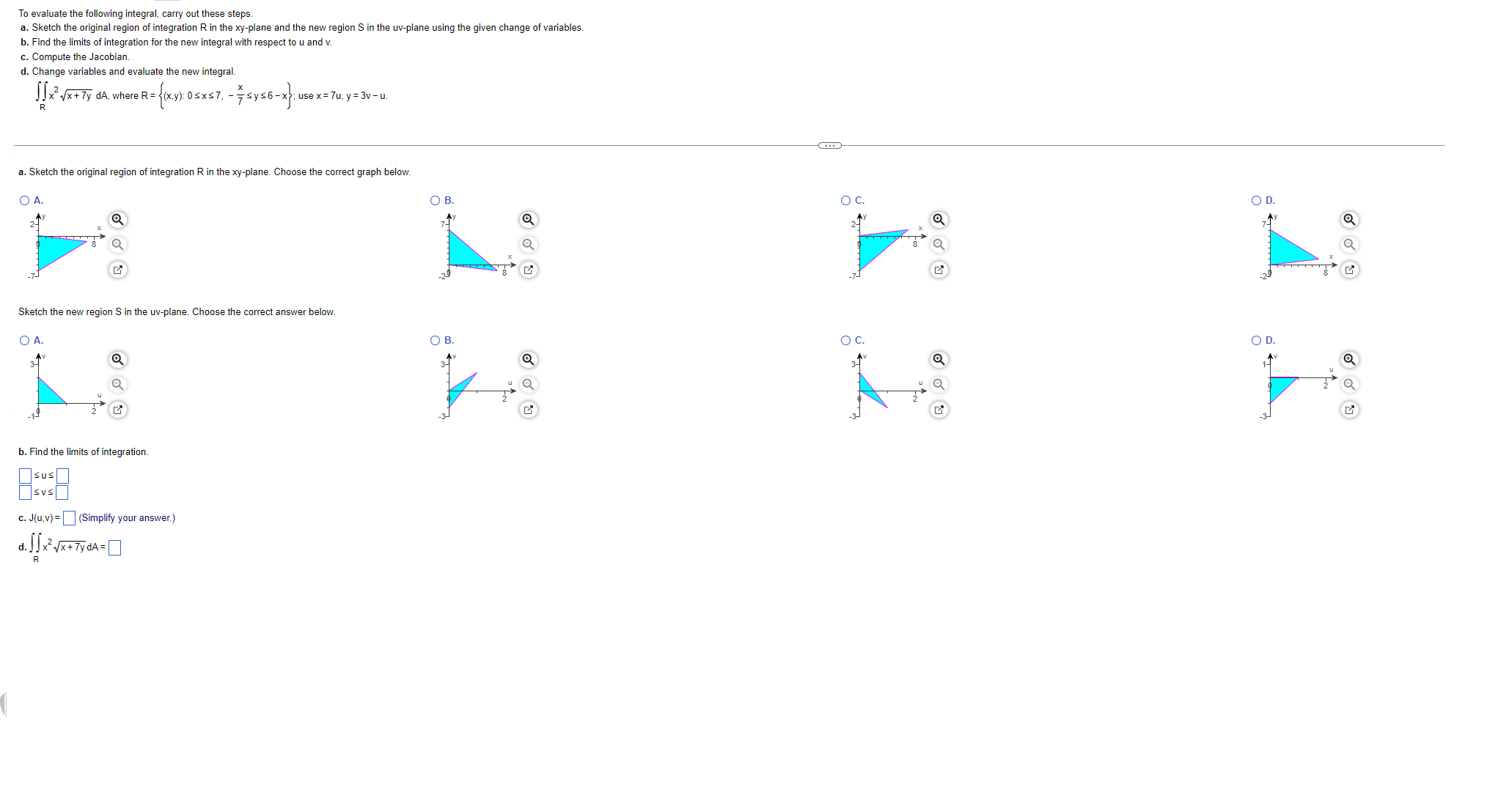
Solve The Following Chegg Here’s the best way to solve it. first, create a payoff matrix for both players with the given values. not the question you’re looking for? post any question and get expert help quickly. There are 2 steps to solve this one. to start solving for the nash equilibrium, first represent player 1 (p1) and player 2 (p2) and their potential payoffs listed in each cell in the provided game matrix. the answer is option 3 is . (b,l) a nash equilibrium is a situation where no player has any incen 1.
