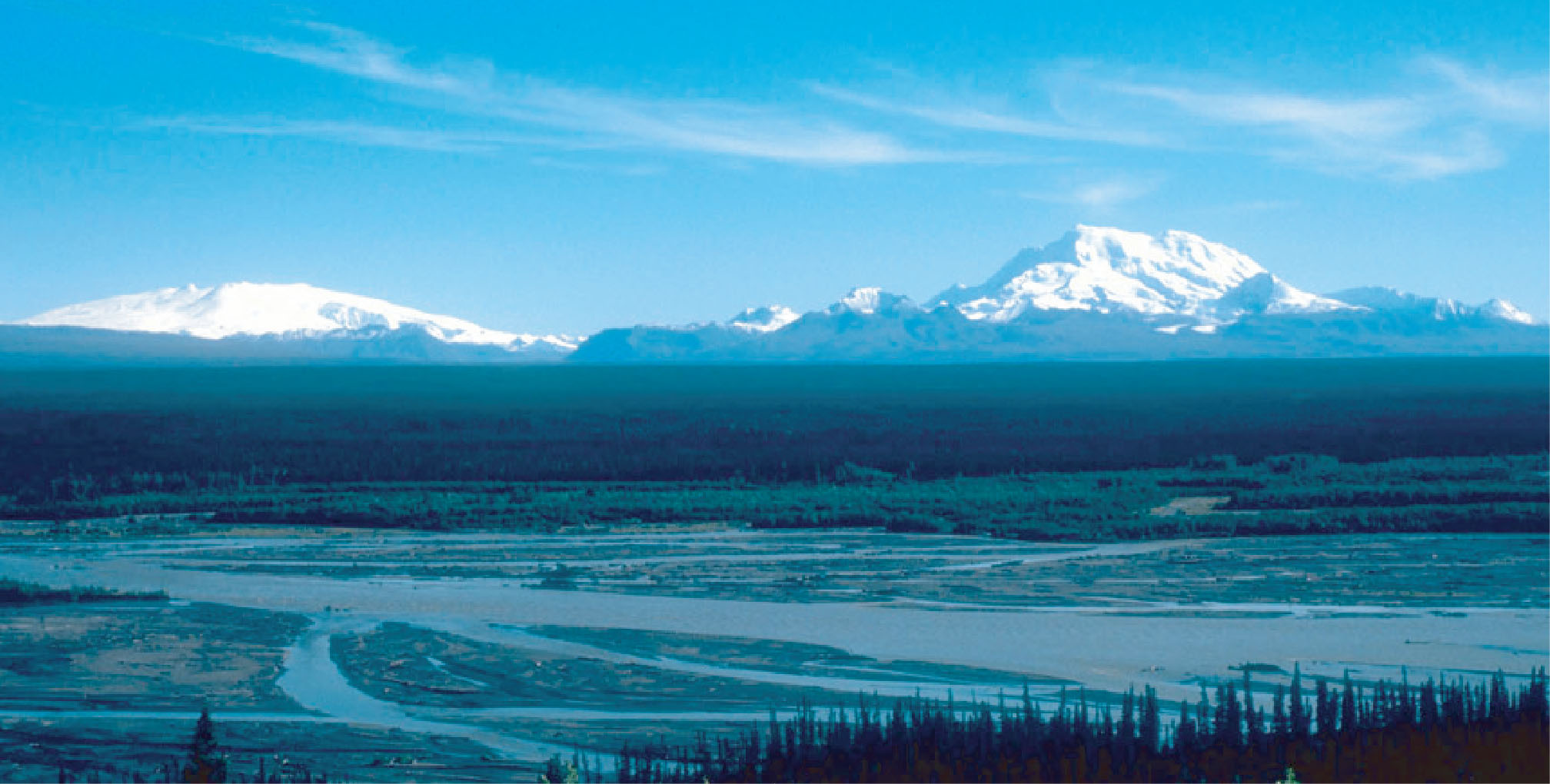

Convergent Plate Boundaries Subduction Zones Geology U S National The second important tectonic setting where many volcanoes occur is along or near converging plate boundaries. at most such boundaries, where two plates collide, the heavier of the two usually an oceanic one sinks (or is pulled) under the other plate, a process called subduction. The earth’s many tectonic plates can be thousands of miles across and underlie both continents and oceans. these plates collide, slide past, and move apart from each other. where they collide and one plate is thrust beneath another (a subduction zone), the most powerful earthquakes, tsunamis, volcanic eruptions, and landslides occur.
