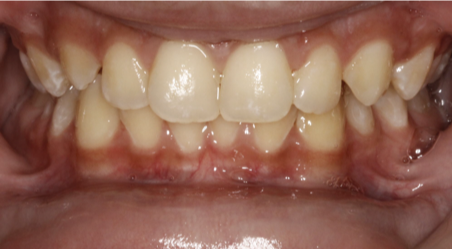
Liuorthodontics Crowding And Class Ii Malocclusion Learn about class i malocclusion, the most common dental misalignment. discover its causes, symptoms, treatment options, and prevention tips. The present case describes orthodontic treatment in a patient with class i malocclusion with severe crowding in the anterior region treated with four premolar extractions. The treatment choice will depend on various factors including the presence of crowding and type of malocclusion, the skeletal pattern, overjet, overbite and buccal segment relationships. A 13 year old female presented with a class i malocclusion on a mild skeletal class ii pattern with average vertical dimensions complicated by moderate upper arch crowding, palatal displacement of the ul2 and a localized crossbite (figure 3.1).

Class 1 Crowding Malocclusion The treatment choice will depend on various factors including the presence of crowding and type of malocclusion, the skeletal pattern, overjet, overbite and buccal segment relationships. A 13 year old female presented with a class i malocclusion on a mild skeletal class ii pattern with average vertical dimensions complicated by moderate upper arch crowding, palatal displacement of the ul2 and a localized crossbite (figure 3.1). This video covers in detail generalised and localised spacing its features, etiology and the generally carried out treatment protocol dental anatomy le. Class i malocclusions with severe crowding and tooth size discrepancies may be successfully treated orthodontically with extraction therapy, and co management with other specialists. Case: this case report aims to describe that non extraction orthodontic treatment in class i malocclusion with mild crowding and mildline shift is a treatment with considerable success. case management: a 19 years old female came with a chief complaint of crowding in upper and lower jaw. Marked transverse skeletal discrepancies between the arches are more commonly associated with class ii or class iii occlusions, but milder transverse discrepancies are often seen in class i cases.

A Class I Malocclusion With Dual Arch Crowding Asymmetric Molar This video covers in detail generalised and localised spacing its features, etiology and the generally carried out treatment protocol dental anatomy le. Class i malocclusions with severe crowding and tooth size discrepancies may be successfully treated orthodontically with extraction therapy, and co management with other specialists. Case: this case report aims to describe that non extraction orthodontic treatment in class i malocclusion with mild crowding and mildline shift is a treatment with considerable success. case management: a 19 years old female came with a chief complaint of crowding in upper and lower jaw. Marked transverse skeletal discrepancies between the arches are more commonly associated with class ii or class iii occlusions, but milder transverse discrepancies are often seen in class i cases.

A Class I Malocclusion With Dual Arch Crowding Asymmetric Molar Case: this case report aims to describe that non extraction orthodontic treatment in class i malocclusion with mild crowding and mildline shift is a treatment with considerable success. case management: a 19 years old female came with a chief complaint of crowding in upper and lower jaw. Marked transverse skeletal discrepancies between the arches are more commonly associated with class ii or class iii occlusions, but milder transverse discrepancies are often seen in class i cases.

4 A Typical Case Of Class I Malocclusion With Crowding Observe Class
Comments are closed.