Social Behavior And Brain Function In Autism Spectrum Disorder

Autism Brain Function Stock Illustration Illustration Of Asperger Objective: to identify patterns of social dysfunction in adolescents with autism spectrum disorder (asd), study the potential linkage between social brain networks and stereotyped behavior, and further explore potential targets of non invasive nerve stimulation to improve social disorders. In sum, the present paper provides an improved understanding of whole brain reorganization with social cognition that may detect asd and its pathological underpinnings in the prodromal stage.
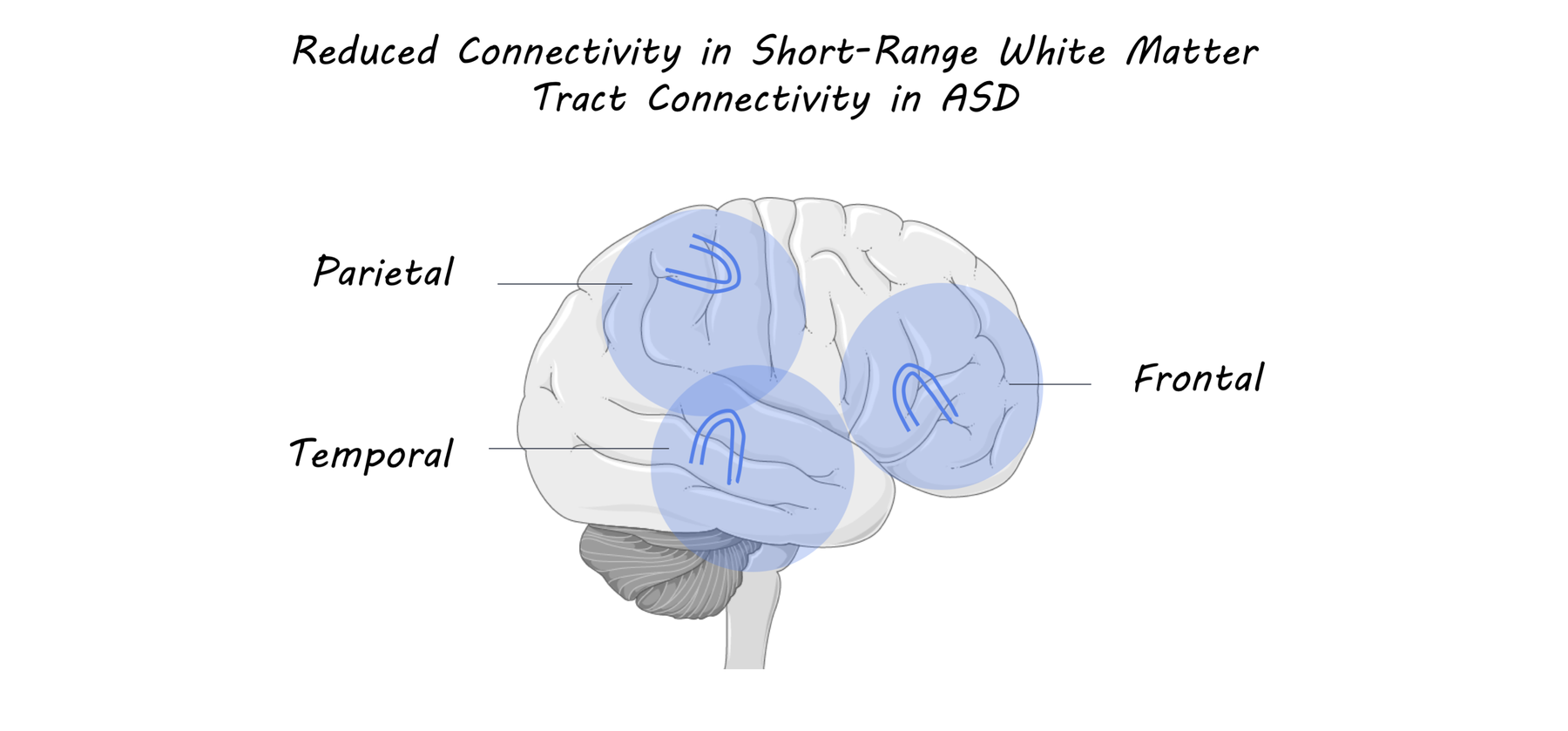
Decreased Short Range Brain Connections Linked To Social Symptoms Of In this issue of brain, d’albis and co workers illustrate the power of state of the art imaging methods to understand how differences in brain connectivity underlie differences in social cognitive abilities among those with asd (d’albis et al., 2018). Autism spectrum disorder (asd) is a lifelong neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by deficits in social communication as well as restricted, repetitive behaviors. these impairments emerge early in development and often present limitations to functioning throughout the life course. asd is also often accompanied by co occurring psychiatric conditions. this chapter presents a brief overview. Background difficulty in social inferences is a core feature in autism spectrum disorders (asd). on the behavioral level, it remains unclear whether reasoning about others’ mental states (theory of mind, tom) and empathic responses to others’ physical states may be similarly or differentially affected in autism. on the neural level, these inferences typically engage distinct brain networks. Autism spectrum disorder (asd) is a neurodevelopmental condition characterized by differences in brain development and function, impacting how individuals perceive others, engage in social interactions, and communicate, often involving restricted or repetitive behaviors.

