Decision Curve Analysis A Decision Curve Analysis To Evaluate The Method: the authors describe decision curve analysis, a simple, novel method of evaluating predictive models. they start by assuming that the threshold probability of a disease or event at which a patient would opt for treatment is informative of how the patient weighs the relative harms of a false positive and a false negative prediction. Decision curve analysis is a method to evaluate prediction models and diagnostic tests that was introduced in a 2006 publication. decision curves are now commonly reported in the literature, but there remains widespread misunderstanding of and confusion about what they mean.
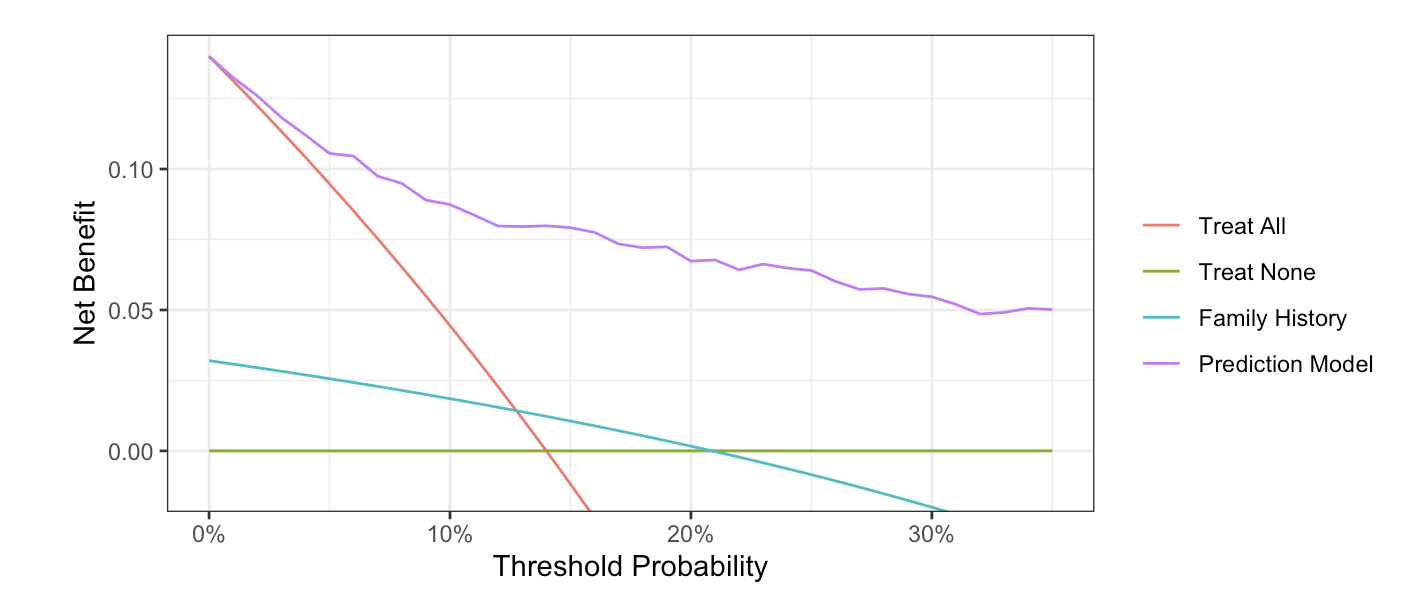
Dca Homepage Decision curve analysis is a suitable method for evaluating alternative diagnostic and prognostic strategies that has advantages over other commonly used measures and techniques. keywords: prediction models, multivariate analysis, decision analysis. Decision curve analysis (dca) is a widely used method to measure this utility. in this framework, a clinical judgment of the relative value of benefits (treating a true positive case) and harms (treating a false positive case) associated with prediction models is made. Decision curve analysis evaluates a predictor for an event as a probability threshold is varied, typically by showing a graphical plot of net benefit against threshold probability. by convention, the default strategies of assuming that all or no observations are positive are also plotted. In contrast to traditional performance measures, decision curve analysis (dca) can assess the utility of models for decision making. dca plots net benefit (nb) at a range of clinically reasonable risk thresholds. objective: to provide recommendations on interpreting and reporting dca when evaluating prediction models.

Decision Curve Analysis A Decision Curve Analysis Of The Training Decision curve analysis evaluates a predictor for an event as a probability threshold is varied, typically by showing a graphical plot of net benefit against threshold probability. by convention, the default strategies of assuming that all or no observations are positive are also plotted. In contrast to traditional performance measures, decision curve analysis (dca) can assess the utility of models for decision making. dca plots net benefit (nb) at a range of clinically reasonable risk thresholds. objective: to provide recommendations on interpreting and reporting dca when evaluating prediction models. Decision curve analysis is a method to evaluate prediction models and diagnostic tests that was introduced in a 2006 publication. decision curves are now commonly reported in the literature, but there remains widespread misunderstanding of and confusion about what they mean. Here we give a brief introduction to decision curve analysis, explaining the critical concepts of net benefit and threshold probability. we briefly review some prediction models reported in the orthopedic literature, demonstrating how use of decision curves has allowed conclusions as to the clinical value of a prediction model. Decision curve analysis is a method for evaluating and comparing prediction models that incorporates clinical consequences, requires only the data set on which the models are tested, and can be applied to models that have either continuous or dichotomous results. Prospective demonstration in 1 setting that use of decision rule improves physicians’ decisions (quality or cost effectiveness of patient care). prospective demonstration in varied settings that use of decision rule improves physicians’ decisions for wide spectrum of patients.
