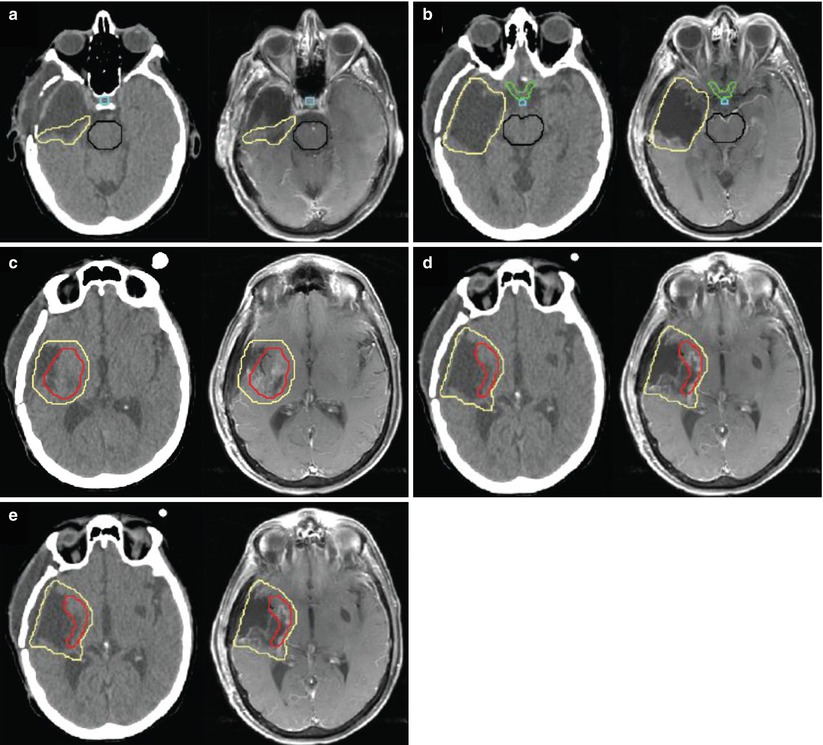
Radiation For Brain Metastases Radiology Key Stereotactic radiosurgery (srs) has been established as an excellent treatment option for a large subset of patients with metastatic brain disease. What is the physiological theory behind srs management of avms? radiation may multiply endothelial cells in the vessels, which increases clot formation, which decreases blood flow in the nidus. is srs or fractionated srt considered more efficacious in controlling acoustic neuroma growth?.

Radiation For Brain Metastases Radiology Key Brain metastases are diagnosed in approximately 20% to 40% of patients with neoplastic diseases 1 – 3 and thereby represent the most common intracranial malignancy, with lung, breast, and renal cancers, and melanoma as the most frequent primary tumors. 4, 5 the incidence of brain metastatic lesions appears to be increasing, possibly due to an. Stereotactic radiosurgery (srs) should be considered in the comprehensive treatment paradigm for all patients with brain metastases. this technique has proven benefits for local tumor control in individuals with as many as 4 lesions, and when combined with structured radiographic follow up, will lik …. Advances in imaging, patient immobilization techniques and radiotherapy planning software have expanded the scope of stereotactic radiosurgery (srs) for the treatment of brain metastases. Five fraction cyberknife radiotherapy for large brain metastases in critical areas: impact on the surrounding brain volumes circumscribed with a single dose equivalent of 14 gy (v14) to avoid radiation necrosis.

