Derivatives Power Rule 2 Open Middle
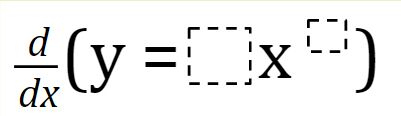
Derivatives Power Rule 2 Open Middle How do i calculate the derivative of a function, for example y = x2 1 using numpy? let's say, i want the value of derivative at x = 5. How do i compute the derivative of an array, y (say), with respect to another array, x (say) both arrays from a certain experiment? e.g. y = [1,2,3,4,4,5,6] and x.

2 1 Power Rule Pdf Derivative Mathematical Concepts How is the derivative of a f(x) typically calculated programmatically to ensure maximum accuracy? i am implementing the newton raphson method, and it requires taking of the derivative of a function. For higher order derivatives, you can repeatedly call jacobian or grad while maintaining the computational graph: create graph (bool, optional) – if true, graph of the derivative will be constructed, allowing to compute higher order derivative products. I have determined derivatives through 2 separate methods, applying a high dof cubic smooth spline and via first and second differences (lightly smoothed) and bootstrapping to approximate errors with both producing comparable results. i note that the "gam.fit3" function facilitates determining upto 2nd order derivatives but is not called directly. As a bonus :), i plotted (by using printf to format data as json and copy pasting from the console) the spline values in the interval [0, 1], for both simple interpolation and the case with derivatives,and one case see the zero derivatives for x (t) and y (t) in the top chart, by the fact that the points are not uniformly distributed, but are.

Power Rule Of Differentiation Pdf Derivative Rates I have determined derivatives through 2 separate methods, applying a high dof cubic smooth spline and via first and second differences (lightly smoothed) and bootstrapping to approximate errors with both producing comparable results. i note that the "gam.fit3" function facilitates determining upto 2nd order derivatives but is not called directly. As a bonus :), i plotted (by using printf to format data as json and copy pasting from the console) the spline values in the interval [0, 1], for both simple interpolation and the case with derivatives,and one case see the zero derivatives for x (t) and y (t) in the top chart, by the fact that the points are not uniformly distributed, but are. I'm interested in computing partial derivatives in python. i've seen functions which compute derivatives for single variable functions, but not others. it would be great to find something that did. Is there a way to get scipy's interp1d (in linear mode) to return the derivative at each interpolated point? i could certainly write my own 1d interpolation routine that does, but presumably scipy'. To calculate higher order derivatives should be done using truncated taylor series. you could also apply above mentioned class to itself the type for the value and derivative values should be a template argument. but this means calculation and storing of derivatives more than once. The problem is that if we work with such small differences the precision of the output derivatives is severely limited, meaning it can only have integer values. therefore we add values slightly larger than eps to allow for higher precisions. % how many floating points the derivatives can have precision = 10;.
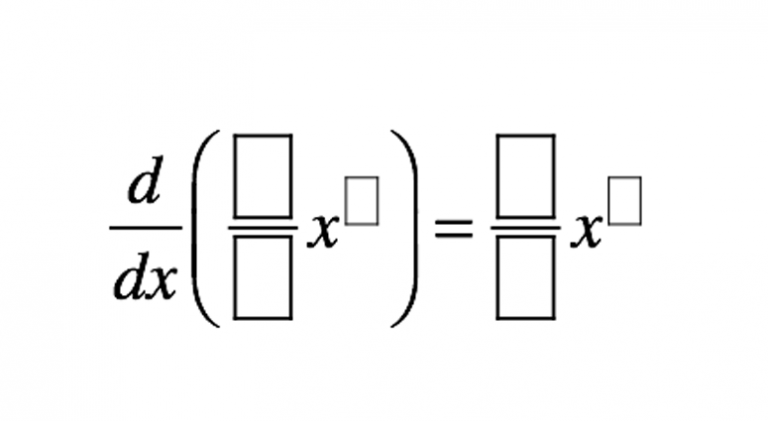
Derivative Power Rule Open Middle I'm interested in computing partial derivatives in python. i've seen functions which compute derivatives for single variable functions, but not others. it would be great to find something that did. Is there a way to get scipy's interp1d (in linear mode) to return the derivative at each interpolated point? i could certainly write my own 1d interpolation routine that does, but presumably scipy'. To calculate higher order derivatives should be done using truncated taylor series. you could also apply above mentioned class to itself the type for the value and derivative values should be a template argument. but this means calculation and storing of derivatives more than once. The problem is that if we work with such small differences the precision of the output derivatives is severely limited, meaning it can only have integer values. therefore we add values slightly larger than eps to allow for higher precisions. % how many floating points the derivatives can have precision = 10;.
Comments are closed.