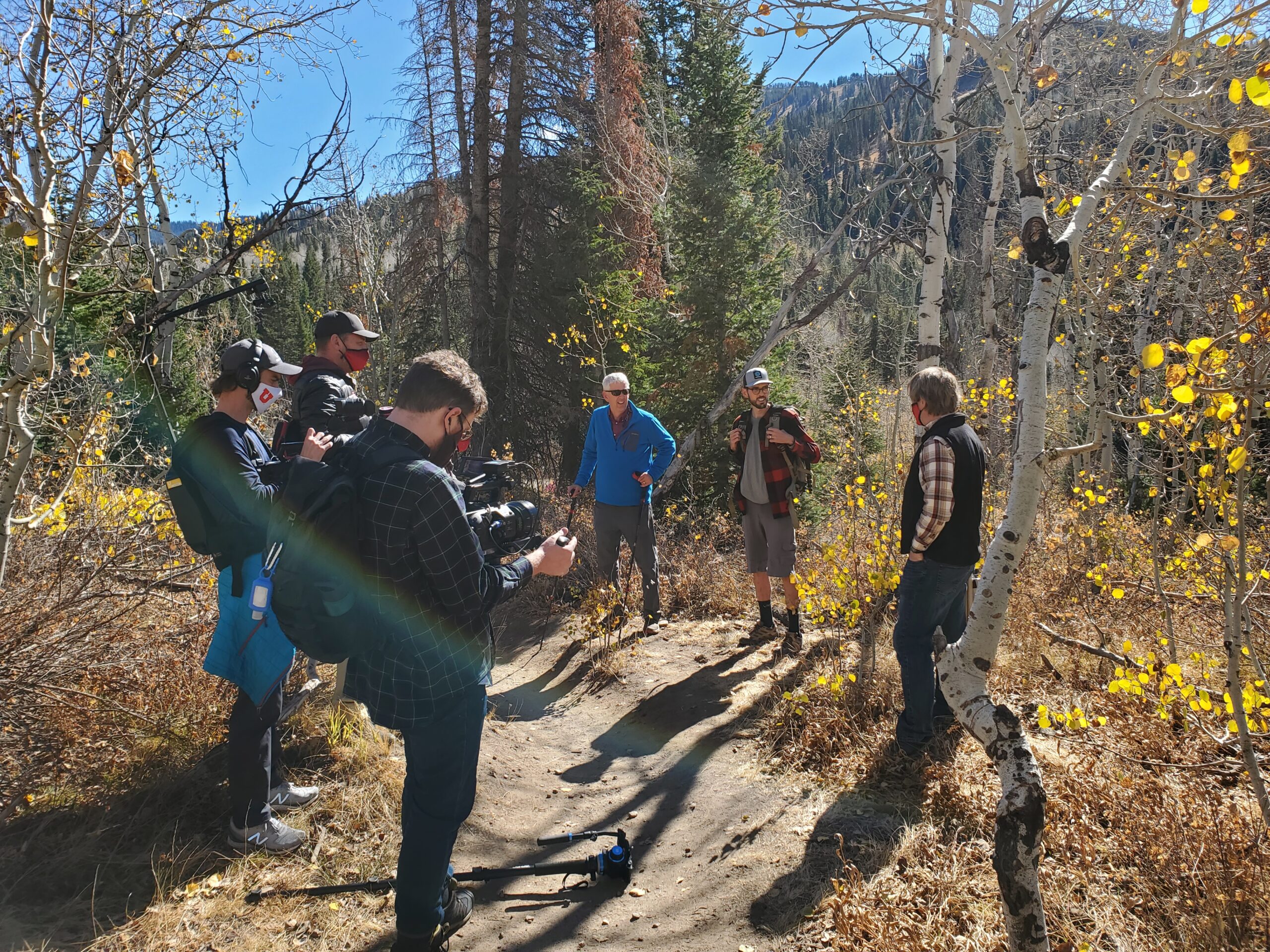

Global Analysis Identifies At Risk Forests School Of Biological Sciences But zooming in to regional forests and taking into account models that forecast carbon loss and changes in vegetation, the researchers found higher risk of carbon loss in southern boreal (just south of the arctic) forests and the drier regions of the amazon and african tropics. Researchers quantify the risk to forests from climate change along three dimensions: carbon storage, biodiversity and forest loss from disturbance, such as fire or drought. the results show.

