
How Does Nurse Burnout Affect Patients Zaggocare How does nurse burnout affect patients? burnout leads to staffing shortages. over the years, even before covid 19, the workload for hospital nurses increased due to a number of factors, including shorter hospital stays, patients requiring an increasing intensity of care, and a nurse shortage. In this systematic review and meta analysis, nurse burnout was found to be associated with lower health care quality and safety and lower patient satisfaction. this association was consistent across nurse and study characteristics.

How Does Lpns Nurse Burnout Influence Patient Care Even with the best nurse patient relationships, hospitals pose risks to patients. read these posts to learn how to reduce your risk of issues: how to choose a hospital. how does nurse burnout affect patients? germs in hospitals and doctor offices – watch out! the dangers of missed bedside alarms. the benefits of participating in hospital rounds. The study, led by researchers from stanford university, reveals a stark connection between nurse burnout and diminished healthcare quality, compromised patient safety, and reduced patient satisfaction. A review of 20 studies found that nurse burnout is associated with worsening safety and quality of patient care, decreased patient satisfaction, and nurses’ organizational commitment and productivity. Limited evidence exists about the direct impact of nurse burnout on patient outcomes. this study explores the relationship between nurse burnout and mortality, failure to rescue, and length of stay, while also considering the effect of a good work environment.

Healthcare Critical Analysis Of Nurse Burnout Issues A review of 20 studies found that nurse burnout is associated with worsening safety and quality of patient care, decreased patient satisfaction, and nurses’ organizational commitment and productivity. Limited evidence exists about the direct impact of nurse burnout on patient outcomes. this study explores the relationship between nurse burnout and mortality, failure to rescue, and length of stay, while also considering the effect of a good work environment. In this systematic review and meta analysis, nurse burnout was found to be associated with lower health care quality and safety and lower patient satisfaction. this association was consistent across nurse and study characteristics. Nurse burnout is an occupational hazard affecting nurses, patients, organizations, and society at large. nurse burnout is associated with worsening safety and quality of care, decreased patient satisfaction, and nurses' organizational commitment and productivity. The effects of nurse burnout extend beyond immediate patient care, potentially influencing long term health outcomes: 1. increased hospital readmission rates: patients cared for by burned out nurses may be more likely to experience complications or receive inadequate discharge instructions, leading to higher readmission rates. Researchers found that burnout is associated with increased rates of hospital acquired infections, patient falls, medication errors, adverse events, lower patient satisfaction, and reduced nurse assessed quality of care. these associations held steady across variations in nurse age, sex, work experience, and geographic location.
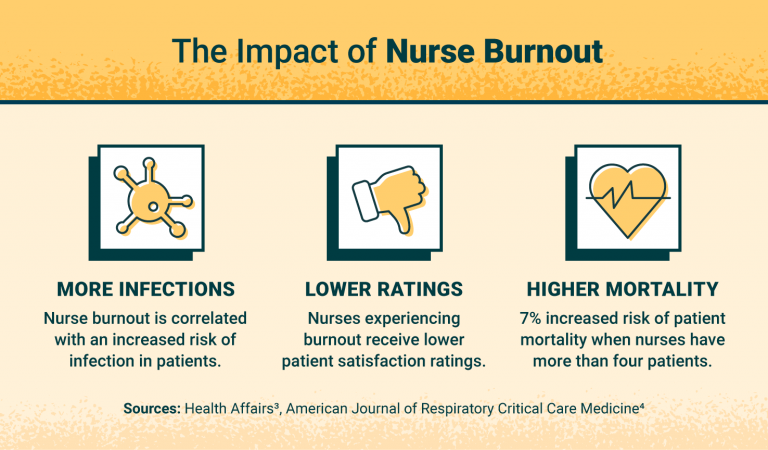
How To Prevent Nurse Burnout Risks Causes And Precautions In this systematic review and meta analysis, nurse burnout was found to be associated with lower health care quality and safety and lower patient satisfaction. this association was consistent across nurse and study characteristics. Nurse burnout is an occupational hazard affecting nurses, patients, organizations, and society at large. nurse burnout is associated with worsening safety and quality of care, decreased patient satisfaction, and nurses' organizational commitment and productivity. The effects of nurse burnout extend beyond immediate patient care, potentially influencing long term health outcomes: 1. increased hospital readmission rates: patients cared for by burned out nurses may be more likely to experience complications or receive inadequate discharge instructions, leading to higher readmission rates. Researchers found that burnout is associated with increased rates of hospital acquired infections, patient falls, medication errors, adverse events, lower patient satisfaction, and reduced nurse assessed quality of care. these associations held steady across variations in nurse age, sex, work experience, and geographic location.
