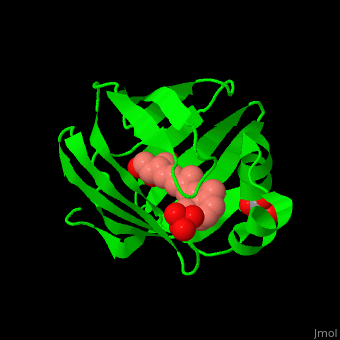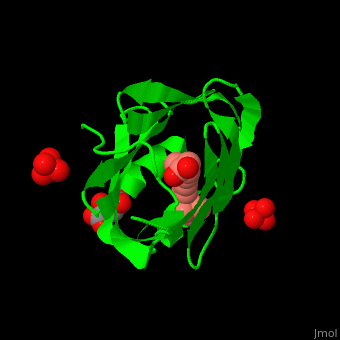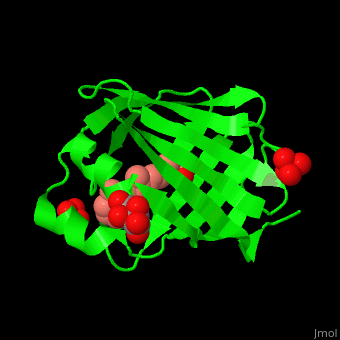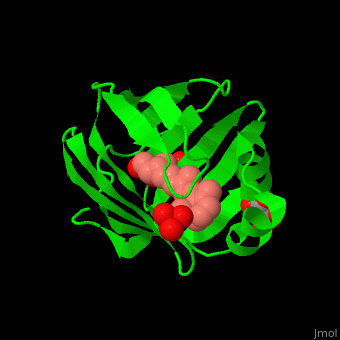
Retinol Binding Protein Proteopedia Life In 3d Purified cellular retinol binding protein (crbp), a potential mediator of vitamin a action, was found to enable retinol to bind in a specific manner to isolated nuclei from livers of vitamin a…. To better understand the physiological role of crbp2, we determined its protein lipid interactome using a fluorescence based retinol replacement assay adapted for a high throughput screening format.
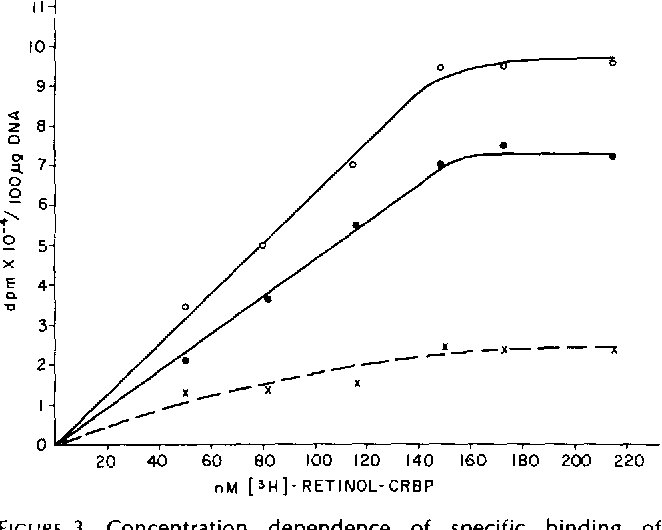
Figure 1 From Interaction Of The Retinol Cellular Retinol Binding The hypothesis that the cellular uptake of retinol in volves the specific interaction of a plasma membrane receptor with serum retinol binding protein (rbp) at the extracellular surface followed by ligand transfer to cytoplasmic cellular retinol binding protein (crbp) has been investigated. Previous studies that characterized the free all trans retinoids exist within the cell (2). cellular catalytic activity of human p450 27c1 utilized a reconstituted retinoid binding proteins mediate retinoid function and in vitro system with free retinoids. The remarkable difference in intrinsic stability between the two homologs appears to modulate their binding properties: the stronger retinol binder crbp i displays a reduced flexibility of the. Cellular retinol binding protein 1 (crbp1) gene is a protein coding gene located on human chromosome 3q21, which codifies a protein named crbp1. crbp1 is widely expressed in many tissues as a chaperone protein to regulate the uptake, subsequent esterification and bioavailability of retinol.
Figure 1 From Interaction Of The Retinol Cellular Retinol Binding The remarkable difference in intrinsic stability between the two homologs appears to modulate their binding properties: the stronger retinol binder crbp i displays a reduced flexibility of the. Cellular retinol binding protein 1 (crbp1) gene is a protein coding gene located on human chromosome 3q21, which codifies a protein named crbp1. crbp1 is widely expressed in many tissues as a chaperone protein to regulate the uptake, subsequent esterification and bioavailability of retinol. Retinol bound to cellular retinol binding protein (crbp) was found to be oxidized to retinoic acid by a soluble activity from calf liver. cytosolic retinoic acid synthesis from retinol crbp was strictly dependent on the exogenous supply of either nad or nadp. Using line shape analysis of nmr signals, we derived a mechanism of ligand binding that suggests that retinol, after an initial nonspecific encounter with the surface of apo crbp i, modulates site specific mobility of the protein by inducing the formation of long lived (millisecond to second) transiently open conformers in the portal region (27). The interactions with retinol and retinol analogs of bovine cellular retinol binding protein (crbp) have been investigated, by means of fluorescence titrations, to obtain more information on the structural features of retinoids that may be required for their interaction with the binding protein. We now report that pure crbp delivers retinol to the specific nuclear binding sites without itself remaining bound. triton x 100 treated nuclei retain the majority of these binding sites .