Brain Metastases Treatment Brainlab Org Advances in imaging, patient immobilization techniques and radiotherapy planning software have expanded the scope of stereotactic radiosurgery (srs) for the treatment of brain metastases. Five fraction cyberknife radiotherapy for large brain metastases in critical areas: impact on the surrounding brain volumes circumscribed with a single dose equivalent of 14 gy (v14) to avoid radiation necrosis. Surgery is probably more effective in relieving symptoms from metastases than other treatments,although formal proof of this is lacking. stereotactic radiosurgery can replace resection when the metastases are smaller than 3 cm and symptoms can be controlled with an acceptable steroid dose. The major treatment options for metastatic brain tumors include surgery, wbrt, and stereotactic radiosurgery. this article outlines the clinical evidence supporting patient selection, prognostic factors, and expected outcomes in the surgical management of metastatic brain tumors. Currently, the options for the management of brain metastasis include surgery, systemic chemotherapy, targeted therapies, stereotactic radiosurgery (srs), postoperative stereotactic radiosurgery, whole brain radiotherapy (wbrt), and their combination variants. By drawing references to these new data, this review outlines the key strategies for the treatment of cerebral metastases with a particular focus on defining the role of surgical resection versus radiation therapy in the overall management of the cancer patient.
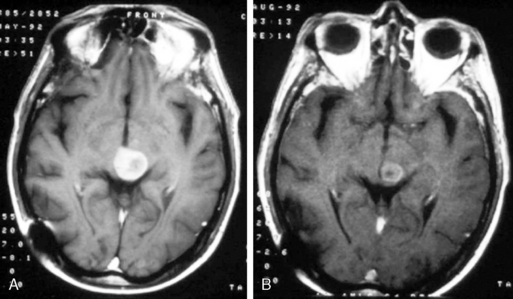
Brain Metastases Neupsy Key Surgery is probably more effective in relieving symptoms from metastases than other treatments,although formal proof of this is lacking. stereotactic radiosurgery can replace resection when the metastases are smaller than 3 cm and symptoms can be controlled with an acceptable steroid dose. The major treatment options for metastatic brain tumors include surgery, wbrt, and stereotactic radiosurgery. this article outlines the clinical evidence supporting patient selection, prognostic factors, and expected outcomes in the surgical management of metastatic brain tumors. Currently, the options for the management of brain metastasis include surgery, systemic chemotherapy, targeted therapies, stereotactic radiosurgery (srs), postoperative stereotactic radiosurgery, whole brain radiotherapy (wbrt), and their combination variants. By drawing references to these new data, this review outlines the key strategies for the treatment of cerebral metastases with a particular focus on defining the role of surgical resection versus radiation therapy in the overall management of the cancer patient.
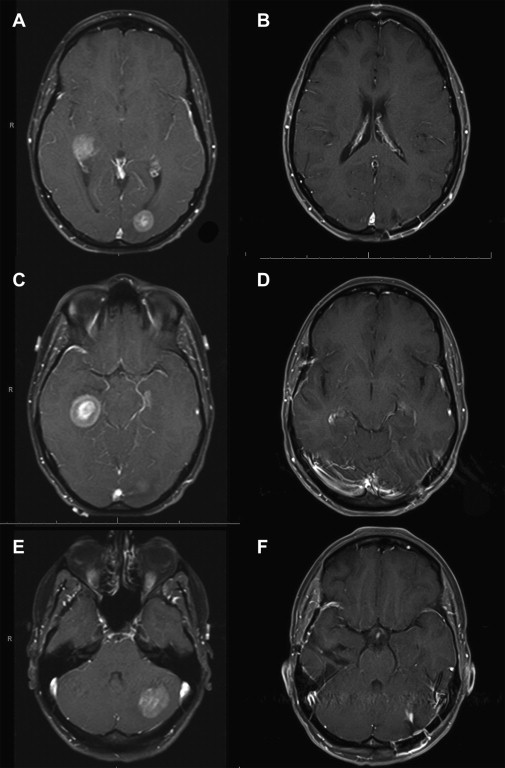
Surgical Management Of Brain Metastases Neupsy Key Currently, the options for the management of brain metastasis include surgery, systemic chemotherapy, targeted therapies, stereotactic radiosurgery (srs), postoperative stereotactic radiosurgery, whole brain radiotherapy (wbrt), and their combination variants. By drawing references to these new data, this review outlines the key strategies for the treatment of cerebral metastases with a particular focus on defining the role of surgical resection versus radiation therapy in the overall management of the cancer patient.
