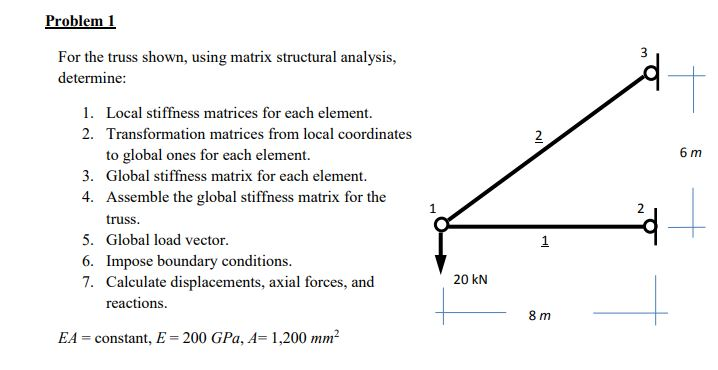
Solved Problem 1 For The Truss Shown Using Matrix Chegg The matrix stiffness method for 2d trusses cee 421l. matrix structural analysis department of civil and environmental engineering duke university henri p. gavin fall, 2014 method 1.number all of the nodes and all of the elements. 2.identify the displacement degrees of freedom in global directions. number all the structural degrees of freedom. An indeterminate truss is supported and loaded as shown above, using the direct stiffness method, obtain the displacements, support reactions, and internal forces that are induced in the members due to the externally applied loads, (ea = constant, dimensions in mm). [the ad id=”498″] (1) establish the x and y global coordinate system.

Structural Analysis For Truss Desklib Our expert help has broken down your problem into an easy to learn solution you can count on. question: problem 1 for the truss shown, using matrix structural analysis, determine 1. local stiffness matrices for each element. 2. transformation matrices from local coordinates 2 to global ones for each element 3. 4. To support the ideas developed here we will introduce some matlab scripts at each point to demonstrate how the theory described can be implemented for computer calculation. this collection of scripts will build into a program that can analyse pin jointed trusses. These local (member) force displacement relationships can be easily established for all the members in the truss, simply by using given material and geometric properties of the different members. For the truss shown, use the stiffness method to: (a) determine the deflections of the loaded joint. (b) determine the end forces of each member and reactions at supports.

Structural Analysis For Truss Desklib These local (member) force displacement relationships can be easily established for all the members in the truss, simply by using given material and geometric properties of the different members. For the truss shown, use the stiffness method to: (a) determine the deflections of the loaded joint. (b) determine the end forces of each member and reactions at supports. The present chapter contains an introduction to application of matrix methods for structural analysis of linear truss and beam structures. in classical mechanics of materials, the differential equations governing deformations of such structures due to given loads have been derived and considered on explicit form. Matrix structural analysis is the process of predicting the performance of a structure under prescribed loading conditions. it provides key structural responses like stresses, deflections, and support reactions. The document discusses applying the matrix method of structural analysis to truss problems. it begins by reviewing the overall philosophy of breaking structures into small elements and writing the force displacement relationship for each element. This document provides an example of using the matrix stiffness method to analyze a truss. it shows: 1) defining the truss members and joints with numbers. 2) assembling the member stiffness matrices based on each member's properties. 3) combining the member matrices into a global stiffness matrix.

Structural Analysis For Truss Desklib The present chapter contains an introduction to application of matrix methods for structural analysis of linear truss and beam structures. in classical mechanics of materials, the differential equations governing deformations of such structures due to given loads have been derived and considered on explicit form. Matrix structural analysis is the process of predicting the performance of a structure under prescribed loading conditions. it provides key structural responses like stresses, deflections, and support reactions. The document discusses applying the matrix method of structural analysis to truss problems. it begins by reviewing the overall philosophy of breaking structures into small elements and writing the force displacement relationship for each element. This document provides an example of using the matrix stiffness method to analyze a truss. it shows: 1) defining the truss members and joints with numbers. 2) assembling the member stiffness matrices based on each member's properties. 3) combining the member matrices into a global stiffness matrix.

Matrix Structural Analysis Truss Matrix Mathematics Structural The document discusses applying the matrix method of structural analysis to truss problems. it begins by reviewing the overall philosophy of breaking structures into small elements and writing the force displacement relationship for each element. This document provides an example of using the matrix stiffness method to analyze a truss. it shows: 1) defining the truss members and joints with numbers. 2) assembling the member stiffness matrices based on each member's properties. 3) combining the member matrices into a global stiffness matrix.
