
Prevention Of Money Laundering Act Pmla 2002 Iasbaba Context: the supreme court will hear a review of its judgment upholding key provisions of the prevention of money laundering act (pmla), 2002. what was the supreme court ruling on pmla? in vijay madanlal choudhary & ors v union of india, the supreme court upheld the key provisions of the pmla. how is a judgment reviewed?. The apex court called the pmla a law against the “scourge of money laundering” and not a hatchet wielded against rival politicians and dissenters. the verdict came on an extensive challenge raised against the amendments introduced to the 2002 act by way of finance acts.
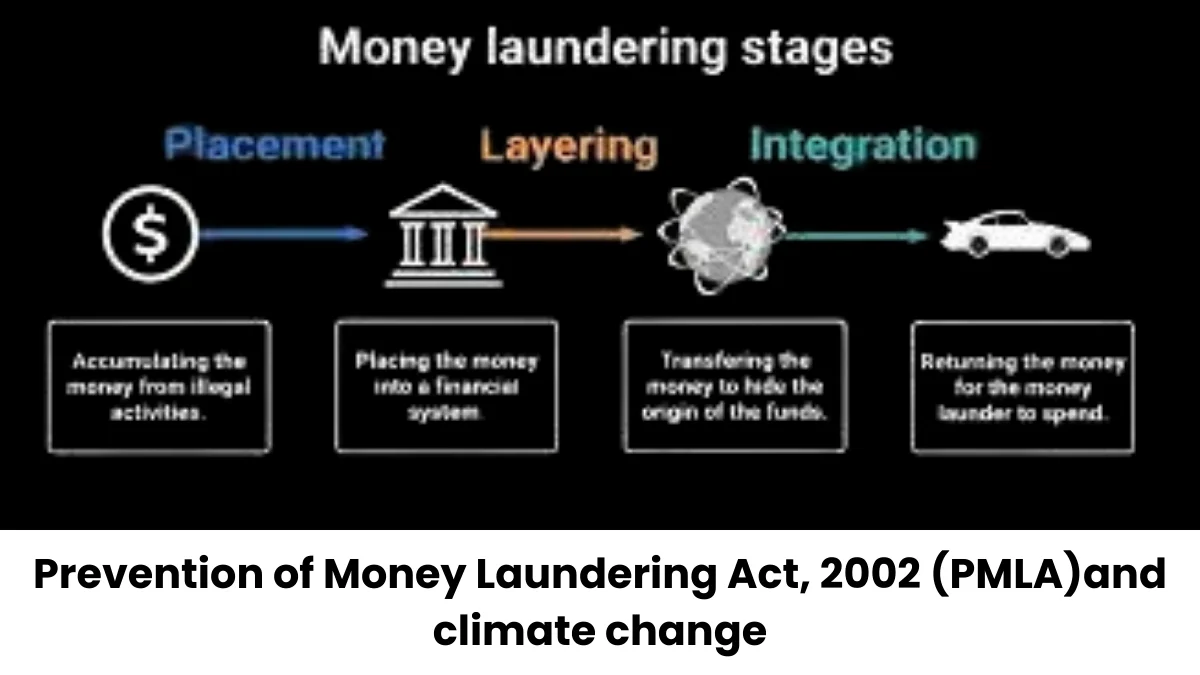
Prevention Of Money Laundering Act 2002 Pmla An act to prevent money laundering and to provide for confiscation of property derived from, or involved in, money laundering and for matters connected therewith or incidental thereto. w hereas the political declaration and global programme of action, annexed to the resolution. The prevention of money laundering act, 2002, was sanctioned with the aim of combating the issue of money laundering. some of its objectives are as follows: to prevent and control the issue of money laundering. The prevention of money laundering act (pmla), 2002, was enacted by the government of india to prevent and control money laundering and to confiscate property derived from illegal activities. it was passed in 2002 and came into force on 1st july 2005. The prevention of money laundering act (pmla), 2002 was enacted in january, 2003. the act seeks to combat money laundering in india and has three main objectives : to prevent and control money laundering.

Pmla Prevention Of Money Laundering Act 2002 Karthick Law Agency The prevention of money laundering act (pmla), 2002, was enacted by the government of india to prevent and control money laundering and to confiscate property derived from illegal activities. it was passed in 2002 and came into force on 1st july 2005. The prevention of money laundering act (pmla), 2002 was enacted in january, 2003. the act seeks to combat money laundering in india and has three main objectives : to prevent and control money laundering. The pmla seeks to combat money laundering in india and has three main objectives: to prevent and control money laundering. to confiscate and seize the property obtained from the laundered money; and; to deal with any other issue connected with money laundering in india. India enacted the prevention of money laundering act, 2002 in response to india’s global commitment to combat money laundering. through penalties and provisions for confiscating properties, the legislation looks to prevent the flow of money into illegal activities. important provisions of pmla, 2002. Objectives of prevention of money laundering act 2002. preventing money laundering; the pmla aims to stop money laundering and the channeling of money into illegal activities. confiscating property; the pmla allows for the seizure of property that is involved in or derived from money laundering. penalizing offenders.
