Determine The Resultant Internal Loadings At C Example 1 1 Mechanics Of Materials Rc Hibbeler
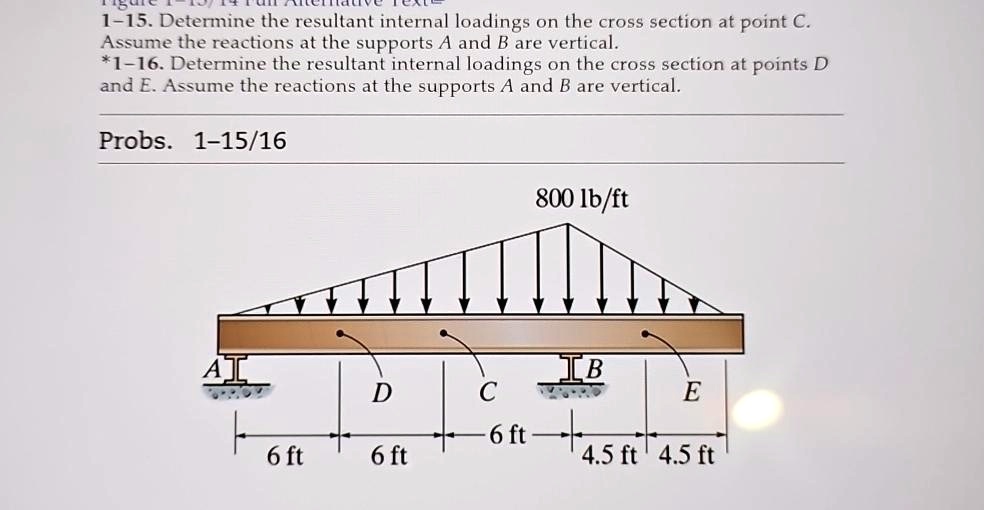
1 15 Determine The Resultant Internal Loadings On The Cross Section At Determine the resultant internal loadings acting on the cross section of the boom at point e . Determine the resultant internal loadings acting on the cross section at point c in the beam. the load d has a mass of 300 kg and is being hoisted by the motor m with constant velocity.
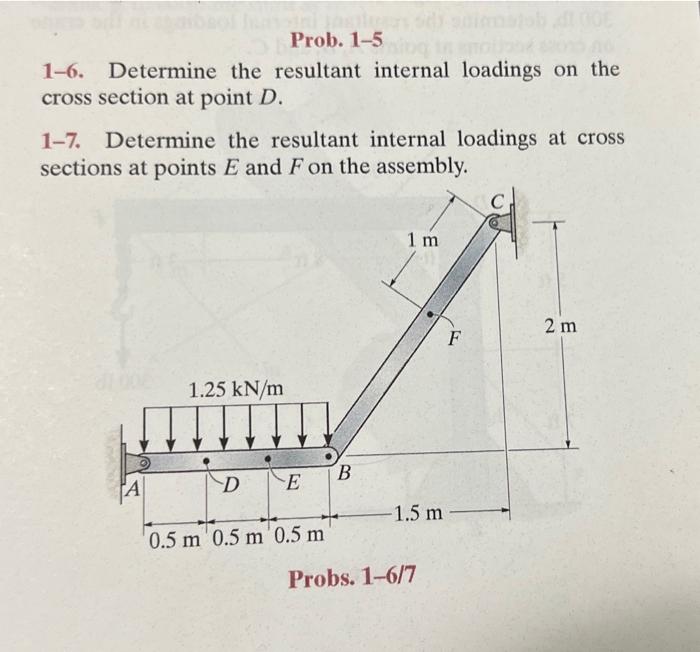
Solved 1 6 Determine The Resultant Internal Loadings On The Chegg Determine the resultant internal loadings acting on section b–b through the centroid c on the beam. the smooth surface at b prevents horizontal motion, and the external pin at a prevents horizontal and vertical motion. as a result, there are three unknown forces in the free body diagram of the beam shown below. Determine the internal normal force, shear force, and moment at points c and d in the simply supported beam. point d is located just to the left of the 2500 lb force. Determine the resultant internal loading on the cross section through point d of the pliers. sample problems and notes are based on the following text book: mechanics of materials 8th edition. It is important to keep the distributed loading on the segment until after the section is made. only then should this loading be replaced by a single resultant force. notice that the intensity of the distributed loading at c is found by proportion, i.e. from fig. 1 4a, w 6 m = (270 n m) 9m, w = 180 n m.

