
Do Students Have Freedom Of Speech In School Synonym A guide to free speech in schools: what is (and isn't) allowed? can students wear symbols showing support for or opposition to something? most likely, yes, thanks to the 1969 supreme court case tinker v. des moines independent community school district. the court declared that three students should have been allowed to wear black armbands, a. Do students have first amendment rights in school? yes. students have the right to share their opinions and ideas ― known as “freedom of expression.” 3. this includes all forms of “speech” and communication, like speaking aloud, writing on paper or in online chat platforms, wearing t shirts with messages or protest.

Do Students Have Freedom Of Speech In School The Classroom Students at public schools have first amendment rights to freedom of expression, but they can be punished for some kinds of speech or other ways of expressing their opinions. schools may restrict speech that is disruptive, dangerous, or lewd; promotes drug use; or is part of the curriculum or school communications. The supreme court ruled in 1969 that students do not "shed their constitutional rights to freedom of speech or expression at the schoolhouse gate." this is true for other fundamental rights, as well. share this issue:. While the first amendment without a doubt endows students with freedom of speech, this does not mean that they can behave in any manner they please. it is very much within the jurisdiction of the school authorities to prevent or prohibit students from indulging in certain activities that may potentially pose a threat to a school environment. The different level of speech protection for students in institutions of higher education, who are generally 18 years or older and thus legally adults, is evident from several cases. students on college and university campuses enjoy more academic freedom than secondary school students. in healy v.

Do Students Have Freedom Of Speech In School Synonym While the first amendment without a doubt endows students with freedom of speech, this does not mean that they can behave in any manner they please. it is very much within the jurisdiction of the school authorities to prevent or prohibit students from indulging in certain activities that may potentially pose a threat to a school environment. The different level of speech protection for students in institutions of higher education, who are generally 18 years or older and thus legally adults, is evident from several cases. students on college and university campuses enjoy more academic freedom than secondary school students. in healy v. Public school students in k 12 schools do not lose their right to free speech when they enter the school building. at the new york civil liberties union, we believe that the first amendment protects students’ right to learn, including the right to receive information, share ideas, and have a free and open exchange about race, gender, and our. The first amendment's guarantee of freedom of speech applies to students in the public schools. in the landmark decision tinker v. des moines independent community school district, the u.s. supreme court formally recognized that students do not "shed their constitutional rights to freedom of speech or expression at the schoolhouse gate". [1]. The court declared that students and teachers do not “shed their constitutional rights to freedom of speech or expression at the schoolhouse gate.” the first amendment ensures that students cannot be punished for exercising free speech rights, even if school administrators don’t approve of what they are saying. Students are not speaking on behalf of the school as often as faculty. students reserve the right to make political opinions known on school property and within school sanctioned clubs. this is a privilege that faculty members do not have. in addition, students have far more freedom outside the classroom than their teachers do.
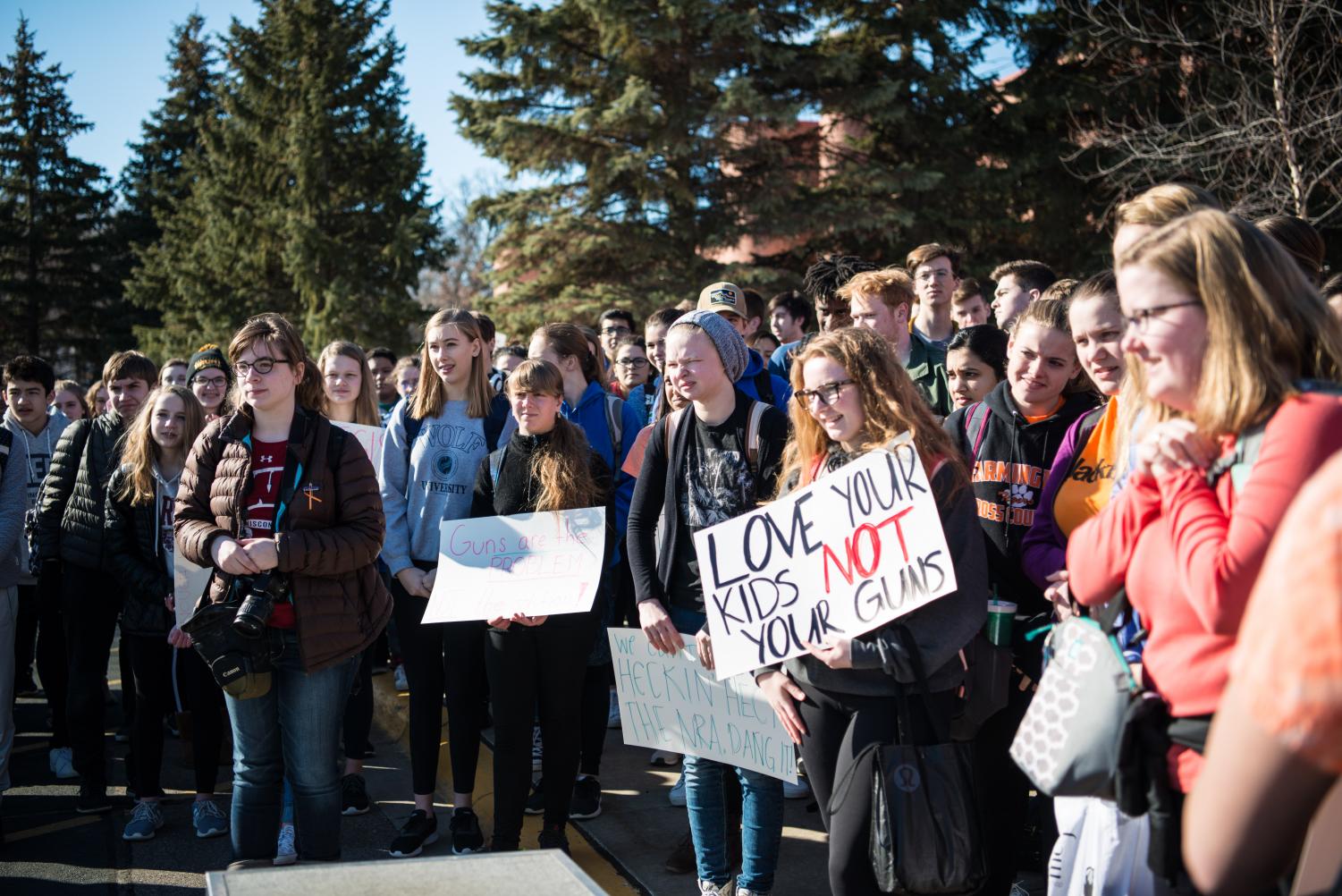
Eagan Independent What Freedom Of Speech Rights Do Students Have In Public school students in k 12 schools do not lose their right to free speech when they enter the school building. at the new york civil liberties union, we believe that the first amendment protects students’ right to learn, including the right to receive information, share ideas, and have a free and open exchange about race, gender, and our. The first amendment's guarantee of freedom of speech applies to students in the public schools. in the landmark decision tinker v. des moines independent community school district, the u.s. supreme court formally recognized that students do not "shed their constitutional rights to freedom of speech or expression at the schoolhouse gate". [1]. The court declared that students and teachers do not “shed their constitutional rights to freedom of speech or expression at the schoolhouse gate.” the first amendment ensures that students cannot be punished for exercising free speech rights, even if school administrators don’t approve of what they are saying. Students are not speaking on behalf of the school as often as faculty. students reserve the right to make political opinions known on school property and within school sanctioned clubs. this is a privilege that faculty members do not have. in addition, students have far more freedom outside the classroom than their teachers do.