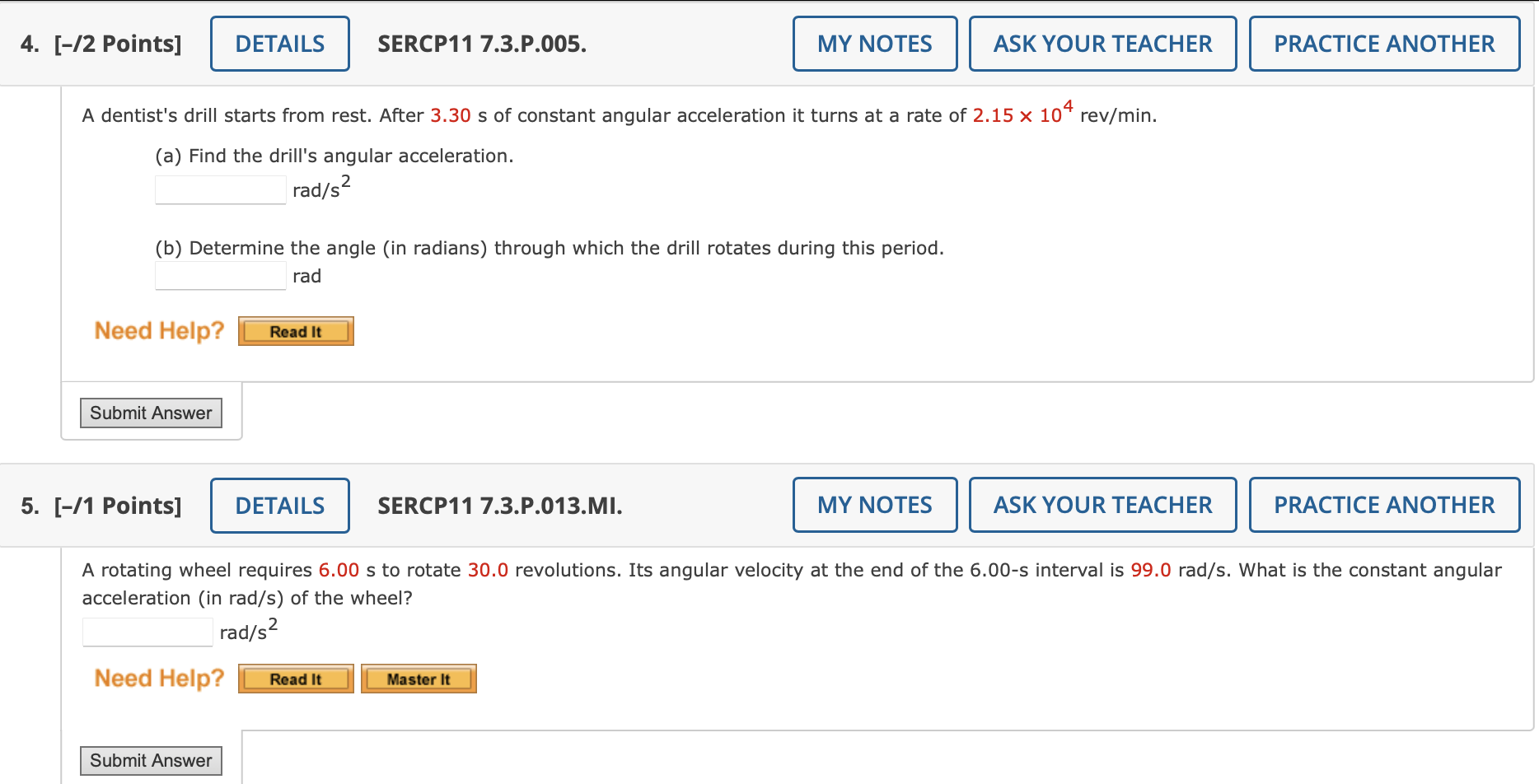
Solved Solve The Following Chegg Our expert help has broken down your problem into an easy to learn solution you can count on. question: solve the following game. there are 2 steps to solve this one. solve the following game. not the question you’re looking for? post any question and get expert help quickly. answer to solve the following game. • since the whole game is always a subgame, every spne is a nash equilibrium, we thus say that spne is a refinement of nash equilibrium • simultaneous move games have no proper subgames and thus every nash equilibrium is subgame perfect • spne can be found using a simple algorithm known as backward induction (cf zermelo 1913). This ai generated tip is based on chegg's full solution. sign up to see more! to solve the game with the given pay off matrix, determine the largest element in each row and the smallest element in each column. Homework 3 solutions extensive form games, subgame perfect equilibrium and repeated games. obtain the nash equilibrium for the following games using backward induction: solution. solution. for \(p 3\), \(b\) dominates \(a\), for \(p 2\), \(b\) dominates \(a\), finally \(a\) dominates \(b\) for \(p 1\): solution. solution.
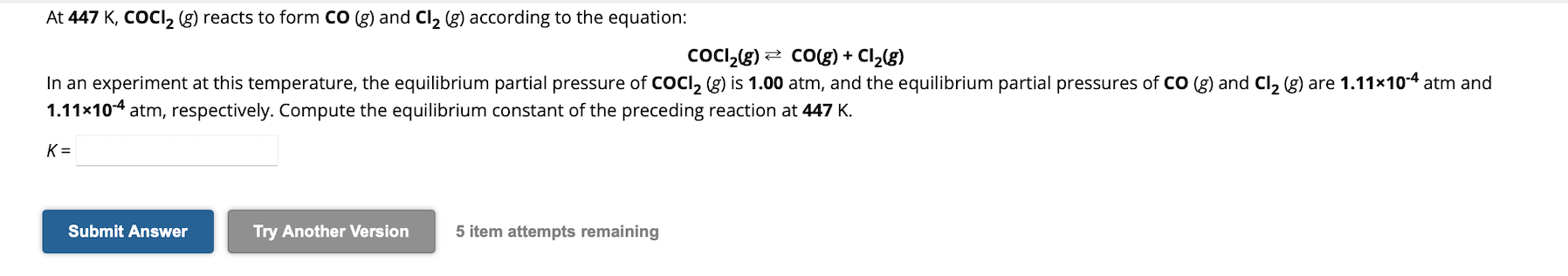
Solved Solve The Following Chegg This ai generated tip is based on chegg's full solution. sign up to see more! to solve the game with the given pay off matrix, determine the largest element in each row and the smallest element in each column. Homework 3 solutions extensive form games, subgame perfect equilibrium and repeated games. obtain the nash equilibrium for the following games using backward induction: solution. solution. for \(p 3\), \(b\) dominates \(a\), for \(p 2\), \(b\) dominates \(a\), finally \(a\) dominates \(b\) for \(p 1\): solution. solution. A subgame perfect nash equilibrium is a nash equilibrium because the entire game is also a subgame. the converse is not true. there can be a nash equilibrium that is not subgame perfect. for example, the above game has the following equilibrium: player 1 plays in the beginning, and they would have played ( ) in the proper subgame, as. When a game does not have any dominant or dominated strategies, or when the iterated deletion of dominated strategies does not yield a unique outcome, we find equilibria using the best response (also called best reply) method. Our expert help has broken down your problem into an easy to learn solution you can count on. question: game theory end of chapter problem solve the following game by trimming the branches of the accompanying game tree. Solution: the only subgame is the game itself, rooted at x:thus, a strategy pro le is subgame perfect if and only if it is a nash equilibrium. the subgame perfect equilibria in.