1 Determine The Resultant Internal Loadings On The Cross Sections Determine the resultant internal loading on the cross section through point d of the pliers. sample problems and notes are based on the following text book: mechanics of materials 8th edition. It is important to keep the distributed loading on the segment until after the section is made. only then should this loading be replaced by a single resultant force. notice that the intensity of the distributed loading at c is found by proportion, i.e. from fig. 1 4a, w 6 m = (270 n m) 9m, w = 180 n m. This video explains in detail the solution to problem 1 4 in the chapter of stress from the book mechanics of materials by r.c. hibbeler 10th edition (9th also). Determine the resultant internal loadings in the 3 kip beam at cross sections through points d and e. point e is 1.5 kip ft just to the right of the 3 kip load. Determine the resultant internal forces and moments at f and g. assume a smooth (frictionless) contact at e. solution: nf = 0, vf = 120 lb, mf = 240 ft lb ng = 25 lb, vg = 108 lb, mg = 162 ft lb. Example: determine the internal normal force, shear force, and the loading moment acting just to the left at point b, and just to the right at point c of the 6 kn force.
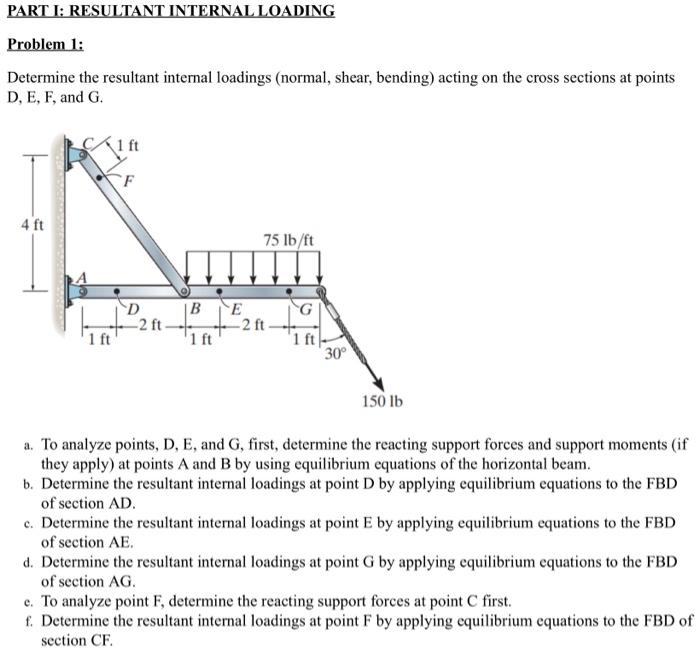
Solved Part I Resultant Internal Loading Problem 1 Chegg This video explains in detail the solution to problem 1 4 in the chapter of stress from the book mechanics of materials by r.c. hibbeler 10th edition (9th also). Determine the resultant internal loadings in the 3 kip beam at cross sections through points d and e. point e is 1.5 kip ft just to the right of the 3 kip load. Determine the resultant internal forces and moments at f and g. assume a smooth (frictionless) contact at e. solution: nf = 0, vf = 120 lb, mf = 240 ft lb ng = 25 lb, vg = 108 lb, mg = 162 ft lb. Example: determine the internal normal force, shear force, and the loading moment acting just to the left at point b, and just to the right at point c of the 6 kn force.
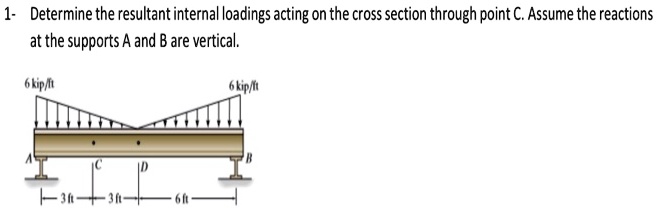
Solved Mechanics Of Materials Problem 1 Determine The Resultant Determine the resultant internal forces and moments at f and g. assume a smooth (frictionless) contact at e. solution: nf = 0, vf = 120 lb, mf = 240 ft lb ng = 25 lb, vg = 108 lb, mg = 162 ft lb. Example: determine the internal normal force, shear force, and the loading moment acting just to the left at point b, and just to the right at point c of the 6 kn force.
Comments are closed.