Hyperbolic Discounting What Makes Something A Priority

Hyperbolic Discounting Egonomics Lab Something becomes a priority when we feel (not just think) that it’s more important than other things. now, here’s where things go wrong. what “feels” important to us (salience) is influenced by an adaptive mechanism called hyperbolic discounting. Individuals with such preferences are described as "present biased". the most important consequence of hyperbolic discounting is that it creates temporary preferences for small rewards that occur sooner over larger, later ones.
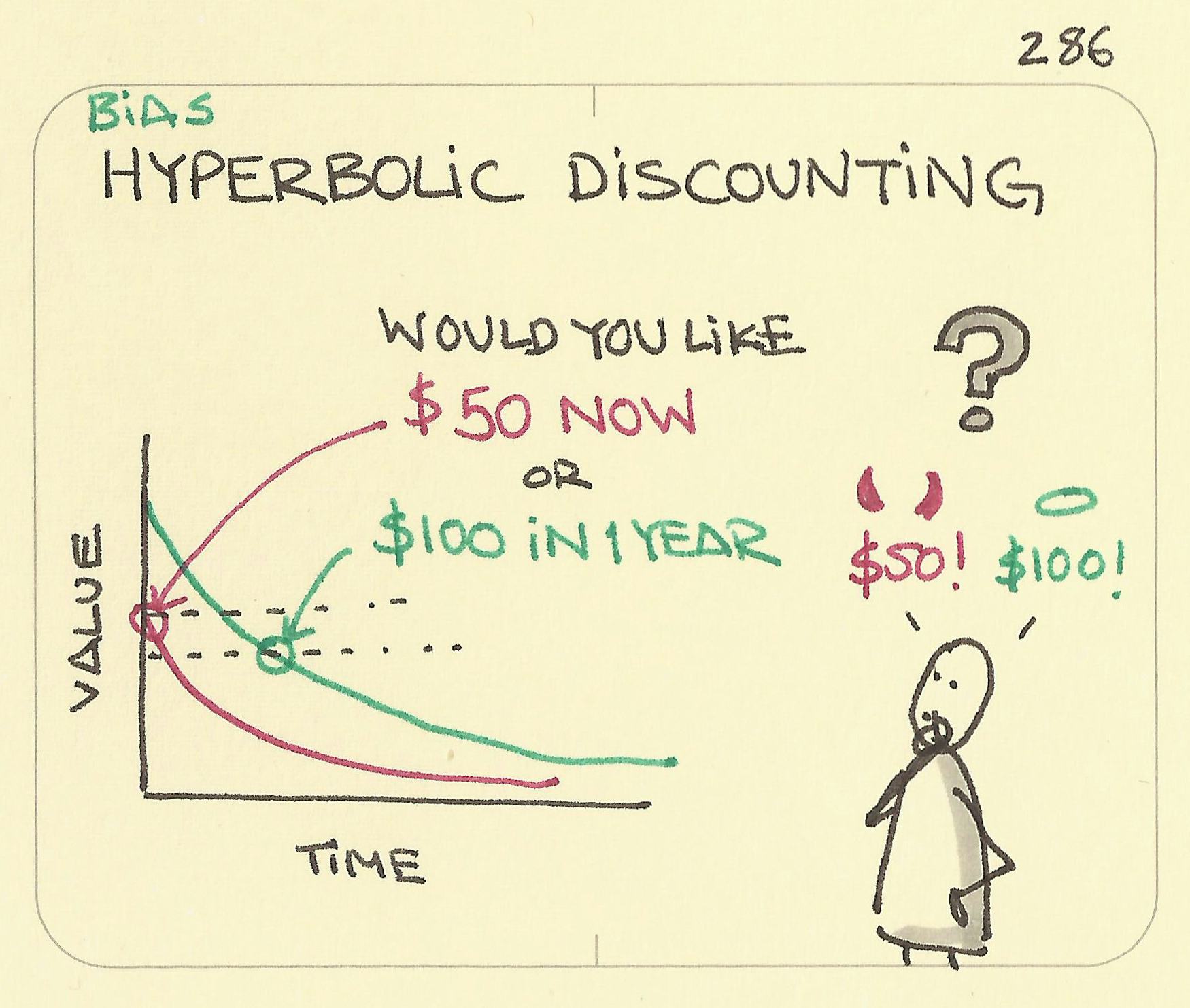
Hyperbolic Discounting Sketchplanations Hyperbolic discounting is our tendency to prioritize immediate rewards over long term benefits, even if the immediate reward is objectively less valuable. it’s a type of cognitive shortcut, a so called heuristic, that evolved through time and was supposed to simplify our decision making. Hyperbolic discounting is something that we encounter every single day, but that doesn’t mean it’s always right. sometimes it does make sense to choose the immediate rewards, especially when it comes to money. in theory, if we are offered $50 today versus $100 in 6 months, we should choose the $100. What is hyperbolic discounting? hyperbolic discounting is the mental inclination to prefer rewards in the short term as opposed to rewards in the long term, even when waiting will result in greater rewards overall. Hyperbolic discounting suggests that the value of future rewards decreases more rapidly as the delay to their receipt increases, leading individuals to show a preference for short term gratification even when waiting would result in a better outcome.
