Consider The Following Balanced Chemical Equation 4ko2s 2h2ol A%e2%80%a0 4kohs 3o2g Determine

Solved Consider The Following Balanced Chemical Equation 4ko2 S In order to determine the mass of koh formed, first we need to find the** limiting reactant **of this reaction. the formula weight of ko₂ is approximately 71.1 g mol and the formula weight of h₂o is near 18.02 g mol. Consider the following balanced chemical equation: 4ko2 (s) 2h2o (l) → 4koh (s) 3o2 (g) determine the mass (in g) of koh formed if 55.6 g of ko2 reacts with 50.6 g of h2o. your solution’s ready to go! our expert help has broken down your problem into an easy to learn solution you can count on.

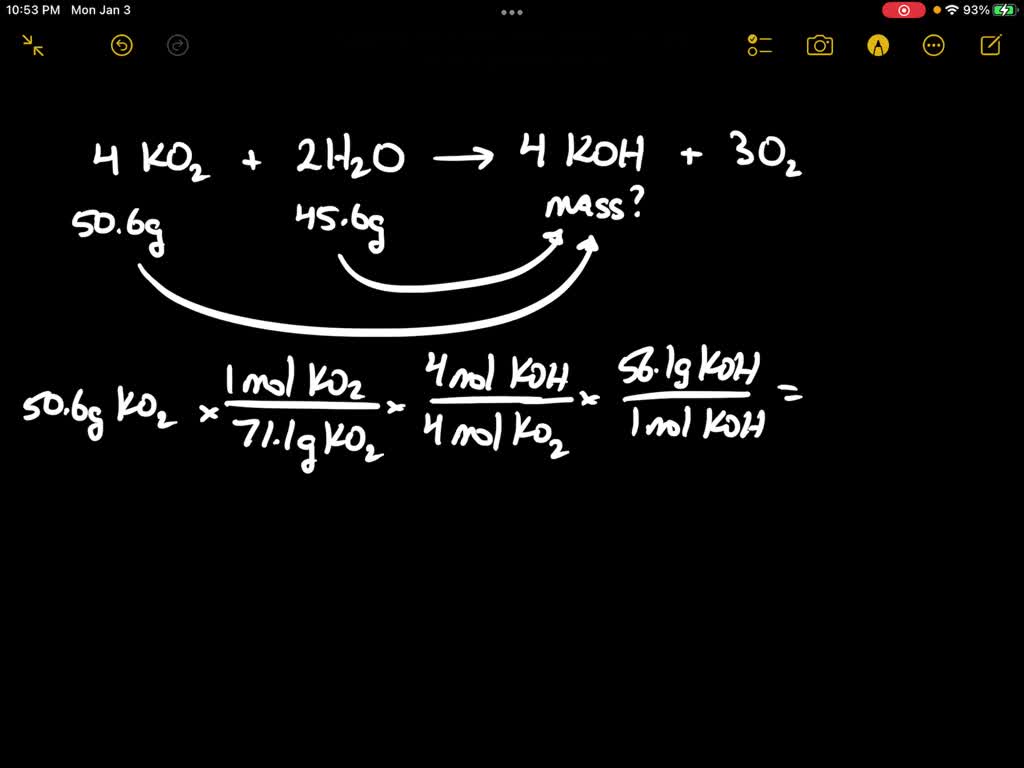
Solved Consider The Following Balanced Chemical Equation 4ko2s Consider the following balanced chemical equation: 4ko2 (s) 2h2o (l) → 4koh (s) 3o2 (g) determine the mass (in g) of koh formed if 50.6 g of ko2 reacts wit. Consider the balanced chemical equation: 4ko2 (s) 2h2o (l) → 4koh (s) 3o2 (g). determine the mass in grams of koh formed if 38.1 grams of ko2 reacts with 38.1 grams of h2o. Determine the mass (in grams) of carbon dioxide obtained when 7.04 g of c6h5oh reacts with 2.80 g of oxygen. use the abbreviated form of the unit in your answer and two decimal places in your molar mass. Consider the following balanced chemical equation: 4ko2 (s) 2h2o (l) → 4koh (s) 3o2 (g) determine the mass (in g) of koh formed if 46.1 g of ko2 reacts with 46.1 g of h2o. your solution’s ready to go! our expert help has broken down your problem into an easy to learn solution you can count on.

Solved Consider The Following Balanced Chemical Equation Chegg Determine the mass (in grams) of carbon dioxide obtained when 7.04 g of c6h5oh reacts with 2.80 g of oxygen. use the abbreviated form of the unit in your answer and two decimal places in your molar mass. Consider the following balanced chemical equation: 4ko2 (s) 2h2o (l) → 4koh (s) 3o2 (g) determine the mass (in g) of koh formed if 46.1 g of ko2 reacts with 46.1 g of h2o. your solution’s ready to go! our expert help has broken down your problem into an easy to learn solution you can count on. Consider the following balanced chemical equation: 4ko2 (s) 2h2o (l) 3o2 (g) 4koh (s) (a) determine the mass (in g) of koh formed if 10.0 g of ko2 reacts with 10.0 g of h2o. Consider the following balanced chemical equation: 4ko2(s) 2h2o(l) → 4koh(s) 3o2(g) determine the mass (in g) of koh formed if 30.1 g of ko2 reacts with 30.1 g of h2o. g koh. the molar mass of ko2 is approximately 71.1 g mol and the molar mass of h2o is approximately 18.02 g mol. show more…. Next, determine the limiting reactant. this can be done by comparing the moles of koh produced from each reactant. convert the moles of each reactant into moles of koh. the limiting reactant will produce the least amount of koh. ko 2 to koh moles koh = 0.2616 mol ko 2 x (4 mol koh 4 mol ko 2) moles koh = 0.2616 mol h 2 o to koh. The relationship between the rates of disappearance and appearance is rooted in the stoichiometry of the balanced equation, which is a fundamental principle in chemical reactions and kinetics.
Solved Consider The Following Balanced Chemical Equation 4ko2 S Consider the following balanced chemical equation: 4ko2 (s) 2h2o (l) 3o2 (g) 4koh (s) (a) determine the mass (in g) of koh formed if 10.0 g of ko2 reacts with 10.0 g of h2o. Consider the following balanced chemical equation: 4ko2(s) 2h2o(l) → 4koh(s) 3o2(g) determine the mass (in g) of koh formed if 30.1 g of ko2 reacts with 30.1 g of h2o. g koh. the molar mass of ko2 is approximately 71.1 g mol and the molar mass of h2o is approximately 18.02 g mol. show more…. Next, determine the limiting reactant. this can be done by comparing the moles of koh produced from each reactant. convert the moles of each reactant into moles of koh. the limiting reactant will produce the least amount of koh. ko 2 to koh moles koh = 0.2616 mol ko 2 x (4 mol koh 4 mol ko 2) moles koh = 0.2616 mol h 2 o to koh. The relationship between the rates of disappearance and appearance is rooted in the stoichiometry of the balanced equation, which is a fundamental principle in chemical reactions and kinetics.
Comments are closed.