Cognitive Errors Belief Perseverence Biases For The Cfa Level 1 Exam
Cognitive And Emotional Biases In Investing Cfa Level 1 Below are the two categories into which cognitive errors can be split: belief perseverance bias. processing errors. the belief perseverance bias results from the discomfort experienced as a result of new information contradicting previously held beliefs. Cognitive errors belief perseverence biases (for the cfa level 1 exams) explores the nature, consequences and suggested corrective measures associated with.

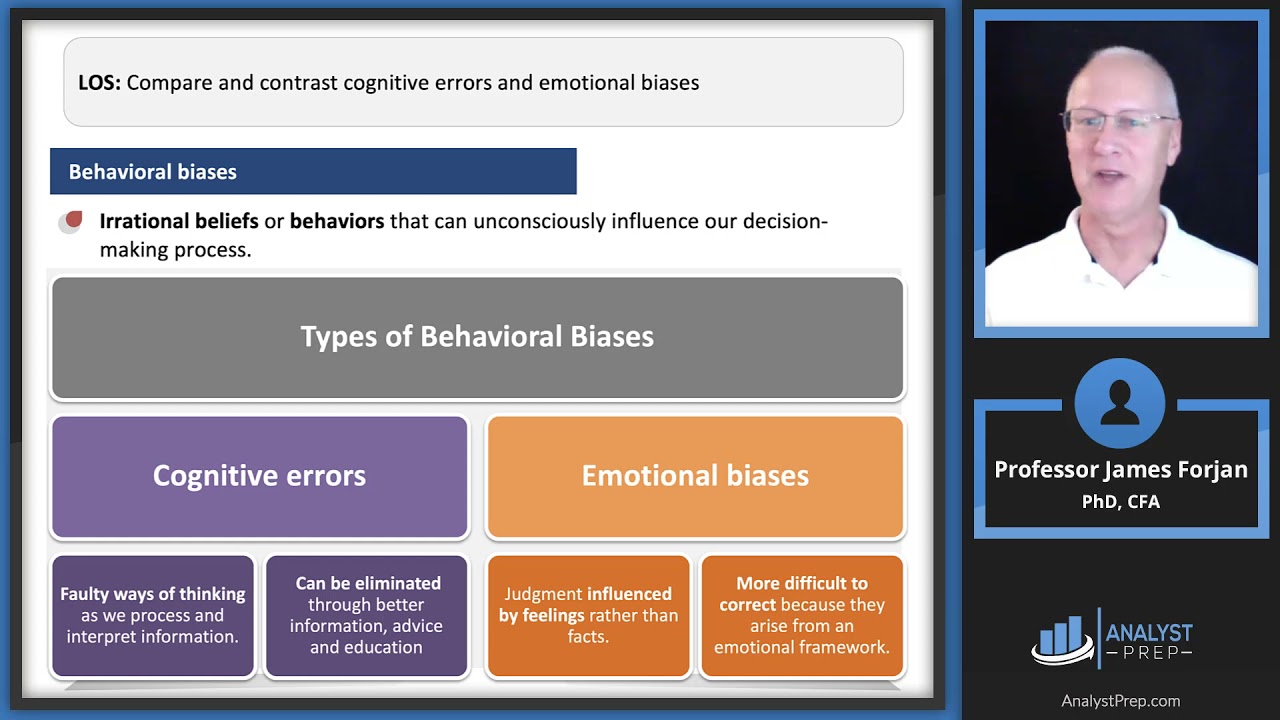
Of Cognitive Biases And Errors Download Scientific Diagram Level 1 cfa exam lesson on cognitive errors. cognitive errors stem from faulty cognitive reasoning and include belief perseverance biases and processing errors. Comprehensive study notes that are based on the cfa institute's study guide for the 2025 cfa level i exam. over 5,700 practice questions that cover the entire cfa curriculum. Biases can be broadly categorized as cognitive errors or emotional biases: cognitive errors stem from irrationality (belief perseverance biases) or faulty reasoning (processing errors). emotional biases arise from feelings, impulses, or intuition and are difficult to overcome. Behavioral biases are either emotional biases or cognitive errors (split into belief perseverance and information processing biases). some other candidates (primarily marc lefebvre, cfa) helped with the acronyms.
