Solved Only A Portion Of The Graph Of F X Is Shown Below But You Question: only a portion of the graph of f (x) is shown below, but you can assume that fx) is a continuous function with domain of all real numbers. give exact answers. f (x) area 13 area 10 1 2 3 4 5 area 5 find the value of each: (a) sax ax = 5 (o> " ccx) 6) dx 16 (c) if f (x) is an even function, find lrx ax | (d) find the average. Give exact answers for f (x) area = 13 area = 10 12345 79 area = 5 find the value of each: a) f #x27; #x27; (x) b) f (x 6)dx c) if f (x) is an even fun more.
Two Graphs Are Shown Below The F X Graph Is The Original Graph [solved] . only a portion of the graph of f (x) is shown below, but you can | course hero [solved] . only a portion of the graph of f (x) is shown below, but you can | course hero . only a portion of the graph of f (x) is shown below, but you can answered step by step solved by verified expert university of notre dame • calculus • calculus 120 . only a portion of the graph of f. Solution for only a portion of the graph of f (x) is shown below, but you can assume that f (x) is a continuous function with domain of all real numbers. give…. Only a portion of the graph of f (x) is shown below, but you can assume that (x) is a continuous function with domain of all real numbers. give exact answers f (x) area 13 area = 10 area = 5 find the value of each: (2) 6 ( (x ) dx 10 ) 60 (r (x ) show more show more. Question: only a portion of the graph of f (x) is shown below, but you can assume that (x) is a continuous function with domain of all real numbers. give exact answers.

Solved The Graph Of F X Is Shown Below Choose Solutioninn Only a portion of the graph of f (x) is shown below, but you can assume that (x) is a continuous function with domain of all real numbers. give exact answers f (x) area 13 area = 10 area = 5 find the value of each: (2) 6 ( (x ) dx 10 ) 60 (r (x ) show more show more. Question: only a portion of the graph of f (x) is shown below, but you can assume that (x) is a continuous function with domain of all real numbers. give exact answers. There are 2 steps to solve this one. given the value of integration. only a portion of the graph of f (x) is shown below, but you can assume that f (x) is a continuous function with domain of all real numbers. A portion of the graph of y = f (x) is shown in red