
Viral Small Rna Semantic Scholar This review summarizes strategies to study rna structures, to identify small molecules recognizing these structures, and to augment the functionality of rna binding small molecules to develop rna targeted small molecules as potential therapeutics in a variety of diseases. Recent efforts of antiviral lead discovery for rna targets have provided drug‐like small molecules that inhibit viral replication and include inhibitors of human immunodeficiency virus (hiv), hepatitis c virus (hcv), severe respiratory syndrome coronavirus (sars cov), and influenza a virus.
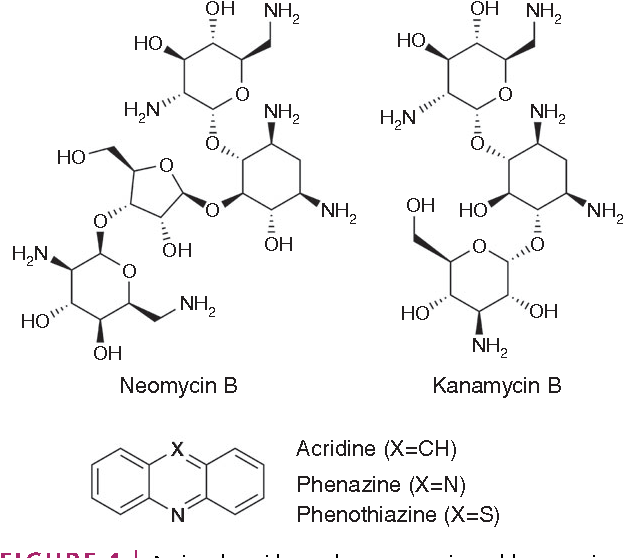
Figure 1 From Small Molecules Targeting Viral Rna Semantic Scholar Here, we discuss methods for the identification of rna targeting compounds, starting from the determination of rna structures either from purified rna or in living cells, followed by in silico screening on rna and phenotypic assays to evaluate viral inhibition. In this review, we discuss three general frameworks (sets of premises and hypotheses) that, in our view, have so far dominated the discovery of small molecule ligands for rna. we highlight the unique merits of each framework as well as the pitfalls associated with exclusive focus of ligand discovery efforts within only one framework. Inhibition of viral rna function by small molecule ligands has been extensively studied for human immunodeficiency virus and hepatitis c virus which provide valuable insight for the future exploration of rna targets in other viral pathogens. Small molecules are more ‘drug like’ than nucleic acids and have better physicochemical properties. structure based identification of small molecules that bind to rna would provide higher specificity than sequence based strategies.

Pdf Small Molecules Targeting Viral Rna Small Molecules Targeting Inhibition of viral rna function by small molecule ligands has been extensively studied for human immunodeficiency virus and hepatitis c virus which provide valuable insight for the future exploration of rna targets in other viral pathogens. Small molecules are more ‘drug like’ than nucleic acids and have better physicochemical properties. structure based identification of small molecules that bind to rna would provide higher specificity than sequence based strategies. Recent studies show that some mirnas can target the viral rna transcripts after viruses enter into cells, and those host mirnas appear to play varied roles in affecting viruses. Here, we discuss methods for the identification of rna targeting compounds, starting from the determination of rna structures either from purified rna or in living cells, followed by in silico screening on rna and phenotypic assays to evaluate viral inhibition. These molecules target rna in a variety of diseases, including cancer, neurodegeneration, and viral infection, in cellular and animal model systems. additionally, we explore the recently fda approved small molecule regulator of rna splicing, risdiplam, for treatment of spinal muscular atrophy. Recent studies identifying small molecules targeting non coding rnas may provide an alternative approach to oligonucleotide methods. here we review recent work investigating new structural and chemical principles for targeting rna with small molecules.

Pdf Small Molecules Targeting Viral Rna Recent studies show that some mirnas can target the viral rna transcripts after viruses enter into cells, and those host mirnas appear to play varied roles in affecting viruses. Here, we discuss methods for the identification of rna targeting compounds, starting from the determination of rna structures either from purified rna or in living cells, followed by in silico screening on rna and phenotypic assays to evaluate viral inhibition. These molecules target rna in a variety of diseases, including cancer, neurodegeneration, and viral infection, in cellular and animal model systems. additionally, we explore the recently fda approved small molecule regulator of rna splicing, risdiplam, for treatment of spinal muscular atrophy. Recent studies identifying small molecules targeting non coding rnas may provide an alternative approach to oligonucleotide methods. here we review recent work investigating new structural and chemical principles for targeting rna with small molecules.

Figure 1 From Design Of Small Molecules Targeting Rna Structure From These molecules target rna in a variety of diseases, including cancer, neurodegeneration, and viral infection, in cellular and animal model systems. additionally, we explore the recently fda approved small molecule regulator of rna splicing, risdiplam, for treatment of spinal muscular atrophy. Recent studies identifying small molecules targeting non coding rnas may provide an alternative approach to oligonucleotide methods. here we review recent work investigating new structural and chemical principles for targeting rna with small molecules.