Brain Connectivity Behavior Flag Four Autism Subtypes Spectrum Background difficulty in social inferences is a core feature in autism spectrum disorders (asd). on the behavioral level, it remains unclear whether reasoning about others’ mental states (theory of mind, tom) and empathic responses to others’ physical states may be similarly or differentially affected in autism. on the neural level, these inferences typically engage distinct brain networks. Autism spectrum disorder (asd) is a neurodevelopmental condition characterized by differences in brain development and function, impacting how individuals perceive others, engage in social interactions, and communicate, often involving restricted or repetitive behaviors. The presented model builds on earlier social brain research, and hypothesizes that four social brain regions largely drive asd symptomatology: amygdala, orbitofrontal cortex (ofc), temporoparietal cortex (tpc), and insula. Asds are neurodevelopmental disorders of social behavior deficits and repetitive restricted behaviors, affecting 1 in 31 children in the u.s. pharmacological interventions for the core symptoms of. Two neuropsychiatric disorders that have prominent social behavior abnormalities are autism spectrum disorders (asd), which is characterized mainly by hyposociability, and williams. Abstract this study aimed to provide a comprehensive overview of how individuals with autism spectrum condition (asc) process social motor coordination, focusing on joint action and its neural correlates, as examined through functional near infrared spectroscopy (fnirs) in comparing to their neurotypical (nt) counterparts.
Autism Spectrum Disorder Overview Vrogue Co The presented model builds on earlier social brain research, and hypothesizes that four social brain regions largely drive asd symptomatology: amygdala, orbitofrontal cortex (ofc), temporoparietal cortex (tpc), and insula. Asds are neurodevelopmental disorders of social behavior deficits and repetitive restricted behaviors, affecting 1 in 31 children in the u.s. pharmacological interventions for the core symptoms of. Two neuropsychiatric disorders that have prominent social behavior abnormalities are autism spectrum disorders (asd), which is characterized mainly by hyposociability, and williams. Abstract this study aimed to provide a comprehensive overview of how individuals with autism spectrum condition (asc) process social motor coordination, focusing on joint action and its neural correlates, as examined through functional near infrared spectroscopy (fnirs) in comparing to their neurotypical (nt) counterparts.
