Common Ion Effect Ksp And Solubility How To Calculate Solubility With Common Ion Effect

Solubility Equilibrium Solubility Product Constant Ksp Commonion Effect In calculations like this, you can always assume that the concentration of the common ion is entirely due to the other solution. this makes the maths a lot easier. Understand the common ion effect for ap chemistry. predict solubility changes, equilibrium shifts, and precipitation using ksp and shared ions.

Solubility Equilibrium Solubility Product Constant Ksp Commonion Effect Write and equilibrium constant expression for a slightly soluble salt: the expression is called the solubility product constant (ksp) example: baso4 is a slightly soluble salt. when a reasonable quantity of solid baso4 is mixed with water, only a very small amount will dissolve to produce ba 2 (aq) and so 4–2 (aq). Solubility product (ksp) and the common ion effect are key concepts in physical chemistry, essential for understanding the solubility and precipitation of ionic compounds in solution. these principles are fundamental in predicting the behavior of such compounds, particularly in aqueous environments. Learn how to calculate the common ion effect on solubility and understand its impact on the dissolution of ionic compounds in solution. This study guide covers the common ion effect on solubility equilibria. it explains how adding a common ion decreases solubility, using le chatelier's principle. it includes practice problems involving ksp calculations, ice tables, and molar solubility with and without common ions.
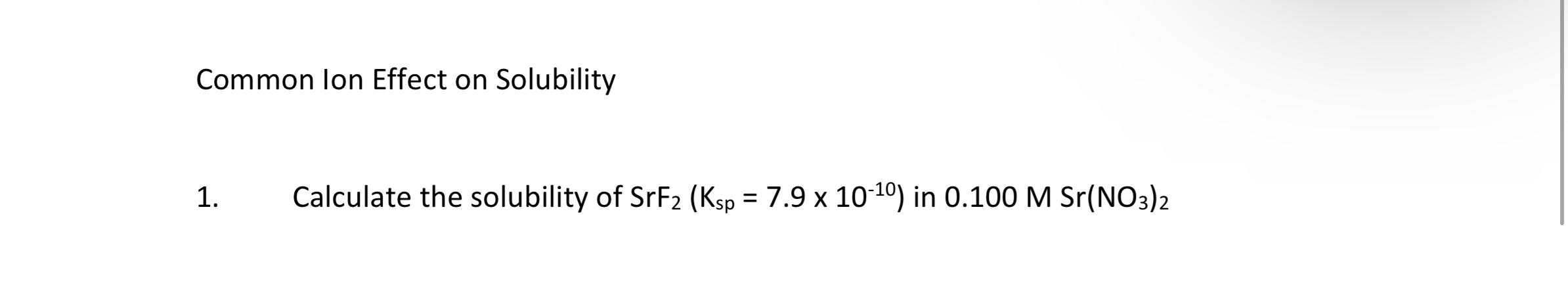
Solved Common Ion Effect On Solubilitycalculate The Chegg Learn how to calculate the common ion effect on solubility and understand its impact on the dissolution of ionic compounds in solution. This study guide covers the common ion effect on solubility equilibria. it explains how adding a common ion decreases solubility, using le chatelier's principle. it includes practice problems involving ksp calculations, ice tables, and molar solubility with and without common ions. Adding calcium ion to the saturated solution of calcium sulfate causes additional caso 4 to precipitate from the solution, lowering its solubility. the addition of a solution containing sulfate ion, such as potassium sulfate, would result in the same common ion effect. By assigning x mol l as the concentration of caf 2 dissolved in a saturated solution, we were able to determine the molar solubility of caf 2 from the ksp. setting up an ice table helps determine the concentrations correctly. so, the expression for ksp can be written as: ksp = [ca 2 ] [ f –] 2 = (x) (2x) = 3.9 x 10 11. therefore,. Adding a common ion decreases solubility, as the reaction shifts toward the left to relieve the stress of the excess product. adding a common ion to a dissociation reaction causes the equilibrium to shift left, toward the reactants, causing precipitation.

Ksp And Common Ion Effect Commonion Effect Similar Adding calcium ion to the saturated solution of calcium sulfate causes additional caso 4 to precipitate from the solution, lowering its solubility. the addition of a solution containing sulfate ion, such as potassium sulfate, would result in the same common ion effect. By assigning x mol l as the concentration of caf 2 dissolved in a saturated solution, we were able to determine the molar solubility of caf 2 from the ksp. setting up an ice table helps determine the concentrations correctly. so, the expression for ksp can be written as: ksp = [ca 2 ] [ f –] 2 = (x) (2x) = 3.9 x 10 11. therefore,. Adding a common ion decreases solubility, as the reaction shifts toward the left to relieve the stress of the excess product. adding a common ion to a dissociation reaction causes the equilibrium to shift left, toward the reactants, causing precipitation.

Solubility Solubility Product Constant Ksp And Ion Effect Pek3013 Adding a common ion decreases solubility, as the reaction shifts toward the left to relieve the stress of the excess product. adding a common ion to a dissociation reaction causes the equilibrium to shift left, toward the reactants, causing precipitation.

Solubility Product Ksp And Solubility Predicting Precipitation Common
Comments are closed.