
Law 241 Lecture Notes On R V Oakes Case R V Oakes 1986 24 C C C Consider the court cases decisions r v. oakes and r v. keegstra and answer the questions below: 1) the right(s) at issue (0.5 marks awarded for each case); 2) the section(s) of the charter. Law 241 lecture notes on r. v. oakes case. r. v. oakes (1986), 24 c.c.c. (3d) 321 (s.c.c.) dickson c.j.c. (chouinard, lamer, wilson and le dain jj. concurring) this appeal concerns the constitutionality of s. 8 of the narcotic control act, r.s.c. 1970, c.n 1. the section provides, in brief, that i.

R V Oakes Case Summary Case Summary R V Oakes R V Oakes 1986 1 S Access all information related to judgment r. v. oakes, 1986 canlii 46 (scc), [1986] 1 scr 103 on canlii. Case – r v oakes. importance of this case: ·sc’s first comprehensive treatment of meaning of s. 1. ·primary referent for 2 nd stage of charter adjudication. facts: narcotic control act created presumption that possession of a narcotic created presumption that the intent was to traffic (unless the accused established the absence of such an. R v. oakes facts david oakes was caught with 8 grams of hash oil and a large sum of cash (619) oakes said the cash was from workers compensation and the oil was for his personal use it was suspected of drug trafficking he was charged with unlawful possession of a narcotic for the purpose of trafficking contrary to s. 8 of the narcotic. The case provided a structured test—commonly known as the oakes test —to assess whether a law that infringes on a charter right is reasonable and demonstrably justified in a free and democratic society.