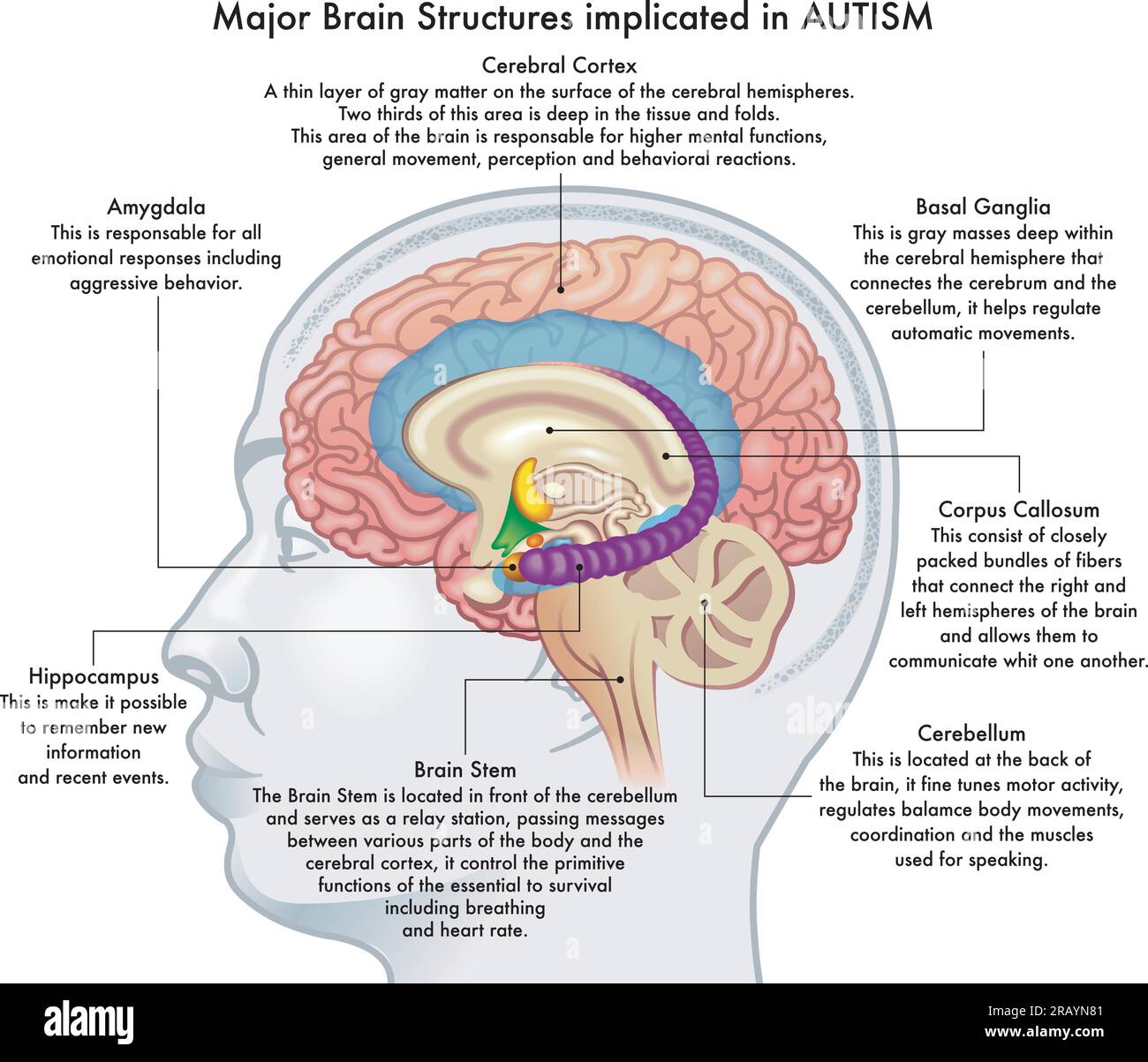
Medical Illustration Showing Major Brain Structures Implicated In Two neuropsychiatric disorders that have prominent social behavior abnormalities are autism spectrum disorders (asd), which is characterized mainly by hyposociability, and williams. Abstract this study aimed to provide a comprehensive overview of how individuals with autism spectrum condition (asc) process social motor coordination, focusing on joint action and its neural correlates, as examined through functional near infrared spectroscopy (fnirs) in comparing to their neurotypical (nt) counterparts.

Ppt Autism Spectrum Disorder Powerpoint Presentation Free Download
Comments are closed.