Protozoans And Its Classification Overall Science Paramecium ( ˌpærəˈmiːs (i) əm parr ə mee s (ee )əm, siəm see əm, plural "paramecia" only when used as a vernacular name) [2] is a genus of eukaryotic, unicellular ciliates, widespread in freshwater, brackish, and marine environments. paramecia are often abundant in stagnant basins and ponds. Paramecium classification. paramecium is unicellular and eukaryotic, so they are kept in the kingdom protista. they are ciliated protozoan and come under phylum ciliophora. the common species of paramecium include: paramecium aurelia. paramecium caudatum. paramecium woodruffi. paramecium trichium.

Paramecium Classification Structure Function And Characteristics My Paramecium can be classified into the following phylum and sub phylum based on their certain characteristics. being a well known ciliate protozoan, paramecium exhibits a high level cellular differentiation containing several complex organelles performing a specific function to make its survival possible. A paramecium is a free living, motile, single cell (unicellular) organism belonging to the kingdom protista that are naturally found in aquatic habitats. they have a lifespan of a hundred, a thousand or even a million years. The current classification of paramecium – chromista kingdom. in this post, we (as well as ) use the 7 kingdom system (bacteria, archaea, protozoa, chromista, plantae, fungi, and animalia) proposed by ruggiero et al. in 2015. Taxonomic hierarchy of genus paramecium müller, 1773. display of synonyms, alternative taxonomic positions, references, number of subtaxa, and phylogenetic bibliographic position can be switched on off. subtaxa can be ordered by name or phylogenetic bibliographic position.

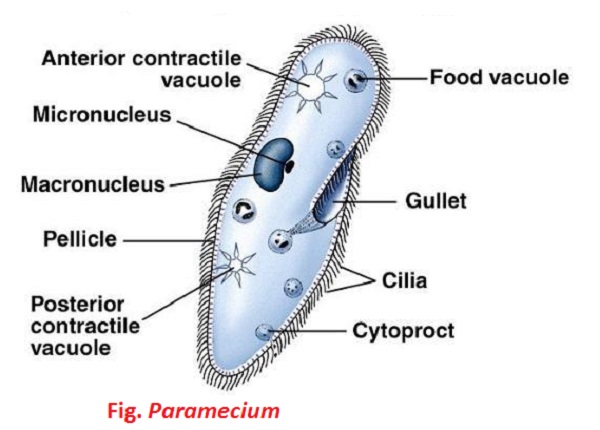
The Biological Classification Of Paramecium Name History And The current classification of paramecium – chromista kingdom. in this post, we (as well as ) use the 7 kingdom system (bacteria, archaea, protozoa, chromista, plantae, fungi, and animalia) proposed by ruggiero et al. in 2015. Taxonomic hierarchy of genus paramecium müller, 1773. display of synonyms, alternative taxonomic positions, references, number of subtaxa, and phylogenetic bibliographic position can be switched on off. subtaxa can be ordered by name or phylogenetic bibliographic position. Paramecium, genus of microscopic, single celled, and free living protozoans. most species can be cultivated easily in the laboratory, making them ideal model organisms, well suited for biological study. paramecium vary in length from about 0.05 to 0.32 mm (0.002 to 0.013 inch). In my opinion, several of what are now referred to as distinct morphologically defined species of paramecium will be found to consist of a complex of sibling species after genetic study and enterase zymogram analysis. for certain of the species, a genetic classification has been made, which is described later. Paramecium classification systematic position of paramecium. following is the classification of paramecium : phylum – protozoa 🡪 microscopic and acellular. sub phylum – ciliophora 🡪 locomotory organs cilia. class – ciliata 🡪 locomotory organs cilia which persists throughout life. Paramecium is a eukaryotic genus commonly used as a ciliate model organism. this article will focus on details of paramecium, diagram , classification, characteristics, size, locomotion, reproduction and more. is paramecium a type of bacteria? what is paramecium? which phylum does paramecium belong to? do paramecium eat bacteria?.
