How Neurons Communicate
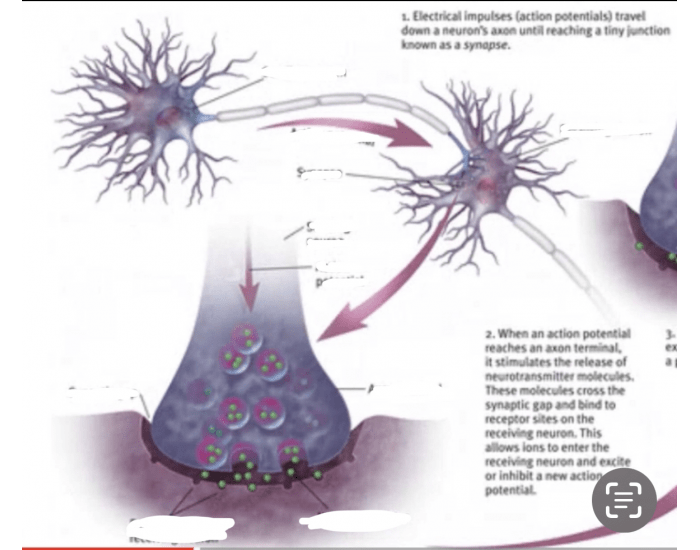
How Neurons Communicate Quiz Khan academy khan academy. Myelin sheaths, nodes of ranvier, and saltatory conduction in neurons. created by sal khan.

Neurons And How They Communicate Neurons And How They Vrogue Co The organization of upper motor neurons (umns), lower motor neurons (lmns), and sensory neurons creates a feedback system that modulates the strength of muscle contraction, maintains passive muscle tone, and mitigates stretch and spinal reflexes. And all of these numbers may vary between different types of neurons, but these would be fairly common values. so many neurons would have a resting membrane potential of around negative 60 millivolts and a threshold potential of around negative 50 millivolts or so that i've drawn with a dashed line. Explore the neuron resting membrane potential, a stable charge separation across the cell membrane. discover the roles of anions and cations, and how their concentration differences create this potential. uncover how neurons use these electrochemical driving forces to perform their functions. Information travels in two directions: from the periphery to the central nervous system via afferent neurons, and from the central nervous system to the periphery via efferent neurons.
How Do Neurons Communicate Tech Faq Explore the neuron resting membrane potential, a stable charge separation across the cell membrane. discover the roles of anions and cations, and how their concentration differences create this potential. uncover how neurons use these electrochemical driving forces to perform their functions. Information travels in two directions: from the periphery to the central nervous system via afferent neurons, and from the central nervous system to the periphery via efferent neurons. In neurons, the cell enters a state of hyperpolarization immediately following the generation of an action potential. while hyperpolarized, the neuron is in a refractory period that lasts roughly 2 milliseconds, during which the neuron is unable to generate subsequent action potentials. This video discusses synapses, where neurons communicate with target cells. it differentiates between two types of synapses: chemical and electrical. it also explains the role of the synaptic cleft, presynaptic and postsynaptic membranes, and neurotransmitters in this process. Explora la estructura y función de las neuronas en el sistema nervioso humano con khan academy. But most of its membrane is actually wrapped around the axon as the myelin sheath. in addition to these functions, schwann cells also appear to influence neurons, and vice versa, through exchange of a variety of substances.
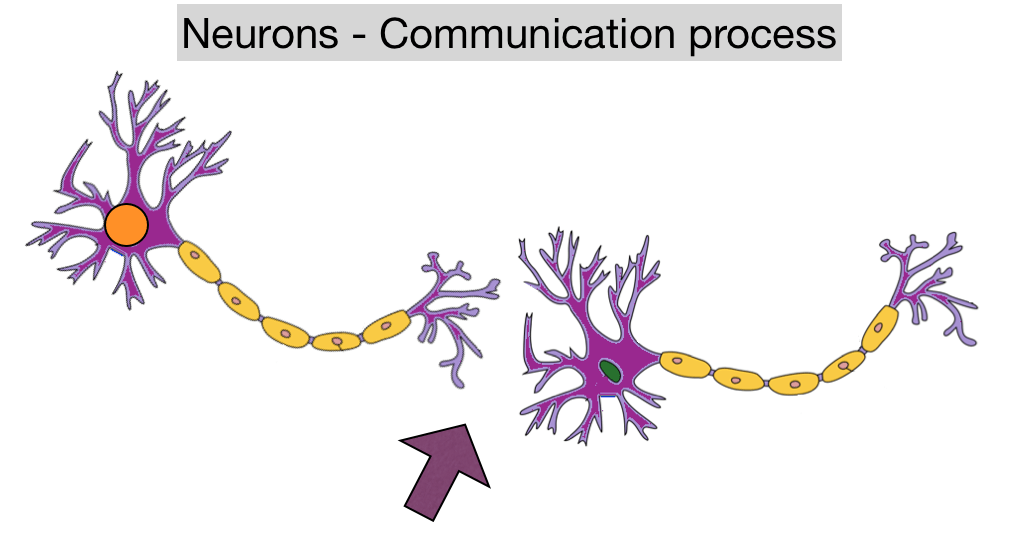
Neurons And How They Communicate Vrogue Co In neurons, the cell enters a state of hyperpolarization immediately following the generation of an action potential. while hyperpolarized, the neuron is in a refractory period that lasts roughly 2 milliseconds, during which the neuron is unable to generate subsequent action potentials. This video discusses synapses, where neurons communicate with target cells. it differentiates between two types of synapses: chemical and electrical. it also explains the role of the synaptic cleft, presynaptic and postsynaptic membranes, and neurotransmitters in this process. Explora la estructura y función de las neuronas en el sistema nervioso humano con khan academy. But most of its membrane is actually wrapped around the axon as the myelin sheath. in addition to these functions, schwann cells also appear to influence neurons, and vice versa, through exchange of a variety of substances.
Comments are closed.