
Soil Health Assessment Nm Healthy Soil Working Group Using these four basic principles is the key to improving the health of your soil. diversify as much as possible using crop rotation and cover crops use the checklist on the back of this page to determine if you’re using some or all of the core soil health management system farming practices. Soil health cannot be measured directly, so we evaluate indicators. indicators are measurable properties of soil or plants that provide clues about how well the soil can function.

Soil Health Assessment Nm Healthy Soil Working Group Together, these three indicators and predicted available water holding capacity can inform stakeholders on how soil health management practices affect soil’s ability to support biomass production; store, filter, and transform nutrients and water; host biodiversity; and regulate c pools. Converting letter quantity readings to amounts an estimated bulk density of 1.29 g cm3 and a sampling depth of 8” (20.3 cm). to convert mg l ( t bulk density multiply the 2.18 factor by the new bulk density divided by 1.29. likewise, for a different soil sampling. Soil ph is a measure of how acidic the soil is and is an important indicator of soil health. it affects crop yields, crop suitability, plant nutrient availability and soil micro organism activity which influence key soil processes. Soil respiration for example estimates how active soil micro organisms are this depends on temperature range (80 105o f is ideal for most) and sufficient moisture (55 78% soil moisture preferred), so when sample matters!.

Soil Health Assessment Nm Healthy Soil Working Group Soil ph is a measure of how acidic the soil is and is an important indicator of soil health. it affects crop yields, crop suitability, plant nutrient availability and soil micro organism activity which influence key soil processes. Soil respiration for example estimates how active soil micro organisms are this depends on temperature range (80 105o f is ideal for most) and sufficient moisture (55 78% soil moisture preferred), so when sample matters!. In this blog, we provide an overview of the (1) physical properties, (2) biological properties, and (3) chemical properties used as soil quality indicators. additional information is provided for those that want to dig deeper with thanks to the nrcs, the soil health institute, and other resources. Schedule soil tests every 1 3 years to monitor changes. employ tools like the soil health card or comprehensive assessment of soil health. watch for compaction, erosion, or sudden changes in crop health. review and improve practices based on monitoring outcomes. use gis mapping, sensors, and iot tools for targeted interventions. Suite of soil health indicators the soil health institute (shi) partnered with over 100 scientists at 124 long term agricultural research sites in the u.s., canada, and mexico to evaluate over 30 soil health indicators and identify a minimum suite of practical, aforda. Use of a soil health assessment allows for comparing results with those from like soils, and to understand where a particular field may be on a soil health continuum.
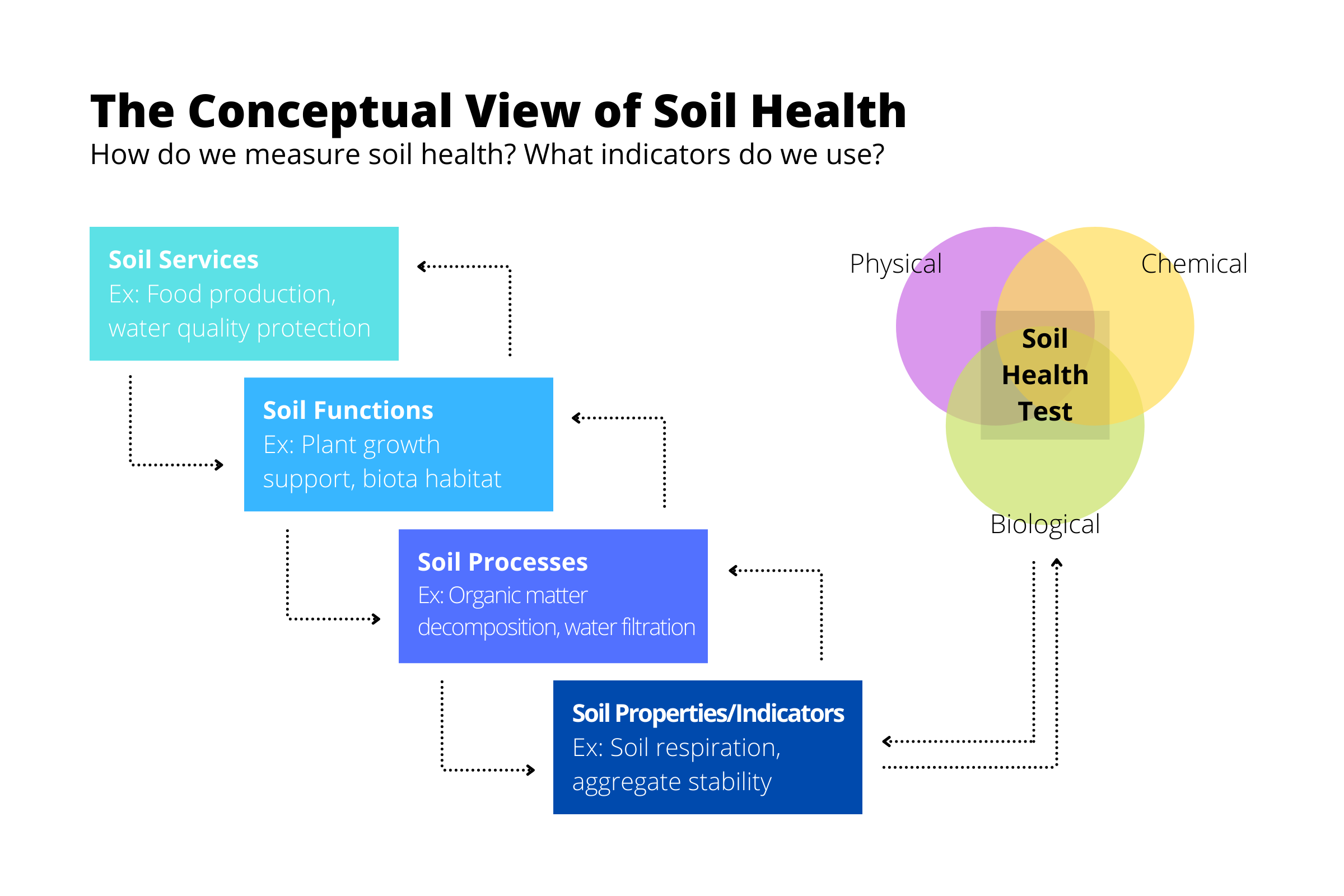
Soil Health What You Should Know Tci In this blog, we provide an overview of the (1) physical properties, (2) biological properties, and (3) chemical properties used as soil quality indicators. additional information is provided for those that want to dig deeper with thanks to the nrcs, the soil health institute, and other resources. Schedule soil tests every 1 3 years to monitor changes. employ tools like the soil health card or comprehensive assessment of soil health. watch for compaction, erosion, or sudden changes in crop health. review and improve practices based on monitoring outcomes. use gis mapping, sensors, and iot tools for targeted interventions. Suite of soil health indicators the soil health institute (shi) partnered with over 100 scientists at 124 long term agricultural research sites in the u.s., canada, and mexico to evaluate over 30 soil health indicators and identify a minimum suite of practical, aforda. Use of a soil health assessment allows for comparing results with those from like soils, and to understand where a particular field may be on a soil health continuum.