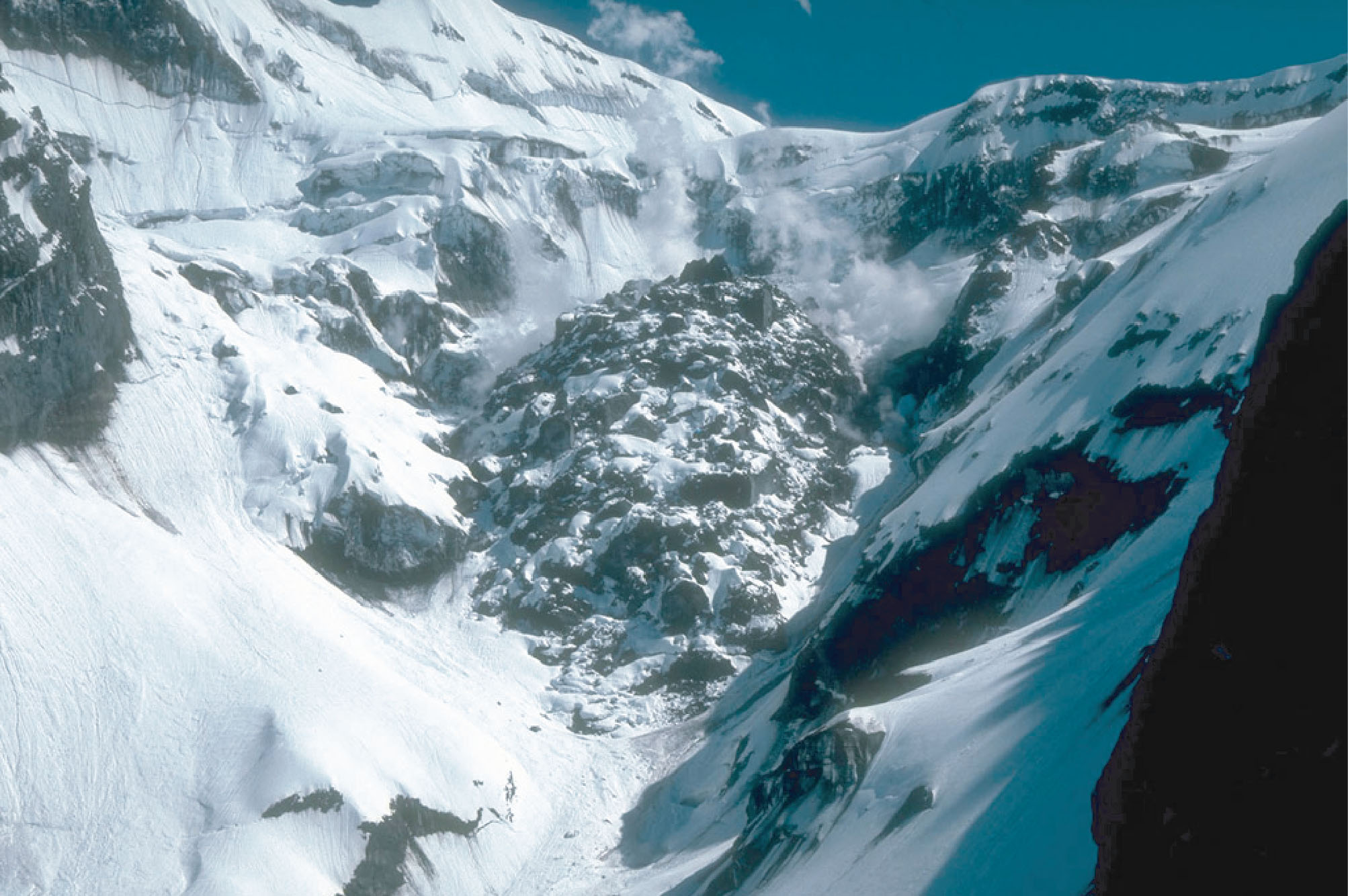

Convergent Plate Boundaries Subduction Zones Geology U S National The sinking of lithosphere in subduction zones provides most of the force needed to drive the plates and cause mid ocean ridges to spread, with the result that plate tectonics and subduction zones are surficial and interior expressions of earth's dominant tectonic mode. Forty million years ago, a large tectonic plate, known as the farallon plate, was between the pacific and north american plates. subduction of the farallon plate beneath the entire west coast created a line of volcanoes from alaska to central america. Subduction zone, oceanic trench area marginal to a continent in which, according to the theory of plate tectonics, older and denser seafloor underthrusts the continental mass, dragging downward into the earth’s upper mantle the accumulated trench sediments. Volcanodiscovery.