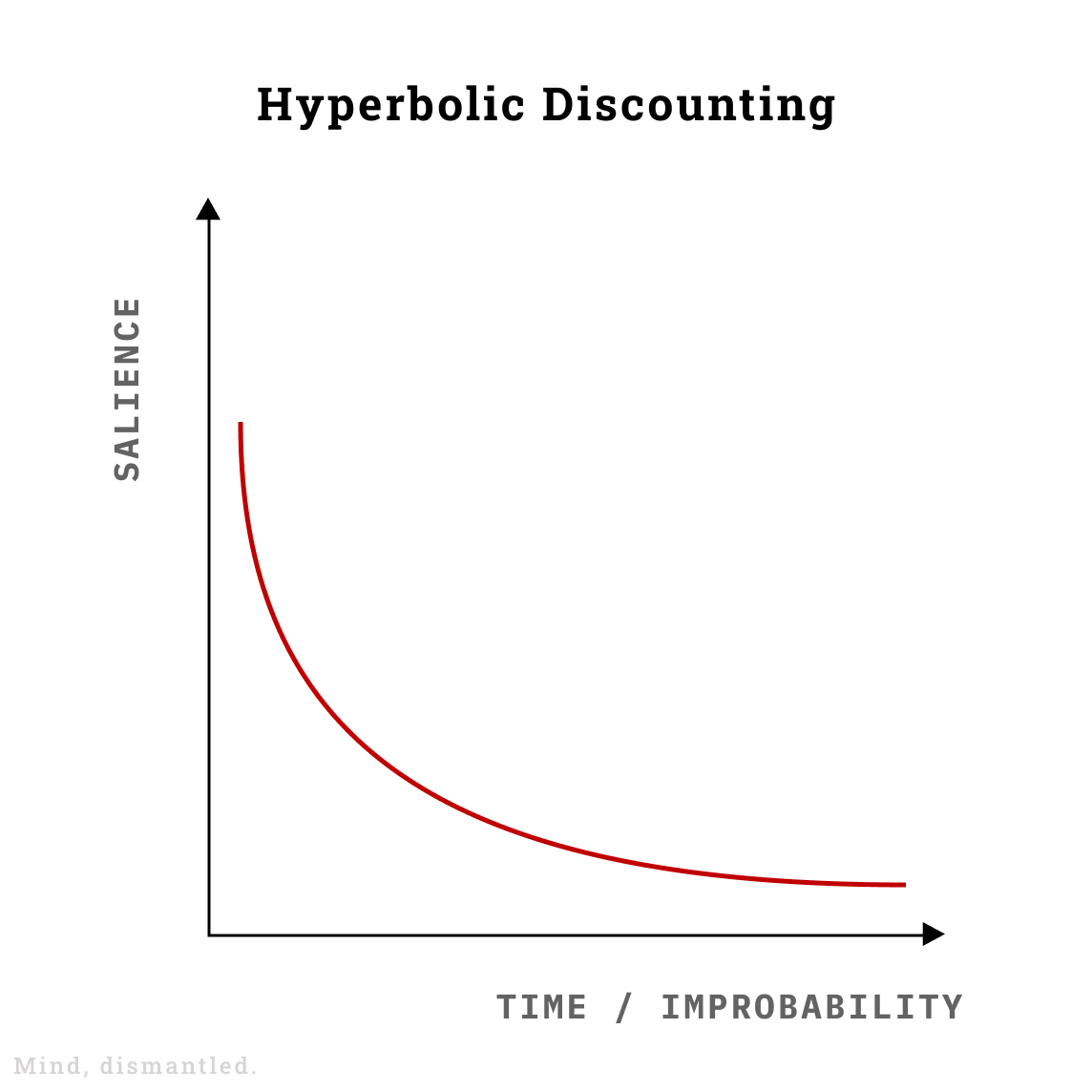
Hyperbolic Discounting What Makes Something A Priority What is hyperbolic discounting? hyperbolic discounting is the mental inclination to prefer rewards in the short term as opposed to rewards in the long term, even when waiting will result in greater rewards overall. Hyperbolic discounting suggests that the value of future rewards decreases more rapidly as the delay to their receipt increases, leading individuals to show a preference for short term gratification even when waiting would result in a better outcome. Hyperbolic discounting is a behavioral economic theory that explains why individuals tend to prefer smaller rewards sooner rather than larger rewards later. this phenomenon influences financial decisions, investment behavior, and everyday choices. In general, hyperbolic discounting makes us choose immediate rewards without thinking about future effects. how to overcome hyperbolic discounting? to counteract this bias, experts suggest several strategies: automatic commitments: establishing automatic saving habits or recurring payments can help avoid impulsive decisions. Key takeaways: hyperbolic discounting explains why we tend to prefer immediate rewards over delayed ones, even if the delayed rewards are greater. this tendency affects everything from spending and saving money to health and fitness decisions. The relevance of the money based discounting paradigm and the robustness of the hyperbolic pattern raise the question of what it is that intertemporal choice over monetary payments actually measures, and how hyperbolicity should be interpreted.

