Paramecium Classification Structure Function Locomotion Nutrition And Reproductiveparamecium

Paramecium Classification Structure Function And Characteristics My Paramecium is a genus of single celled, microscopic organisms belonging to the group of protists called ciliates. these organisms are characterized by their cilia, which are hair like structures that cover their outer surface and are used for locomotion and feeding. A paramecium is a free living, motile, single cell (unicellular) organism belonging to the kingdom protista that are naturally found in aquatic habitats. they have a lifespan of a hundred, a thousand or even a million years.

Pdf Lesson 11 Paramecium Structure Function Dokumen Tips Discover the classification, structure, and functions of paramecium, a unicellular eukaryote, and its ecological role in freshwater habitats. A comprehensive guide on paramecium, covering its classification, features, locomotion, nutrition, and reproduction. understand the life cycle and key characteristics of this unicellular ciliated protozoa. Algae are present as an endosymbiont and provide food to paramecium by photosynthesis, in turn, the algae get a safe and protective habitat. paramecium may have intracellular bacteria known as kappa particles. paramecium with kappa particles has the ability to kill other strains of paramecium. This overview provides insight into the anatomy, behavior, and classification of paramecium, making it a helpful resource for those interested in learning more about this fascinating microorganism.
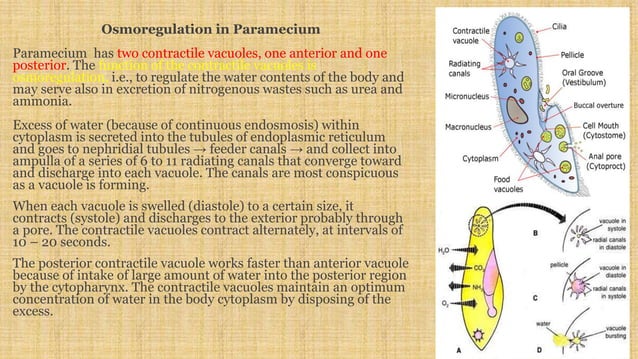
Paramecium Locomotion Ppt Algae are present as an endosymbiont and provide food to paramecium by photosynthesis, in turn, the algae get a safe and protective habitat. paramecium may have intracellular bacteria known as kappa particles. paramecium with kappa particles has the ability to kill other strains of paramecium. This overview provides insight into the anatomy, behavior, and classification of paramecium, making it a helpful resource for those interested in learning more about this fascinating microorganism. Cilia help in locomotion as well as in food collection. in paramecium, the entire body surface is covered by numerous, tiny hair. these cilia are arranged in longitudinal rows throughout the body. the length of the cilia is uniform but a few longer cilia are present at the posterior end. Paramecium is a eukaryotic genus commonly used as a ciliate model organism. this article will focus on details of paramecium, diagram , classification, characteristics, size, locomotion, reproduction and more. Paramecium is a well known animal like protist. this post covers the structure, sexual and asexual reproduction, mode of nutrition, and other life processes of paramecium. Despite its small size, paramecium exhibits complex cellular organization and behaviors, making it a frequent subject of biological study. paramecium’s place in classification paramecium belongs to the kingdom protista, a diverse group of eukaryotic organisms that are not animals, plants, or fungi.
.jpg)
Locomotion In Paramecium Superb Learning Destination Cilia help in locomotion as well as in food collection. in paramecium, the entire body surface is covered by numerous, tiny hair. these cilia are arranged in longitudinal rows throughout the body. the length of the cilia is uniform but a few longer cilia are present at the posterior end. Paramecium is a eukaryotic genus commonly used as a ciliate model organism. this article will focus on details of paramecium, diagram , classification, characteristics, size, locomotion, reproduction and more. Paramecium is a well known animal like protist. this post covers the structure, sexual and asexual reproduction, mode of nutrition, and other life processes of paramecium. Despite its small size, paramecium exhibits complex cellular organization and behaviors, making it a frequent subject of biological study. paramecium’s place in classification paramecium belongs to the kingdom protista, a diverse group of eukaryotic organisms that are not animals, plants, or fungi.
Comments are closed.