Ossification Bone Formation Histogenesis Of Bone Bone Histology Embryology Of The Skeleton

Ossification Bone Formation Histogenesis Of Bone Chords Ossification (also called osteogenesis or bone mineralization) in bone remodeling is the process of laying down new bone material by cells named osteoblasts. it is synonymous with bone tissue formation. [1]. Ossification, also known as osteogenesis or bone formation, is the process by which bone tissue is created. it begins during embryonic development and continues until early adulthood, with slight individual variations. there are two types of ossification: intramembranous and endochondral.
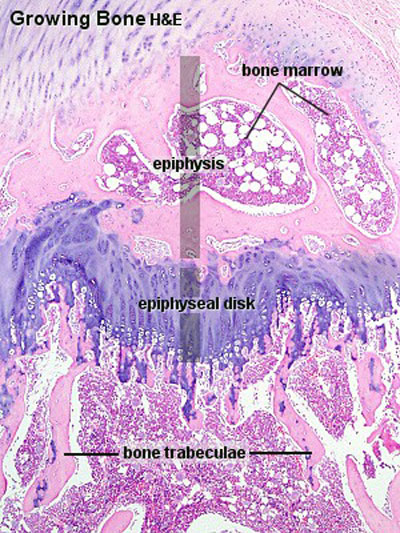
Bone Histology Embryology Bone ossification is the formation of new bone, which can occur in two ways: intramembranous ossification and endochondral ossification. this article will discuss both forms as well as clinically relevant examples. In the early stages of embryonic development, the embryo’s skeleton consists of fibrous membranes and hyaline cartilage. by the sixth or seventh week of embryonic life, the actual process of bone development, ossification (osteogenesis), begins. Bone formation in a developing embryo begins in mesenchyme and occurs through one of two processes: either endochondral or intramembranous osteogenesis (ossification). Ossification, also known as osteogenesis, is the process by which new bone is formed. it is a complex biological process that occurs in two primary forms: intramembranous ossification and endochondral ossification.
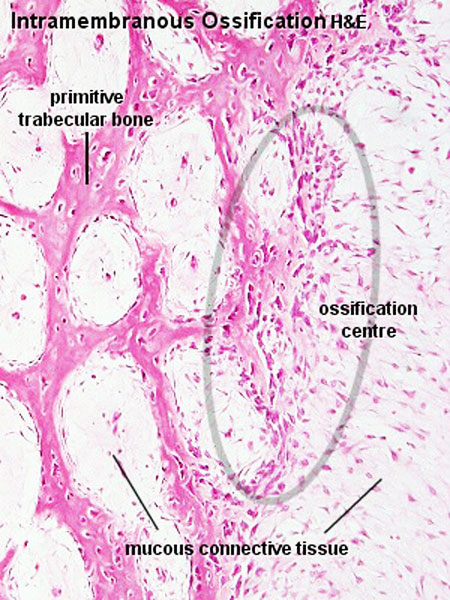
Bone Histology Embryology Bone formation in a developing embryo begins in mesenchyme and occurs through one of two processes: either endochondral or intramembranous osteogenesis (ossification). Ossification, also known as osteogenesis, is the process by which new bone is formed. it is a complex biological process that occurs in two primary forms: intramembranous ossification and endochondral ossification. Ossification or osteogenesis (osteo = bone, genesis = creation) is the process that transforms the embryonic skeleton into bone. ossification is a feature of normal growth and development and proceeds at different rates in different bones. Bone formation, process by which new bone is produced. ossification begins about the third month of fetal life in humans and is completed by late adolescence. Ossification is the biological process by which bone tissue is formed. it plays a critical role in skeletal development, growth, and fracture repair. there are two primary types of ossification endochondral and intramembranous. each differs in its mechanism and anatomical roles. Ossification the process of conversion of other tissues into bone. most bone forms from cartilage but some is laid down by other connective tissue (membranous bone). ossification may also occur in tissues that have been the site of disease such as long term inflammation. collins dictionary of medicine © robert m. youngson 2004, 2005.
Comments are closed.