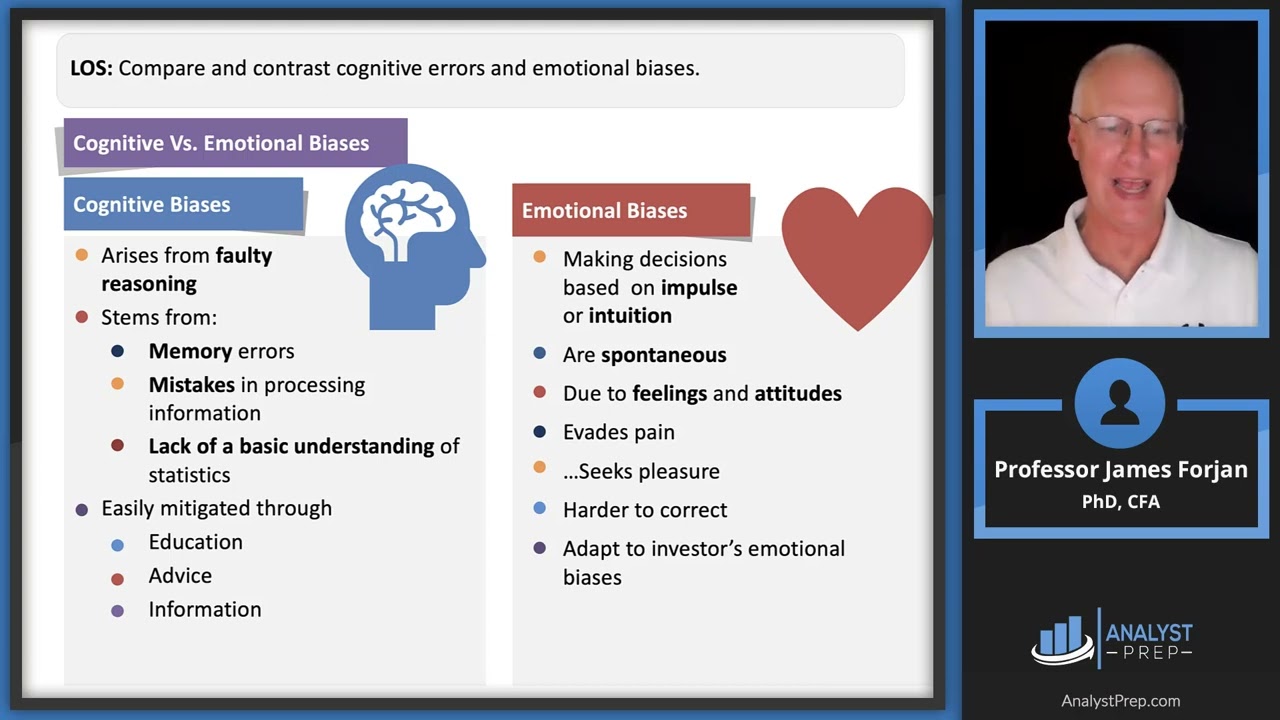
Cognitive Errors Vs Emotional Biases Cfa Frm And Actuarial Exams Biases can be broadly categorized as cognitive errors or emotional biases: cognitive errors stem from irrationality (belief perseverance biases) or faulty reasoning (processing errors). emotional biases arise from feelings, impulses, or intuition and are difficult to overcome. Behavioral biases are either emotional biases or cognitive errors (split into belief perseverance and information processing biases). some other candidates (primarily marc lefebvre, cfa) helped with the acronyms. Sections 3 and 4 discuss specific behavioral biases within two broad categories: cognitive errors and emotional biases. the discussion includes a description of each bias, potential consequences, and guidance on detecting and mitigating the effects of the bias. It is often associated with emotional biases: illusion of knowledge (belief you know things you do not know), self attribution (belief you personally caused something to happen), and overconfidence biases (an unwarranted belief you are correct). Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like describe the difference between cognitive errors and emotional biases, describe belief perseverance bias and its relatedness to cognitive errors, describe the difference between conservatism bias and confirmation bias and more. Origin: cognitive errors are rooted in faulty reasoning processes, while emotional biases stem from feelings and impulses. mitigation: cognitive errors can be often be mitigated through education, improved information processing, and deliberate effort to challenge existing beliefs.
Comments are closed.