
An Analysis Of Key Bipolar Junction Transistor Concepts Through A It is a semiconductor device and it comes in two general types: the bipolar junction transistor (bjt) and the field effect transistor (fet). here we will describe the system characteristics of the bjt configuration and explore its use in fundamental signal shaping and amplifier circuits. What is bipolar junction transistor? the concept of bjt refers to a three terminal semiconductor device consisting of two p n junctions that are formed by sandwiching either p type or n type semiconductors between two p type semiconductors. transistors can be used to transfer input signals through the circuits having lower to higher resistance.

Bipolar Transistor Tutorial The Bjt Transistor Pdf Bipolar Introduction to bipolar junction transistors. a bipolar junction transistor is formed by joining three sections of semiconductors with alternative different dopings. the middle section (base) is narrow and one of the other two regions (emitter) is heavily doped. the other region is called the collector. Learn about bipolar junction transistors (bjt) fundamentals: structure, doping, biasing, current gains, and more in electronics. In pnp transistor, its emitter – base junction is forward biased and collector base junction is reverse biased. the forward bias on the emitter – base junction causes the holes in the. The document provides an introduction to bipolar junction transistors (bjts). it describes how bjts are constructed with three doped semiconductor regions (emitter, base, and collector) separated by two pn junctions.

Chapter 3 Bjt Pdf Bipolar Junction Transistor Semiconductor Devices In pnp transistor, its emitter – base junction is forward biased and collector base junction is reverse biased. the forward bias on the emitter – base junction causes the holes in the. The document provides an introduction to bipolar junction transistors (bjts). it describes how bjts are constructed with three doped semiconductor regions (emitter, base, and collector) separated by two pn junctions. Analog electronics: introduction to bipolar junction transistors (bjt)topics covered: 1. invention of transistor.2. use of bjt.3. types of bjt (npn and pnp t. Introduction to bjt (bipolar junction transistor) the bjt stands for bipolar junction transistor is an electronic device that has 3 terminals and used in different amplification circuits. it is also known as a current controlling instrument. 1. bjt: structure and basic operation bipolar junction transistor: excellent for analog and front end communications applications. n n n n n polysilicon contact metal contact to base to emitter region p p n p type base n buried layer p type substrate metal contact to collector field oxide n buried layer p n sandwich p edge of n.

Bipolar Junction Transistor Explained Topics It Works Basic Analog electronics: introduction to bipolar junction transistors (bjt)topics covered: 1. invention of transistor.2. use of bjt.3. types of bjt (npn and pnp t. Introduction to bjt (bipolar junction transistor) the bjt stands for bipolar junction transistor is an electronic device that has 3 terminals and used in different amplification circuits. it is also known as a current controlling instrument. 1. bjt: structure and basic operation bipolar junction transistor: excellent for analog and front end communications applications. n n n n n polysilicon contact metal contact to base to emitter region p p n p type base n buried layer p type substrate metal contact to collector field oxide n buried layer p n sandwich p edge of n.
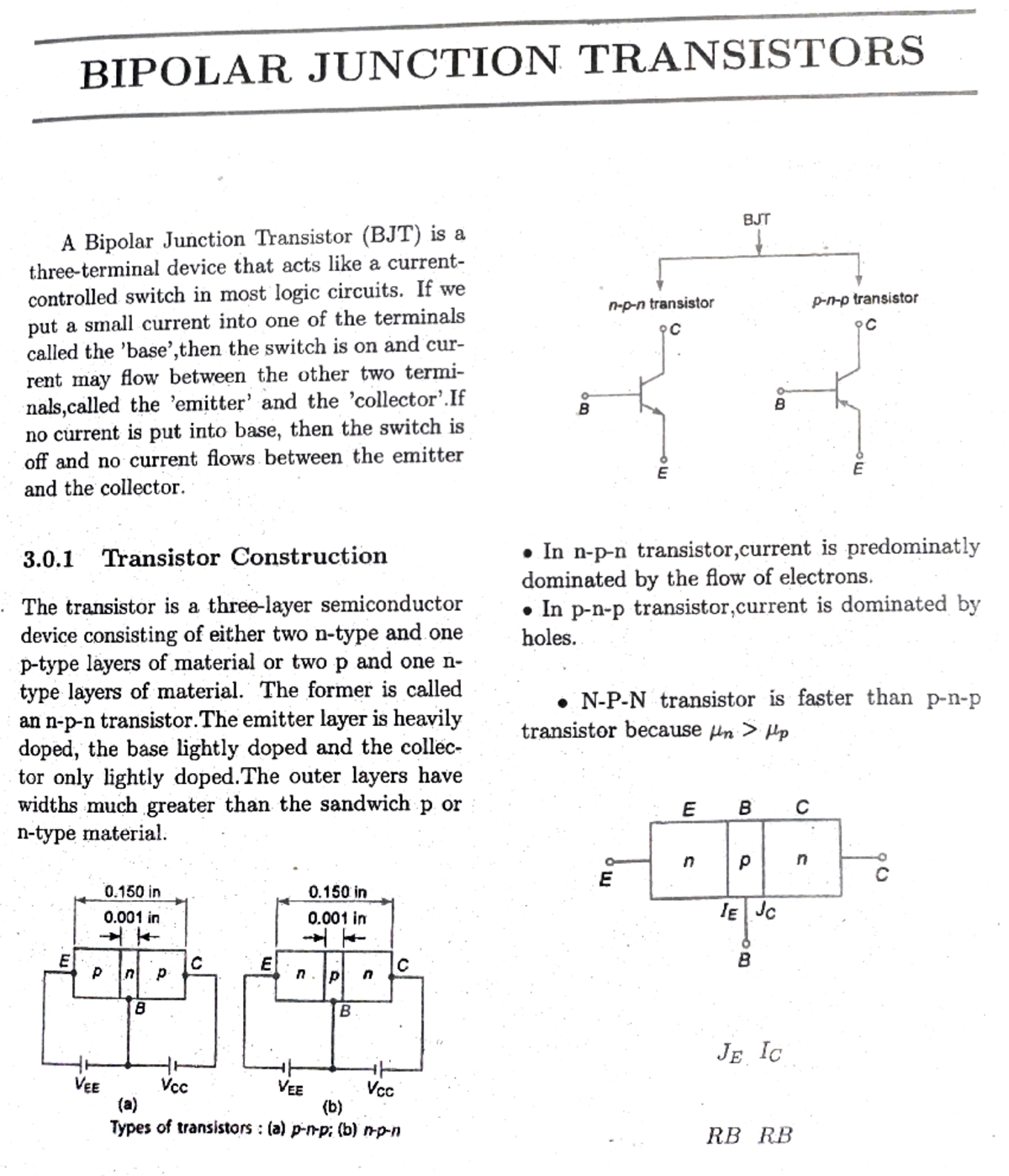
Bjt Bipolar Junction Transistors Bipolar Junction Transistors Bjt A 1. bjt: structure and basic operation bipolar junction transistor: excellent for analog and front end communications applications. n n n n n polysilicon contact metal contact to base to emitter region p p n p type base n buried layer p type substrate metal contact to collector field oxide n buried layer p n sandwich p edge of n.
