Common Ion Effect Ksp Calculation Precipitate

Common Ion Effect Ksp Calculation Precipitate That is, as the concentration of the anion increases, the maximum concentration of the cation needed for precipitation to occur decreases—and vice versa—so that ksp is constant. consequently, the solubility of an ionic compound depends on the concentrations of other salts that contain the same ions. Problem #2: calculate the ph at which zinc hydroxide just starts to precipitate from a 0.00857 m solution of zinc nitrate. k sp for zinc hydroxide = 3.0 x 10 17.

Solution Solubitiy Product Common Ion Effect Ksp Calculation Predicting when precipitation occurs q e.g. will the addition of a nacl solution to a saturated pbcl2 solution result in a precipitate forming?. Predicting when precipitation occurs q e.g. will the addition of a nacl solution to a saturated pbcl2 solution result in a precipitate forming?. If this ion product exceeds the ksp value for that salt, it indicates that a precipitate will form. this method is widely used in chemistry to predict the outcome of reactions in solution, particularly in qualitative analysis and in industrial processes where controlling precipitation is crucial. The ‘common ion’ effect explained with examples most of you should be becoming confident in calculations involving: using the solubility data of a compound to calculate its ksp value and using ksp values to determine how much of a solid dissolves or when a precipitate will form when you add two ions when the solvent involved is pure water.

Solution Solubitiy Product Common Ion Effect Ksp Calculation If this ion product exceeds the ksp value for that salt, it indicates that a precipitate will form. this method is widely used in chemistry to predict the outcome of reactions in solution, particularly in qualitative analysis and in industrial processes where controlling precipitation is crucial. The ‘common ion’ effect explained with examples most of you should be becoming confident in calculations involving: using the solubility data of a compound to calculate its ksp value and using ksp values to determine how much of a solid dissolves or when a precipitate will form when you add two ions when the solvent involved is pure water. Understand the common ion effect for ap chemistry. predict solubility changes, equilibrium shifts, and precipitation using ksp and shared ions. The document provides examples of calculating ksp from solubility data and vice versa. it also explains how to use ksp values to determine whether mixing solutions will result in precipitation. If on mixing solutions containing the two constituent ions the k sp expression is exceeded, precipitation will take place until the product of the ion concentrations equals the k sp value. if the ksp expression is not exceeded, no precipitation will take place. Comparing q and ksp enables us to determine whether a precipitate will form when solutions of two soluble salts are mixed. adding a common cation or common anion to a solution of a sparingly soluble salt shifts the solubility equilibrium in the direction predicted by le chatelier’s principle.

Solution Solubitiy Product Common Ion Effect Ksp Calculation Understand the common ion effect for ap chemistry. predict solubility changes, equilibrium shifts, and precipitation using ksp and shared ions. The document provides examples of calculating ksp from solubility data and vice versa. it also explains how to use ksp values to determine whether mixing solutions will result in precipitation. If on mixing solutions containing the two constituent ions the k sp expression is exceeded, precipitation will take place until the product of the ion concentrations equals the k sp value. if the ksp expression is not exceeded, no precipitation will take place. Comparing q and ksp enables us to determine whether a precipitate will form when solutions of two soluble salts are mixed. adding a common cation or common anion to a solution of a sparingly soluble salt shifts the solubility equilibrium in the direction predicted by le chatelier’s principle.

Solution Solubitiy Product Common Ion Effect Ksp Calculation If on mixing solutions containing the two constituent ions the k sp expression is exceeded, precipitation will take place until the product of the ion concentrations equals the k sp value. if the ksp expression is not exceeded, no precipitation will take place. Comparing q and ksp enables us to determine whether a precipitate will form when solutions of two soluble salts are mixed. adding a common cation or common anion to a solution of a sparingly soluble salt shifts the solubility equilibrium in the direction predicted by le chatelier’s principle.
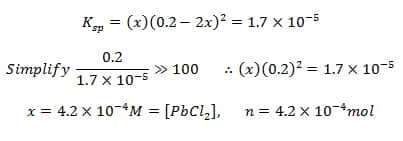
Common Ion Effect Schoolworkhelper
Comments are closed.