Lesson 2 A Catalog Of Essential Functions Ppt

Module 2 Ppt 1 Pdf Lesson 2: a catalog of essential functions download as a pdf or view online for free. The document provides an overview of mathematical models and functions. it defines a mathematical model as a mathematical description of a real world phenomenon using equations or functions.
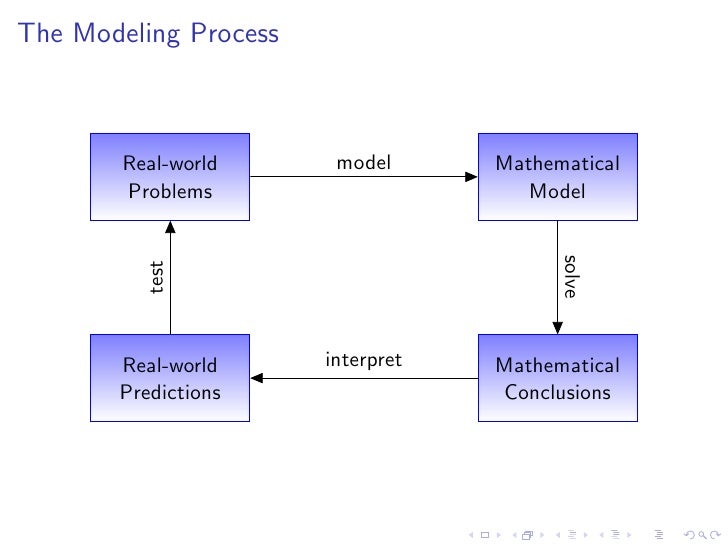
Lesson 2 A Catalog Of Essential Functions There are many different types of functions that can be used to model relationships observed in the real world. in what follows, we discuss the behavior and graphs of some of these functions and give examples of situations appropriately modeled by such functions. The numbers an, an−1, , a1, a0 are called coefficients. an is called the leading coefficient. the domain of f(x) is r if n = 0, f(x) = a0 is a constant function. if n = 1, f(x) = a1x a0 is a linear function. if n = 2, f(x) = a2x2 a1x a0 is a quadratic function. if n = 3, f(x) = a3x3 a2x2 a1x a0 is a cubic function. 1.2 mathematical models: a catalogue of essential functions should be familiar with the following types of functions. Just knowing these basic shapes, domains, and ranges, we can build many, many more functions and know what they look like as well all without a calculator. the beauty of this technique is that it works for any function. ex f(x) = ? f(x 1) = ? 2f(x) = ? f( x) = ?.
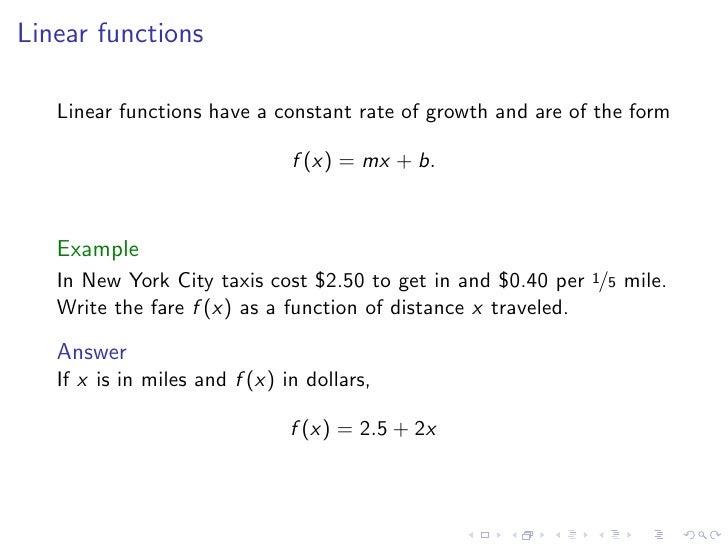
Lesson 2 A Catalog Of Essential Functions 1.2 mathematical models: a catalogue of essential functions should be familiar with the following types of functions. Just knowing these basic shapes, domains, and ranges, we can build many, many more functions and know what they look like as well all without a calculator. the beauty of this technique is that it works for any function. ex f(x) = ? f(x 1) = ? 2f(x) = ? f( x) = ?. Graph each function, not by plotting points, but by starting with the graph of one of the standard functions given in section 1.2, and then applying the appropriate transformations. Ch 1: functions as models 1.2 mathematical models: a catalog of essential functions this section studies the common function we will use in this class. 1. linear function: f (x) = ax b is a function whose graph is a straight line. The document uses examples to illustrate concepts like linear functions, other polynomial functions, and trigonometric functions. it also explains how vertical and horizontal shifts can transform the graph of a function. download as a pdf or view online for free. Graphs of quadratic functions are parabolas, and their behaviour is con trolled by the value of the constant coe⁚ⴁcient in front of the quadratic factor (ie. the number in front of the x2).

Lesson 2 A Catalog Of Essential Functions Graph each function, not by plotting points, but by starting with the graph of one of the standard functions given in section 1.2, and then applying the appropriate transformations. Ch 1: functions as models 1.2 mathematical models: a catalog of essential functions this section studies the common function we will use in this class. 1. linear function: f (x) = ax b is a function whose graph is a straight line. The document uses examples to illustrate concepts like linear functions, other polynomial functions, and trigonometric functions. it also explains how vertical and horizontal shifts can transform the graph of a function. download as a pdf or view online for free. Graphs of quadratic functions are parabolas, and their behaviour is con trolled by the value of the constant coe⁚ⴁcient in front of the quadratic factor (ie. the number in front of the x2).
Comments are closed.