Hyperbolic Discounting What Makes Something A Priority Hyperbolic discounting is a behavioral economic theory that explains why individuals tend to prefer smaller rewards sooner rather than larger rewards later. this phenomenon influences financial decisions, investment behavior, and everyday choices. In general, hyperbolic discounting makes us choose immediate rewards without thinking about future effects. how to overcome hyperbolic discounting? to counteract this bias, experts suggest several strategies: automatic commitments: establishing automatic saving habits or recurring payments can help avoid impulsive decisions. Key takeaways: hyperbolic discounting explains why we tend to prefer immediate rewards over delayed ones, even if the delayed rewards are greater. this tendency affects everything from spending and saving money to health and fitness decisions. The relevance of the money based discounting paradigm and the robustness of the hyperbolic pattern raise the question of what it is that intertemporal choice over monetary payments actually measures, and how hyperbolicity should be interpreted.

Hyperbolic Discounting Fourweekmba Key takeaways: hyperbolic discounting explains why we tend to prefer immediate rewards over delayed ones, even if the delayed rewards are greater. this tendency affects everything from spending and saving money to health and fitness decisions. The relevance of the money based discounting paradigm and the robustness of the hyperbolic pattern raise the question of what it is that intertemporal choice over monetary payments actually measures, and how hyperbolicity should be interpreted.
Comments are closed.