
Gcse Physics Revision Potential Difference In Series Circuits Gcse Diagram showing the behaviour of current in series and parallel circuits. potential difference in series & parallel. in a series circuit, the voltage of the power supply is shared between the components. in a parallel circuit, the voltage across each component is the same. Components can either be connected in series or parallel. the type of circuit can have an effect on the current, potential difference and resistance of the circuit. in a series circuit, circuit components are connected in a single loop, one after another.

Series Circuits Aqa Gcse Physics Pango In series circuits: current is the same through each component; the total potential difference of the power supply is shared between the components. Learn about direct and alternating potential difference for your gcse physics exam. this revision note covers the key differences between ac & dc power supplies. Learn about and revise how series and parallel circuits work and resistance in series and parallel circuits with gcse bitesize combined science. Potential difference in a series circuit. in a series circuit, the potential difference is shared between the components. the sum of potential differences across all of the components is equal to the potential difference across the cell or battery. so we can say: v total = v 1 v 2 v 3 … potential difference (v) is measured in volts (v).

Series And Parallel Circuits Gcse Physics Combined Science Aqa Learn about and revise how series and parallel circuits work and resistance in series and parallel circuits with gcse bitesize combined science. Potential difference in a series circuit. in a series circuit, the potential difference is shared between the components. the sum of potential differences across all of the components is equal to the potential difference across the cell or battery. so we can say: v total = v 1 v 2 v 3 … potential difference (v) is measured in volts (v). A potential difference of 1 volt tells us that 1 joule of energy is transferred for each coulomb of charge that is moving through the circuit. when two or more components are connected in series, the total potential difference of the supply is shared between them. This section explains series and parallel circuits covering, series circuits, total resistance, and the total resistance equation, parallel circuits and the key differences between series and parallel circuits. series circuits a series circuit is a type of electrical circuit where all components are connected end to end in a single loop. in a series circuit, the current flows through every. The current in a circuit depends on the potential difference provided by the cells and the total resistance of the circuit. (a) figure 1 shows the graph of current against potential difference for a component. what is the name of the component? draw a ring around the correct answer. diode filament bulb thermistor (1). We can explain the energy transferred in an electrical circuit using the idea of potential difference (voltage) potential difference is also called voltage. potential difference (volatage) a potential difference of 1 volt tells us that 1 joule of energy is transferred for each coulomb of charge moving through the circuit.

Series And Parallel Circuits Gcse Physics Combined Science Aqa A potential difference of 1 volt tells us that 1 joule of energy is transferred for each coulomb of charge that is moving through the circuit. when two or more components are connected in series, the total potential difference of the supply is shared between them. This section explains series and parallel circuits covering, series circuits, total resistance, and the total resistance equation, parallel circuits and the key differences between series and parallel circuits. series circuits a series circuit is a type of electrical circuit where all components are connected end to end in a single loop. in a series circuit, the current flows through every. The current in a circuit depends on the potential difference provided by the cells and the total resistance of the circuit. (a) figure 1 shows the graph of current against potential difference for a component. what is the name of the component? draw a ring around the correct answer. diode filament bulb thermistor (1). We can explain the energy transferred in an electrical circuit using the idea of potential difference (voltage) potential difference is also called voltage. potential difference (volatage) a potential difference of 1 volt tells us that 1 joule of energy is transferred for each coulomb of charge moving through the circuit.
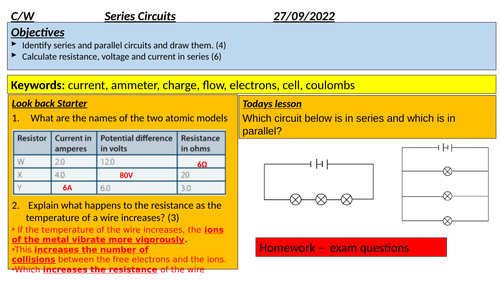
Series Circuits Gcse Physics Teaching Resources The current in a circuit depends on the potential difference provided by the cells and the total resistance of the circuit. (a) figure 1 shows the graph of current against potential difference for a component. what is the name of the component? draw a ring around the correct answer. diode filament bulb thermistor (1). We can explain the energy transferred in an electrical circuit using the idea of potential difference (voltage) potential difference is also called voltage. potential difference (volatage) a potential difference of 1 volt tells us that 1 joule of energy is transferred for each coulomb of charge moving through the circuit.

Circuits Current And Potential Difference Gcse Physics Teaching Resources