R V Oakes Wikiwand R v. oakes facts david oakes was caught with 8 grams of hash oil and a large sum of cash (619) oakes said the cash was from workers compensation and the oil was for his personal use it was suspected of drug trafficking he was charged with unlawful possession of a narcotic for the purpose of trafficking contrary to s. 8 of the narcotic. The case provided a structured test—commonly known as the oakes test —to assess whether a law that infringes on a charter right is reasonable and demonstrably justified in a free and democratic society. Ater reviewing r. v. oakes, supra, and r. v. carroll, supra, hart j. concluded at pp. 435 36: secion 8 of the narcoic control act is a piece of legislaion that atempts to relieve the crown of its normal burden of proof by use of what is known as a reverse onus. Oakes was charged with unlawful possession of a narcotic for the purpose of trafficking. when the judge found him guilty of possession of hashish oil, oakes brought a motion challenging the constitutional validity of s. 8 of the narcotic control act, r.s.c., 1970 which stated:. Case brief: r v oakes. citation r. v. oakes, [1986] 1 s.c. 103 facts oakes was charged with possession of narcotics for the purposes of trafficking but was only convicted for possession of a narcotic. In r v oakes (1986), the supreme court of canada ruled that a law requiring the accused to disprove possession for trafficking violated the presumption of innocence under the charter. this decision established the "oakes test", setting criteria for limiting rights under section 1 of the charter.
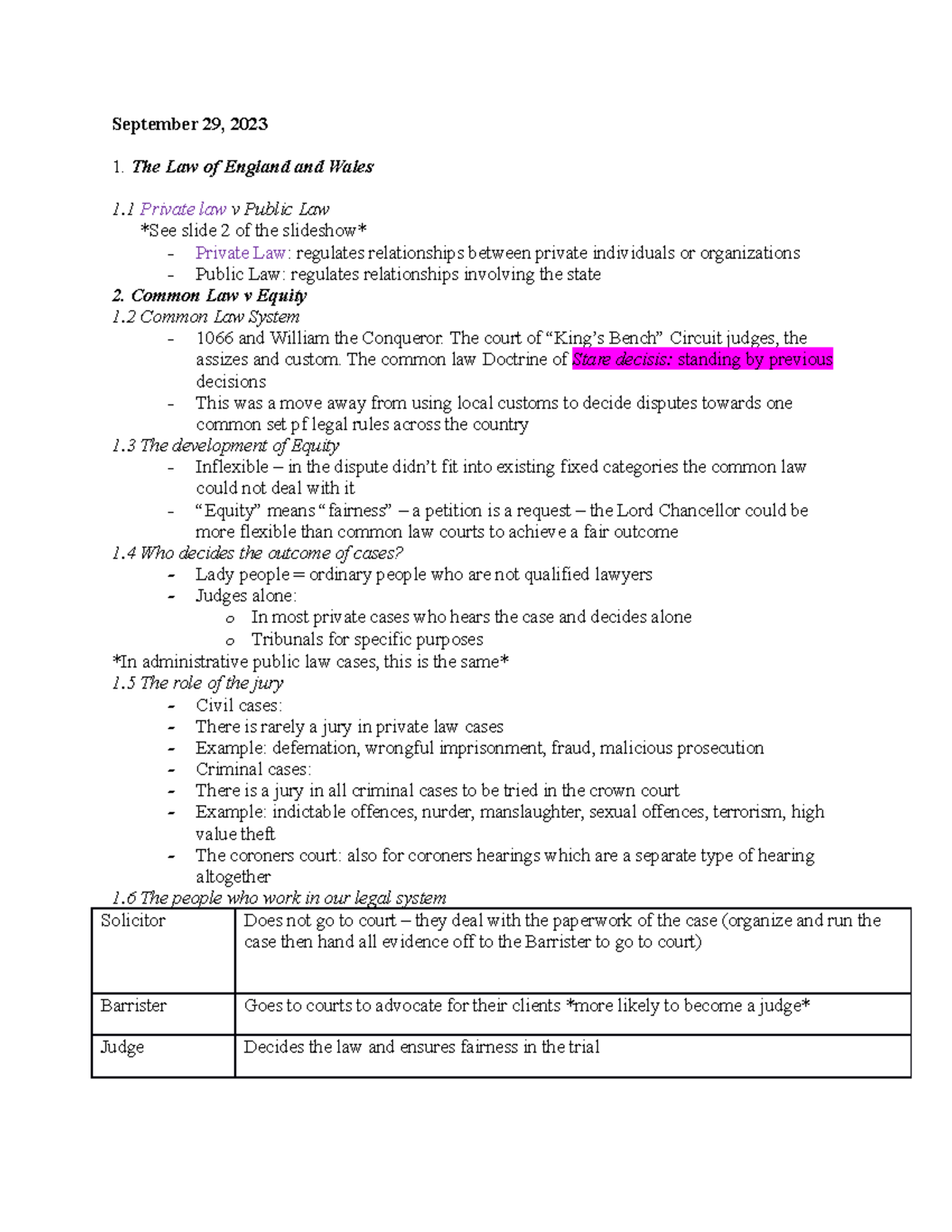
Common Law Lecture Notes September 29 2023 1 The Law Of England And Ater reviewing r. v. oakes, supra, and r. v. carroll, supra, hart j. concluded at pp. 435 36: secion 8 of the narcoic control act is a piece of legislaion that atempts to relieve the crown of its normal burden of proof by use of what is known as a reverse onus. Oakes was charged with unlawful possession of a narcotic for the purpose of trafficking. when the judge found him guilty of possession of hashish oil, oakes brought a motion challenging the constitutional validity of s. 8 of the narcotic control act, r.s.c., 1970 which stated:. Case brief: r v oakes. citation r. v. oakes, [1986] 1 s.c. 103 facts oakes was charged with possession of narcotics for the purposes of trafficking but was only convicted for possession of a narcotic. In r v oakes (1986), the supreme court of canada ruled that a law requiring the accused to disprove possession for trafficking violated the presumption of innocence under the charter. this decision established the "oakes test", setting criteria for limiting rights under section 1 of the charter.

Criminal Law Case Laws Notes Criminal Law Case Laws Week 1 Case Case brief: r v oakes. citation r. v. oakes, [1986] 1 s.c. 103 facts oakes was charged with possession of narcotics for the purposes of trafficking but was only convicted for possession of a narcotic. In r v oakes (1986), the supreme court of canada ruled that a law requiring the accused to disprove possession for trafficking violated the presumption of innocence under the charter. this decision established the "oakes test", setting criteria for limiting rights under section 1 of the charter.
