
Energy Flow Through The Ecosystem Pdf Food Web Primary Production It describes how primary production and net primary production incorporate and account for energy used versus stored by plants. models of linear and y shaped energy flow through ecosystems are provided, with the y shaped model separating grazing and detritus food chains. How does energy flow in an ecosystem? energy flow is the transfer of energy from one organism to another in an ecosystem. every organism interacts with its ecosystem in two ways: how are energy flow and feeding relationships in ecosystems modelled? 1. food chains: food chains show the flow of energy from plant to animal and from animal to animal.

12 3 Energy Flow Pdf Food Web Primary Production Feeding relationships between organisms of an ecosystem determine routes of energy flow and chemical cycling in an ecosystem trophic structure is a key factor in ecosystem dynamics. Food webs illustrate how energy flows directionally through ecosystems, including how efficiently organisms acquire it, use it, and how much remains for use by other organisms of the food web. Primaryproductionand energy flow in ecosystems ecosystem an energy processing and nutrient components. the properties and functionsof ecosystems that we drink, provide the food that we eat, pollutants and toxins that we release from our energy trophic structure structure (f ofod web). the trophic structuredescribes the. Food chain the transfer of energy from sun to producer to primary consumer to secondary consumer to tertiary consumer can be shown in a.
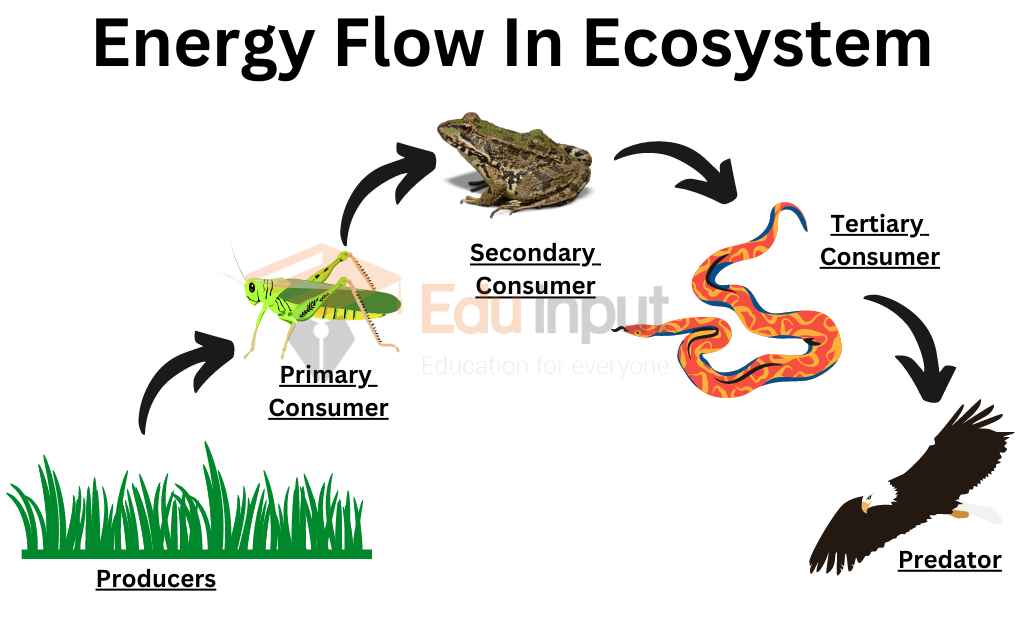
Energy Flow In Ecosystems Worksheet Energy Flow 1 Foo Vrogue Co Primaryproductionand energy flow in ecosystems ecosystem an energy processing and nutrient components. the properties and functionsof ecosystems that we drink, provide the food that we eat, pollutants and toxins that we release from our energy trophic structure structure (f ofod web). the trophic structuredescribes the. Food chain the transfer of energy from sun to producer to primary consumer to secondary consumer to tertiary consumer can be shown in a. Most (90%) of the energy the primary consumer gets from the producer is used by the consumer. some of the energy moves into the atmosphere as heat. some energy in the primary consumer is not lost to the atmosphere or used by the consumer itself. this 10% of energy is available for another consumer. Fig: flow of energy at different level of ecosystem [primary production is the rate of organic biomass growth or accumulation by plants. primary production is commonly split into two components, gross primary productivity (gpp) and net primary productivity (npp). Energy moves through the ecosystem by a series of events that link organisms together. plants have green pigments, called chlorophyll which captures energy from the sun (solar energy) to split carbon dioxide atoms and then combine the carbon atoms with oxygen and hydrogen (photosynthesis) to make sugars (food). An ecosystem's gross primary productivity (gpp) is the total amount of organic matter that it produces through photosynthesis. net primary productivity (npp) describes the amount of energy that remains available for plant growth after subtracting the fraction that plants use for respiration.

Fillable Online Food Webs And Energy Flows Fax Email Print Pdffiller Most (90%) of the energy the primary consumer gets from the producer is used by the consumer. some of the energy moves into the atmosphere as heat. some energy in the primary consumer is not lost to the atmosphere or used by the consumer itself. this 10% of energy is available for another consumer. Fig: flow of energy at different level of ecosystem [primary production is the rate of organic biomass growth or accumulation by plants. primary production is commonly split into two components, gross primary productivity (gpp) and net primary productivity (npp). Energy moves through the ecosystem by a series of events that link organisms together. plants have green pigments, called chlorophyll which captures energy from the sun (solar energy) to split carbon dioxide atoms and then combine the carbon atoms with oxygen and hydrogen (photosynthesis) to make sugars (food). An ecosystem's gross primary productivity (gpp) is the total amount of organic matter that it produces through photosynthesis. net primary productivity (npp) describes the amount of energy that remains available for plant growth after subtracting the fraction that plants use for respiration.

Ecosystem And Energy Flow Pdf Primary Production Food Web Energy moves through the ecosystem by a series of events that link organisms together. plants have green pigments, called chlorophyll which captures energy from the sun (solar energy) to split carbon dioxide atoms and then combine the carbon atoms with oxygen and hydrogen (photosynthesis) to make sugars (food). An ecosystem's gross primary productivity (gpp) is the total amount of organic matter that it produces through photosynthesis. net primary productivity (npp) describes the amount of energy that remains available for plant growth after subtracting the fraction that plants use for respiration.

Ecosystems And Energy Flow Pdf Food Web Primary Production
