
E Mc2 Proof Pdf Momentum Mass If the law e=mc^2 is true, then if i throw a pen near black hole it should have become the size of a planet near reaching it, and who knows that there might be a period of time where the size and mass becomes so high that it would not affect the suctioning speed of black hole and it would create an object in midway between the blackhole and we. Einstein's famous equation, e=mc², pops up on everything from baseball caps to bumper stickers. it's even the title of a 2008 mariah carey album. but what does albert einstein's famous equation really mean? read on to learn more about the meaning and origins of this well known equation.

E Mc 2 Real Or Just An Mathematical Proof Thelonearisttheory This page explains, with minimal mathematics, how e = mc 2 is derived from special relativity. in doing so it follows the same theoretical arguments that einstein used. however, for reasons of completeness, and although advanced and difficult to follow, english translations of einstein’s original special relativity and e = mc 2 papers are. E = mc 2, equation in german born physicist albert einstein’s theory of special relativity that expresses the fact that mass and energy are the same physical entity and can be changed into each other. in the equation, the increased relativistic mass (m) of a body times the speed of light squared (c 2) is equal to the kinetic energy (e) of. How to understand $e=mc^2$? i also noticed that someone who asked a question what the physical reason is of why $c$ is squared in the most famous equation of all. which is not fully known, but i try to explain there as well. but so a more modern view about how einstein realized that $e$ equals $mc^2$ is as follows:. In this post, we’re going to prove the most famous formula in all of science, e = mc^2! we’ll do this using a simplified version of einstein’s original 1905 proof. in this post i will assume that you are familiar with special relativity and lorentz transformations. consider a box of mass m which is at rest. at a certain moment, it.
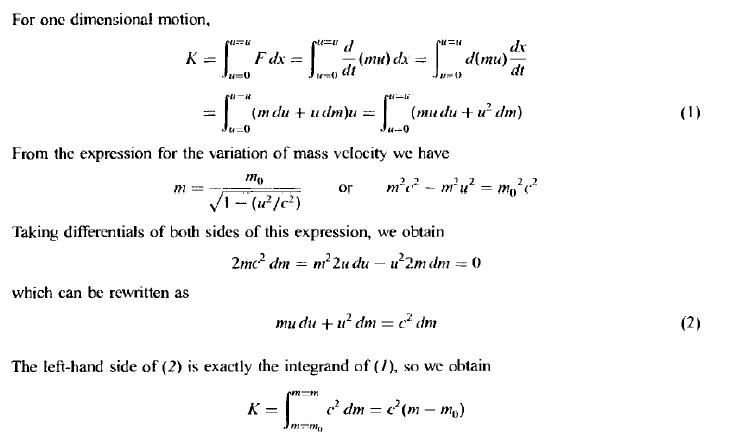
Emc2 Mathematical Proof Payment Proof 2020 How to understand $e=mc^2$? i also noticed that someone who asked a question what the physical reason is of why $c$ is squared in the most famous equation of all. which is not fully known, but i try to explain there as well. but so a more modern view about how einstein realized that $e$ equals $mc^2$ is as follows:. In this post, we’re going to prove the most famous formula in all of science, e = mc^2! we’ll do this using a simplified version of einstein’s original 1905 proof. in this post i will assume that you are familiar with special relativity and lorentz transformations. consider a box of mass m which is at rest. at a certain moment, it. In your demonstration of the derivation of e=mc^2, you have the equation: e’ = e (1 2)mv^2 o(v^3). consider: a – let o(v^3) = epsilon; as limit epsilon > 0; then o(v^3) > 0. this may represent the difference between the ideal yield and actual yield of mass fission into energy?. Whereas einstein’s original argument considers a mass emitting two photons in several different reference frames, the argument here considers a large mass breaking up into two equal smaller masses. We want to show that in unit time the energy e gained by the body due to the action of the force is equal to mc 2, where m is the mass gained by the body. we have two relations between energy, force and momentum from earlier discussion. applying them to the case at hand and combining the two outcomes returns e=mc 2. It is this conception of mass that enters into the relation e=mc 2. einstein's later "on the inertia of energy" paper derives what we now call e=mc 2 for the mass of an electron at rest. in this special case, longitudinal and transverse masses reduce to the same number. e=mc 2 for all forms of energy.