Global Analysis Identifies At Risk Forests School Of Biological Sciences Global analysis identifies at risk forests. forests are engaged in a delicate, deadly dance with climate change, hosting abundant biodiversity and sucking carbon dioxide out of the air with billions of leafy straws. Global analysis identifies at risk forests sep. 1, 2022 — researchers quantify the risk to forests from climate change along three dimensions: carbon storage, biodiversity and forest loss. Anderegg et al. compared results from three major modeling approaches that provide information on different facets of risk: a global mechanistic vegetation model, which estimates forest carbon loss; a climate envelope model, which provides information on species shifts; and empirical assessment of forest loss to disturbance using satellite imagery. In a study published in science, william anderegg and colleagues quantify the risk to forests from climate change along three dimensions: carbon storage, biodiversity and forest loss from disturbance, such as fire or drought. the results show forests in some regions experiencing clear and consistent risks.
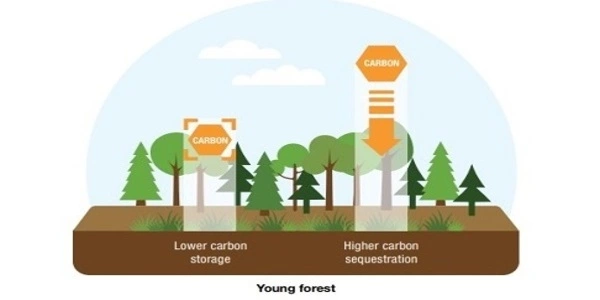
Global Research Identifies Endangered Forests Assignment Point Anderegg et al. compared results from three major modeling approaches that provide information on different facets of risk: a global mechanistic vegetation model, which estimates forest carbon loss; a climate envelope model, which provides information on species shifts; and empirical assessment of forest loss to disturbance using satellite imagery. In a study published in science, william anderegg and colleagues quantify the risk to forests from climate change along three dimensions: carbon storage, biodiversity and forest loss from disturbance, such as fire or drought. the results show forests in some regions experiencing clear and consistent risks. Forests and taking into account models that forecast carbon loss and changes in vegetation, the researchers found higher risk of carbon loss in southern boreal (just south of the arctic) forests. Abstract. earth observation data are increasingly used to estimate the magnitude and geographic distribution of greenhouse gas (ghg) fluxes and reduce overall uncertainty in the global carbon budget, including for forests. here, we report on a revised and updated geospatial, earth observation based modeling framework that maps ghg emissions, carbon removals, and the net balance between them. Climate driven forest mortality events have been extensively observed in recent decades, prompting the question of how quickly these affected forests can recover their functionality following such. Humanity stands at a critical crossroads, faced with the dual planetary crises of biodiversity loss and climate change. 1 as climate change accelerates and species disappear at an accelerating rate, it is necessary to radically rethink the relationship with nature and reshape land management strategies. 2, 3 forests cover approximately 31% of the world’s land surface and play an invaluable.

Global Risk Analysis And Reporting Undrr Forests and taking into account models that forecast carbon loss and changes in vegetation, the researchers found higher risk of carbon loss in southern boreal (just south of the arctic) forests. Abstract. earth observation data are increasingly used to estimate the magnitude and geographic distribution of greenhouse gas (ghg) fluxes and reduce overall uncertainty in the global carbon budget, including for forests. here, we report on a revised and updated geospatial, earth observation based modeling framework that maps ghg emissions, carbon removals, and the net balance between them. Climate driven forest mortality events have been extensively observed in recent decades, prompting the question of how quickly these affected forests can recover their functionality following such. Humanity stands at a critical crossroads, faced with the dual planetary crises of biodiversity loss and climate change. 1 as climate change accelerates and species disappear at an accelerating rate, it is necessary to radically rethink the relationship with nature and reshape land management strategies. 2, 3 forests cover approximately 31% of the world’s land surface and play an invaluable.

Global Analysis Identifies At Risk Forests Climate driven forest mortality events have been extensively observed in recent decades, prompting the question of how quickly these affected forests can recover their functionality following such. Humanity stands at a critical crossroads, faced with the dual planetary crises of biodiversity loss and climate change. 1 as climate change accelerates and species disappear at an accelerating rate, it is necessary to radically rethink the relationship with nature and reshape land management strategies. 2, 3 forests cover approximately 31% of the world’s land surface and play an invaluable.
