Problem 2 On Normal Stress On One Plane Accompanied By A Simple Shear Stress Strength Of Materials

Solved Question2 For The Case Of Plane Stress The Normal Chegg Subject strength of materials video name problem 2 on normal stress on one plane accompanied by a simple shear stress chapter principal stresses and planes. The video discusses the problem of finding normal and tangential stresses on an oblique plane in a strained material. the data provided includes the values of sigma x and tau shear stress.
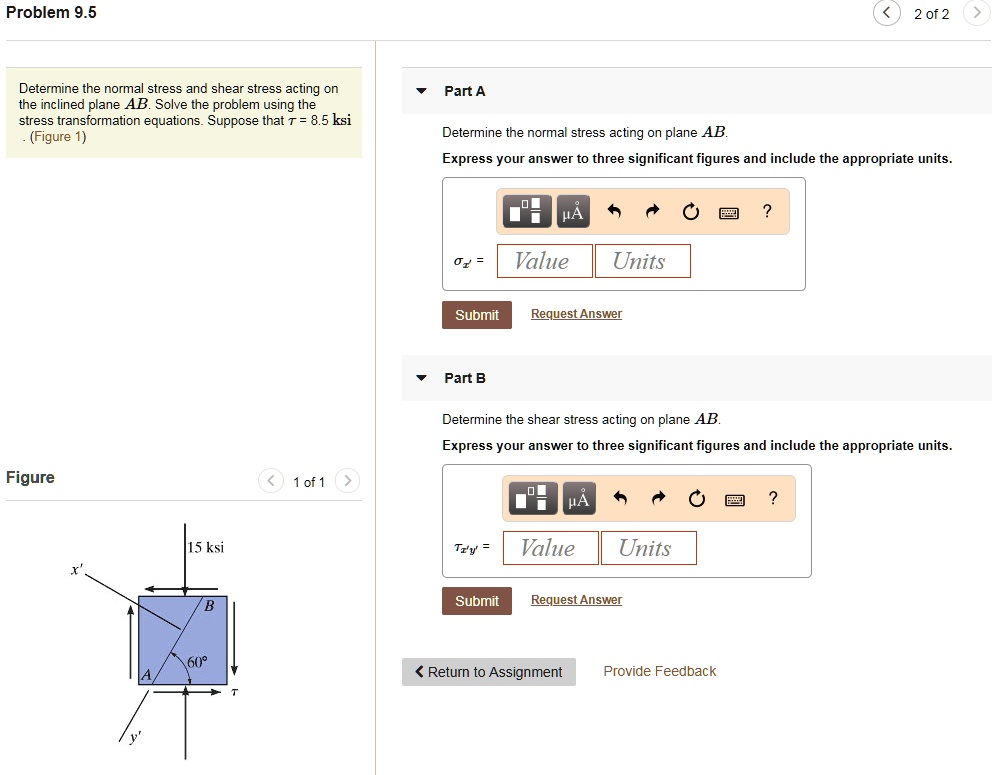
Solved Problem 9 5 2 Of 2 Determine The Normal Stress And Shear Stress A body is subjected to direct stresses in two mutually perpendicular directions accompanied by a simple shear stress. draw the mohrs circle of stresses and explain how will you obtain the principal stresses and principal planes. A quick glance at the stress matrix on the left shows a shear stress of 2 mpa on one plane and three normal stresses of 2, 5 and –5 mpa. the stress matrix on the right shows no shear stresses with three normal stresses of 1, –5 and 6 mpa. The given problem involves determining the maximum shear stress when the major and minor principal stresses are provided. let’s break down the solution step by step. Methodology to calculate the normal and the shear stress on an arbitrary plane that crosses a point in a rigid body in equilibrium.

Determine The Normal Stress And Shear Stress Acting Chegg The given problem involves determining the maximum shear stress when the major and minor principal stresses are provided. let’s break down the solution step by step. Methodology to calculate the normal and the shear stress on an arbitrary plane that crosses a point in a rigid body in equilibrium. The normal and shear stresses can be calculated on a plane of any orientation if the magnitude and direction of two of the three principal stresses (s 1, s 2, and s 3) are known. Mechanical engineering questions and answers section on "strength of materials section 8" for placement interviews and competitive exams: fully solved mechanical engineering problems with detailed answer descriptions and explanations are given for the "strength of materials section 8" section page 7. Stress is defined as the strength of a material per unit area, it is also called the unit strength. it is the force on a member divided by area, which carries the force, formerly express in psi, now in n mm 2 or mpa. A body is subjected to a direct tensile stress of 300 mpa in one plane accompanied by a simple shear stress of 200 mpa. the maximum normal stress on the plane will be.
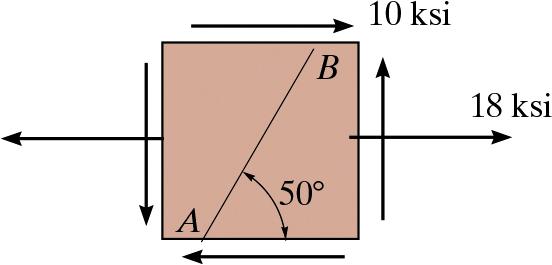
Solved Determine The Normal Stress And Shear Stress Acting Chegg The normal and shear stresses can be calculated on a plane of any orientation if the magnitude and direction of two of the three principal stresses (s 1, s 2, and s 3) are known. Mechanical engineering questions and answers section on "strength of materials section 8" for placement interviews and competitive exams: fully solved mechanical engineering problems with detailed answer descriptions and explanations are given for the "strength of materials section 8" section page 7. Stress is defined as the strength of a material per unit area, it is also called the unit strength. it is the force on a member divided by area, which carries the force, formerly express in psi, now in n mm 2 or mpa. A body is subjected to a direct tensile stress of 300 mpa in one plane accompanied by a simple shear stress of 200 mpa. the maximum normal stress on the plane will be.

Solved Determine The Normal Stress And Shear Stress Acting Chegg Stress is defined as the strength of a material per unit area, it is also called the unit strength. it is the force on a member divided by area, which carries the force, formerly express in psi, now in n mm 2 or mpa. A body is subjected to a direct tensile stress of 300 mpa in one plane accompanied by a simple shear stress of 200 mpa. the maximum normal stress on the plane will be.

Solved In The State Of The Plane Stress Shown Determine The Chegg
Comments are closed.