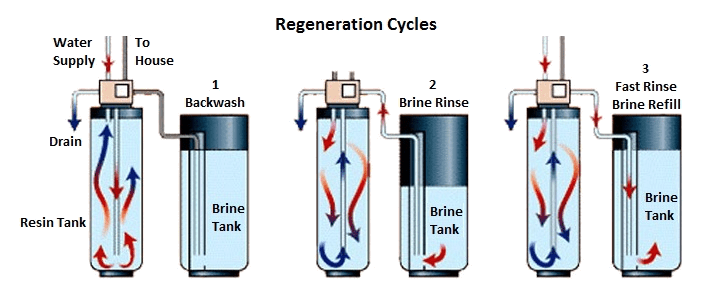
How Does A Water Softener Work Ion Xchange How does an ion exchange water softener work? the operation of an ion exchange water softener can be broken down into several key stages: the service cycle, regeneration cycle, and rinse cycle. 1. service cycle. during the service cycle, hard water enters the water softener tank. the hard water flows through the resin bed, where the ion. Benefits of ion exchange resin in water softening. the use of ion exchange resin in water softening offers several benefits, including: effective removal of water hardness: ion exchange resin is highly effective in removing calcium and magnesium ions, resulting in softened water that is gentler on skin and hair, and reduces scaling in pipes and.

How Does Ion Exchange Water Softener Working How do ion exchange water softeners work? the process of ion exchange involves replacing the hard minerals in the water with sodium or potassium ions (soft minerals). here’s a step by step breakdown of the components and how they work: resin beads: the core component of an ion exchange water softener is a tank filled with resin beads. these. Water softeners work by removing hard water minerals through an ion exchange process. here’s how it works. a water softener contains a mineral tank with a bed of negatively charged resin beads. these spherical beads are typically made of polystyrene and hold a negative charge known as anions. Ion exchange water softeners operate on a fascinating principle of ionic swapping, effectively transforming your hard water into soft, gentle water. let's dive into the nitty gritty of this scientific process, demystifying its magic and unveiling how it tackles the troublesome minerals. What is an ion exchange water softener? an ion exchange water softener is a device that removes hardness causing minerals like calcium and magnesium from water through a chemical process called ion exchange. these systems utilize resin beads that are charged with sodium ions.

How Does A Water Softener Work Ion exchange water softeners operate on a fascinating principle of ionic swapping, effectively transforming your hard water into soft, gentle water. let's dive into the nitty gritty of this scientific process, demystifying its magic and unveiling how it tackles the troublesome minerals. What is an ion exchange water softener? an ion exchange water softener is a device that removes hardness causing minerals like calcium and magnesium from water through a chemical process called ion exchange. these systems utilize resin beads that are charged with sodium ions. How do ion exchange water treatment systems work? ion exchange systems specialized to operate as water softeners eliminate water hardness by simply substituting the hardness ions (magnesium and calcium) for soft ions ( sodium or potassium). In the ion exchange process, the smaller sodium ions are used to coat an exchange medium in the softener. the exchange medium can be natural “zeolites” or synthetic resin beads that resemble wet sand. (figure 1). The ion exchange in water softening, is a process that involves the exchange of the hardness minerals in water, chiefly calcium and magnesium, for sodium minerals. the exchange is possible because the minerals are ionic in nature, which means they have an electrical charge. An ion exchange water softener is one of the most common components of a water treatment. its function is to remove scale forming calcium and magnesium ions from hard water. in many cases soluble iron (ferrous) can also be removed with softeners.

How Does An Ion Exchange Water Softener Work Faq Taiyuan Lanlang How do ion exchange water treatment systems work? ion exchange systems specialized to operate as water softeners eliminate water hardness by simply substituting the hardness ions (magnesium and calcium) for soft ions ( sodium or potassium). In the ion exchange process, the smaller sodium ions are used to coat an exchange medium in the softener. the exchange medium can be natural “zeolites” or synthetic resin beads that resemble wet sand. (figure 1). The ion exchange in water softening, is a process that involves the exchange of the hardness minerals in water, chiefly calcium and magnesium, for sodium minerals. the exchange is possible because the minerals are ionic in nature, which means they have an electrical charge. An ion exchange water softener is one of the most common components of a water treatment. its function is to remove scale forming calcium and magnesium ions from hard water. in many cases soluble iron (ferrous) can also be removed with softeners.