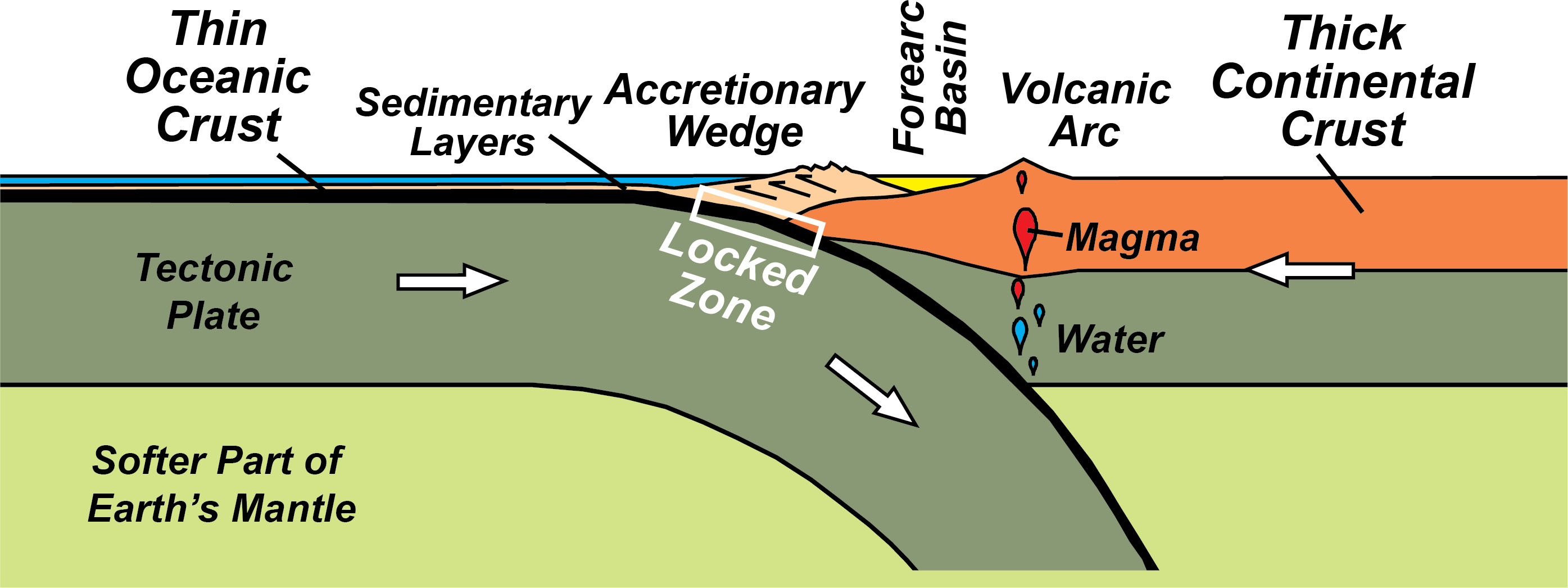
Convergent Plate Boundaries Subduction Zones Geology U S National Subduction zone, oceanic trench area marginal to a continent in which, according to the theory of plate tectonics, older and denser seafloor underthrusts the continental mass, dragging downward into the earth’s upper mantle the accumulated trench sediments. Volcanodiscovery. [1] subduction zones are where sediments, oceanic crust, and mantle lithosphere return to and reequilibrate with earth’s mantle. subduction zones are interior ex pressions of earth’s 55,000 km of convergent plate mar gins and are the geodynamic system that builds island arcs. Subduction zones pose threats to many societies, as they are the locus of destructive volcanic eruptions, earthquakes, and tsunamis. earth’s rocky outer layer is continuously being recycled. Explain how movement at the three types of plate boundaries causes earthquakes, volcanoes, and mountain building. identify convergent boundaries, including subduction and collisions, as places where plates come together. identify divergent boundaries, including rifts and mid ocean ridges, as places where plates separate. Plate tectonics is a scientific theory that explains how major landforms are created as a result of earth’s subterranean movements. the theory, which solidified in the 1960s, transformed the earth sciences by explaining many phenomena, including mountain building events, volcanoes, and earthquakes.

Convergent Plate Boundaries Subduction Zones Geology U S National [1] subduction zones are where sediments, oceanic crust, and mantle lithosphere return to and reequilibrate with earth’s mantle. subduction zones are interior ex pressions of earth’s 55,000 km of convergent plate mar gins and are the geodynamic system that builds island arcs. Subduction zones pose threats to many societies, as they are the locus of destructive volcanic eruptions, earthquakes, and tsunamis. earth’s rocky outer layer is continuously being recycled. Explain how movement at the three types of plate boundaries causes earthquakes, volcanoes, and mountain building. identify convergent boundaries, including subduction and collisions, as places where plates come together. identify divergent boundaries, including rifts and mid ocean ridges, as places where plates separate. Plate tectonics is a scientific theory that explains how major landforms are created as a result of earth’s subterranean movements. the theory, which solidified in the 1960s, transformed the earth sciences by explaining many phenomena, including mountain building events, volcanoes, and earthquakes.