below, where f (x) is a quadratic function. the distance between grid lines is 1 unit. what is the sum of all distinct numbers x such that f (f (f (x)))= 3 ?. A function f is continuous when, for every value c in its domain: f (c) is defined, and lim x→c f (x) = f (c) "the limit of f (x) as x approaches c equals f (c) ". A portion of the graph of f (x) is shown below: use the graph to answer the questions below. when necessary, assume that the trends established in the graph continue outside of the viewing window. (a) for which values of a in the domain of f (x) does lim x > a f (x) ≠ f (a) ? explain your reasoning. (b) evaluate each of the following.
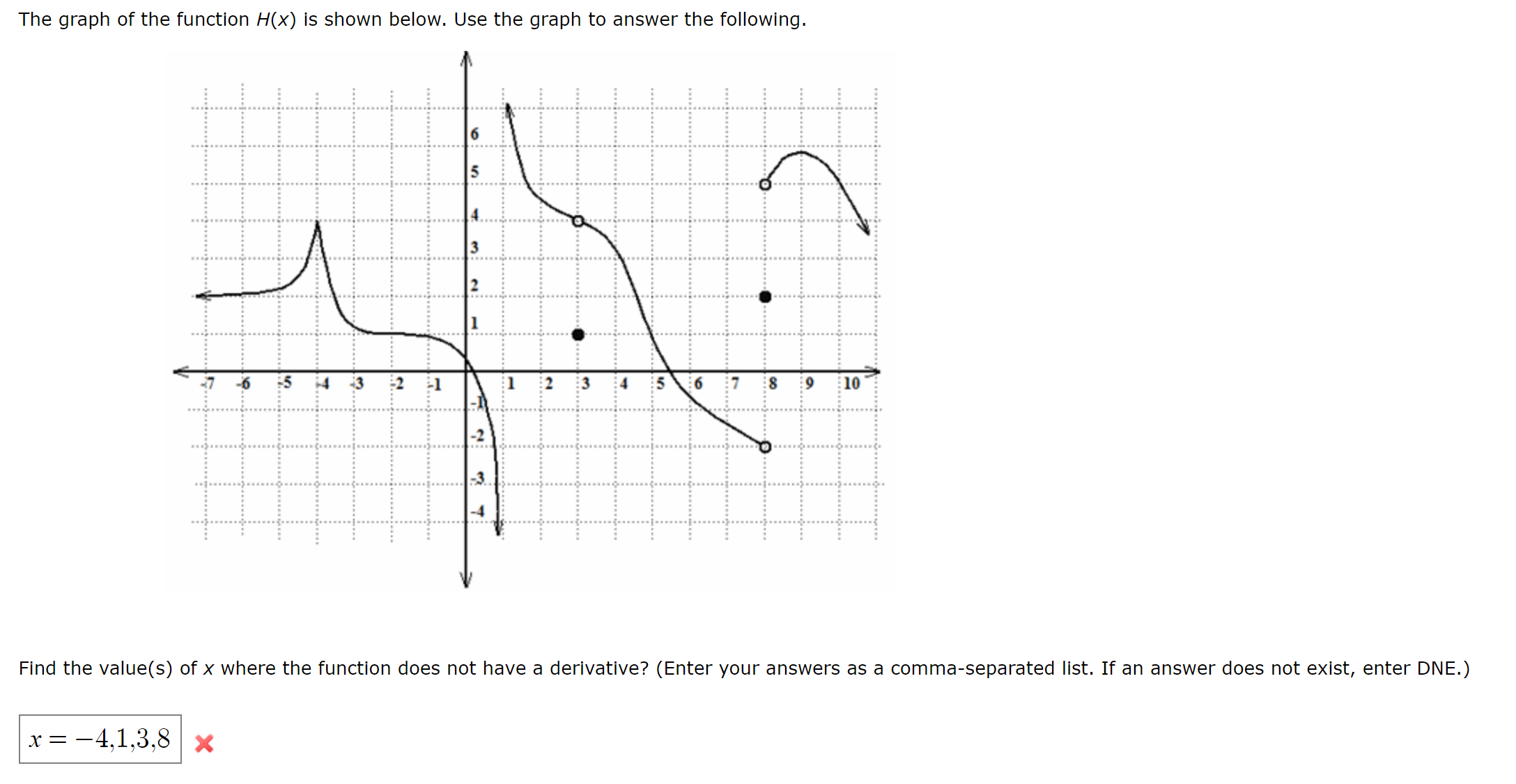
Solved The Graph Of The Function Fx Is Shown Below Use The Chegg There are 2 steps to solve this one. given the value of integration. only a portion of the graph of f (x) is shown below, but you can assume that f (x) is a continuous function with domain of all real numbers. A portion of the graph of y = f (x) is shown in red below, where f (x) is a quadratic function. the distance between grid lines is 1 unit. what is the sum of all distinct numbers x such that f (f (f (x)))= 3 ?. A function f is continuous when, for every value c in its domain: f (c) is defined, and lim x→c f (x) = f (c) "the limit of f (x) as x approaches c equals f (c) ". A portion of the graph of f (x) is shown below: use the graph to answer the questions below. when necessary, assume that the trends established in the graph continue outside of the viewing window. (a) for which values of a in the domain of f (x) does lim x > a f (x) ≠ f (a) ? explain your reasoning. (b) evaluate each of the following.
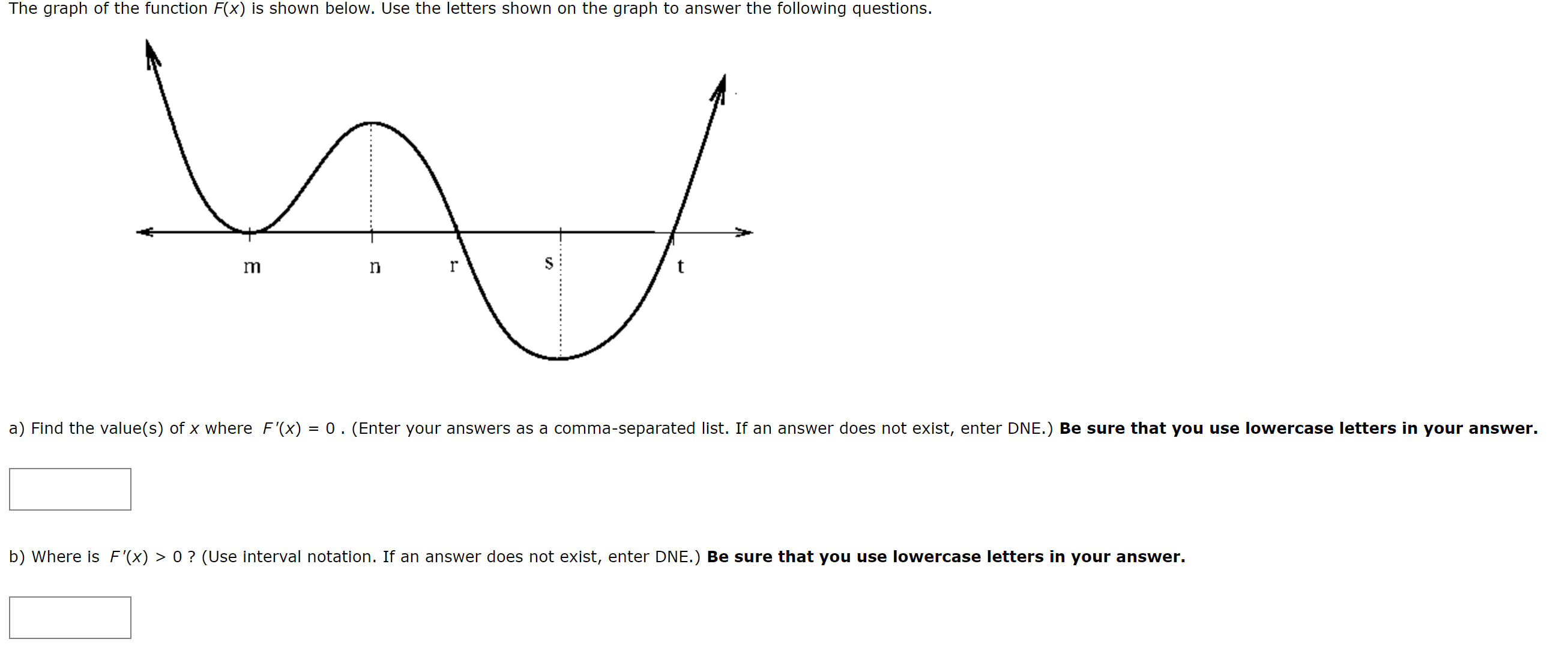
Solved The Graph Of The Function Fx Is Shown Below Use The Chegg A function f is continuous when, for every value c in its domain: f (c) is defined, and lim x→c f (x) = f (c) "the limit of f (x) as x approaches c equals f (c) ". A portion of the graph of f (x) is shown below: use the graph to answer the questions below. when necessary, assume that the trends established in the graph continue outside of the viewing window. (a) for which values of a in the domain of f (x) does lim x > a f (x) ≠ f (a) ? explain your reasoning. (b) evaluate each of the following.
Solved The Graph Of Fx Shown Below Resembles The Graph O Algebra
