Shorts 42 Difference Between The Volar Plate Of The Mcp Joint And The Pip Joint The Significance

A Skeletal View Of Normal Mcp Joint With Normally Placed Volar Plate B Get started creating shorts shorts is a way for anyone to connect with a new audience using just a smartphone and the shorts camera in the app. ’s shorts creation tools makes it easy to create short form videos that are up to 3 minutes long with our multi segment camera. changes to shorts views count. Да, shorts можно монетизировать. Вы сможете вступить в Партнерскую программу , если за последние 90 дней ваши shorts наберут 10 миллионов действительных просмотров и привлекут 1000 подписчиков.

A Skeletal View Of Normal Mcp Joint With Normally Placed Volar Plate B Shorts permite a los usuarios conectar con nuevos usuarios solo con un smartphone y la cámara de shorts en la aplicación . con las herramientas de creación de shorts de , puedes. 上传 shorts 短视频 有了 shorts,任何人只要发挥创意,就有机会吸引来自世界各地的新观众。 使用 的 shorts 创作工具,您可以上传短小精炼的竖屏短视频。. Для shorts продолжительностью менее одной минуты ограничения не изменились. Подробнее о требованиях к музыке для shorts … Часто задаваемые вопросы Какую музыку можно использовать?. 開始製作 shorts 有了 shorts,創作者只要準備智慧型手機,就能使用 應用程式內建的 shorts 相機拍短片,與新觀眾互動。 的 shorts 創作工具可讓你利用多段式相機拍攝多部短篇影片,輕鬆製作出長度 3 分鐘內的內容。 shorts 觀看次數計算方式.

A Skeletal View Of Normal Mcp Joint With Normally Placed Volar Plate B Для shorts продолжительностью менее одной минуты ограничения не изменились. Подробнее о требованиях к музыке для shorts … Часто задаваемые вопросы Какую музыку можно использовать?. 開始製作 shorts 有了 shorts,創作者只要準備智慧型手機,就能使用 應用程式內建的 shorts 相機拍短片,與新觀眾互動。 的 shorts 創作工具可讓你利用多段式相機拍攝多部短篇影片,輕鬆製作出長度 3 分鐘內的內容。 shorts 觀看次數計算方式. Shorts позволяет создавать короткие видео: их можно снимать камерой приложения или загружать с телефона. Кроме того, можно использовать фотографии. В этой статье рассказано, какие инст. Los shorts permiten que cualquier persona se conecte con un público nuevo. simplemente se necesitan un smartphone y la cámara de shorts en la app de . con las herramientas de creación de shorts de , se pueden producir fácilmente videos de formato corto de hasta 3 minutos con la cámara de varios segmentos. Shorts not getting on shorts feed i have face this multiple times , my shorts which suppose to be in shorts feed but not going there tried multiple time but face this same issue. more than 6 hours passed not a single feed recommendation , and some time even with a high audience retention video got stuck after 1000 1500 recommendation. Grâce à shorts, tous les créateurs peuvent toucher une nouvelle audience avec un simple smartphone et la caméra shorts disponible dans l'application . les outils de création de shorts permettent de créer facilement des vidéos courtes d'une durée maximum de 3 minutes pouvant combiner plusieurs extraits vidéo.

Scanning Protocols 6 Musculo Skeletal Joints And Tendons Case 6 4 Shorts позволяет создавать короткие видео: их можно снимать камерой приложения или загружать с телефона. Кроме того, можно использовать фотографии. В этой статье рассказано, какие инст. Los shorts permiten que cualquier persona se conecte con un público nuevo. simplemente se necesitan un smartphone y la cámara de shorts en la app de . con las herramientas de creación de shorts de , se pueden producir fácilmente videos de formato corto de hasta 3 minutos con la cámara de varios segmentos. Shorts not getting on shorts feed i have face this multiple times , my shorts which suppose to be in shorts feed but not going there tried multiple time but face this same issue. more than 6 hours passed not a single feed recommendation , and some time even with a high audience retention video got stuck after 1000 1500 recommendation. Grâce à shorts, tous les créateurs peuvent toucher une nouvelle audience avec un simple smartphone et la caméra shorts disponible dans l'application . les outils de création de shorts permettent de créer facilement des vidéos courtes d'une durée maximum de 3 minutes pouvant combiner plusieurs extraits vidéo.
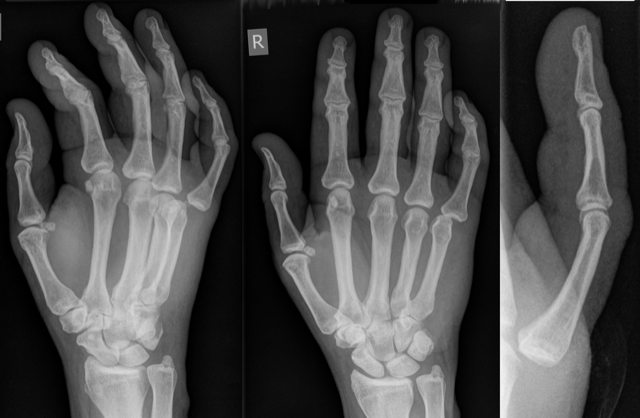
Deciphering Mcp Joint Deformity Shorts not getting on shorts feed i have face this multiple times , my shorts which suppose to be in shorts feed but not going there tried multiple time but face this same issue. more than 6 hours passed not a single feed recommendation , and some time even with a high audience retention video got stuck after 1000 1500 recommendation. Grâce à shorts, tous les créateurs peuvent toucher une nouvelle audience avec un simple smartphone et la caméra shorts disponible dans l'application . les outils de création de shorts permettent de créer facilement des vidéos courtes d'une durée maximum de 3 minutes pouvant combiner plusieurs extraits vidéo.

A Normal Mcp Joint On A Longitudinal Ultrasound View Note The Joint
Comments are closed.