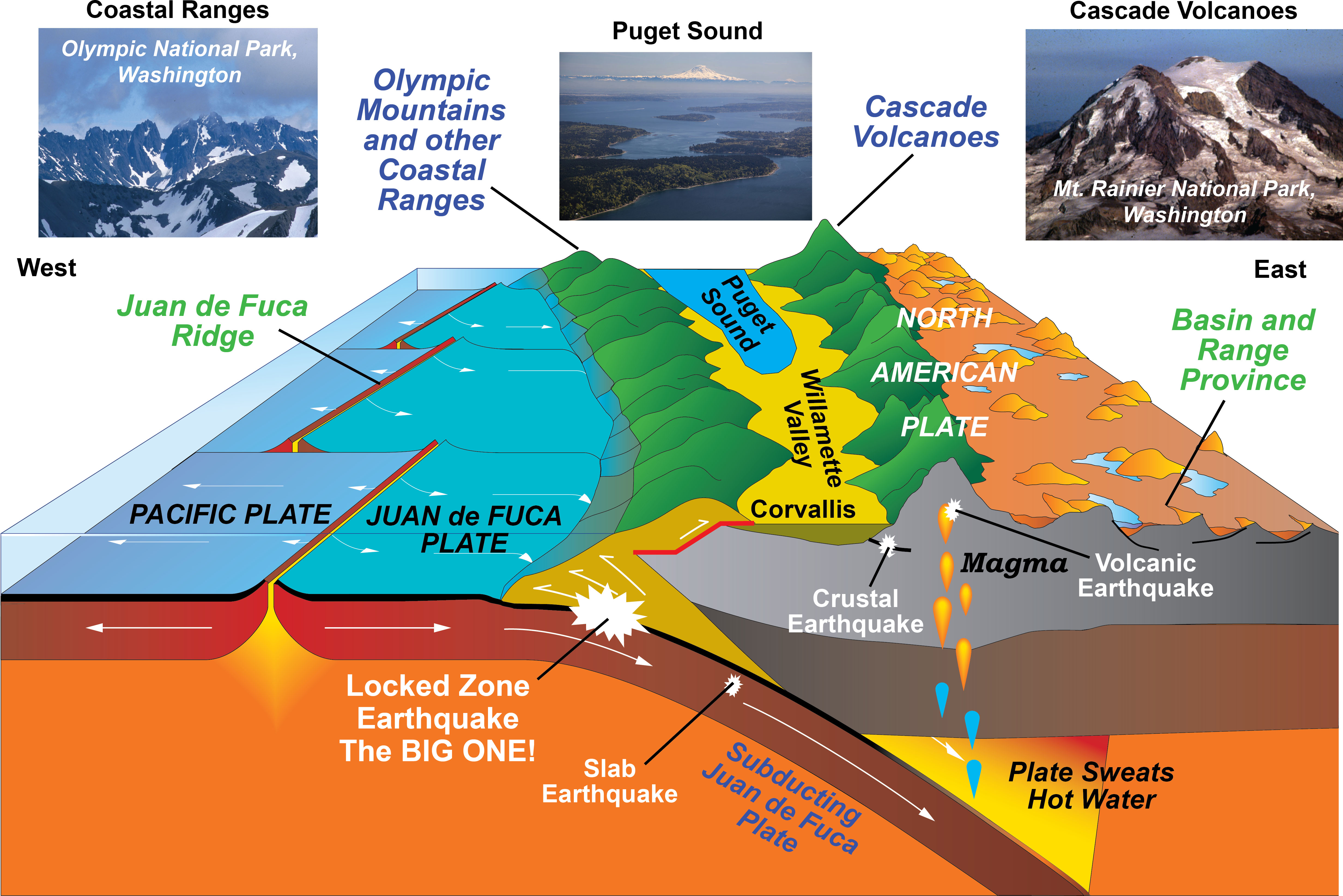
Convergent Plate Boundaries Subduction Zones Geology U S National Explain how movement at the three types of plate boundaries causes earthquakes, volcanoes, and mountain building. identify convergent boundaries, including subduction and collisions, as places where plates come together. identify divergent boundaries, including rifts and mid ocean ridges, as places where plates separate. Plate tectonics is a scientific theory that explains how major landforms are created as a result of earth’s subterranean movements. the theory, which solidified in the 1960s, transformed the earth sciences by explaining many phenomena, including mountain building events, volcanoes, and earthquakes.
