
Solved Let U 1 2 3 4 5 A 1 2 4 5 7 B 2 3 5 6 Let Chegg Our expert help has broken down your problem into an easy to learn solution you can count on. question: 1. a. let ~u = (1, 2, −3, 5, 0), ~v = (0, 4, −1, 1, 2), and ~w = (7, 1, −4, −2, 3). find the components of i. ~v ~w ii. 3 (2~u − ~v) iii. (3~u − ~v) − (2~u 4 ~w) iv. 1 2 ( ~w − 5~v 2~u) ~v b. Given the vectors \mathbf {u} = (1, 2, 3, 5, 0), \mathbf {v} = (0, 4, 1, 1, 2), and \mathbf {w} = (7, 1, brainly . to find the components of v ~w, simply add the corresponding components of the two vectors together. to find the components of 3 (2 u v), subtract ~v from 2 u, then multiply the result by 3.

Solved 1 Let U 2 0 4 V 3 1 6 And W 2 5 5 Chegg (a) among all the points on the plane v in r4 spanned by the vectors vi= (1,1,1,1) and u2 = ( 1,0,1,2), find the one that is closest to the vector y = ( 5,3,2,6). moreover, express this closest vector as a linear combination of v1 and u2. [4] (b) consider the data points x 1.0 1.0 1. let w be the columnspace of the matrix 4 31 1 m = 1. Free math problem solver answers your algebra homework questions with step by step explanations. Let ~u = (1, 2, −3, 5, 0), ~v = (0, 4, −1, 1, 2), and ~w = (7, 1, −4, −2, 3). find the components of. i) 4 (3u v) 2) ( 2u v) (3u 4w) 3) 1 2 ( w − 5v 2u) v. can some one explained to me how to solve the above questions. am not really intresting in how the anwer was derived but rather the step in getting the final answer. thanks. (1). Find the components of the vector x that satisfies the equation 2u v x = 7x w (b) find the unit vector in the direction of (5,0,12). (c) let u = (2,1,0,1, 1) and v = ( 2,3,1,0,2). find scalars a and b so that au bv = ( 8,8, 3, 1,7). here’s the best way to solve it. q5 (a) let u = (1, 2, 3,5,0), v = (0,4, 1,1,2), and w = (7,1, 4, 2,3).
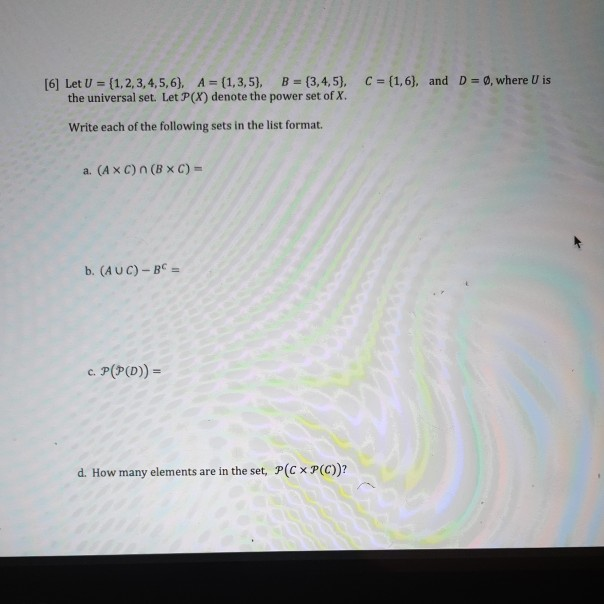
Solved 6 Let U 1 2 3 4 5 6 A 1 3 5 B 3 4 5 Chegg Let ~u = (1, 2, −3, 5, 0), ~v = (0, 4, −1, 1, 2), and ~w = (7, 1, −4, −2, 3). find the components of. i) 4 (3u v) 2) ( 2u v) (3u 4w) 3) 1 2 ( w − 5v 2u) v. can some one explained to me how to solve the above questions. am not really intresting in how the anwer was derived but rather the step in getting the final answer. thanks. (1). Find the components of the vector x that satisfies the equation 2u v x = 7x w (b) find the unit vector in the direction of (5,0,12). (c) let u = (2,1,0,1, 1) and v = ( 2,3,1,0,2). find scalars a and b so that au bv = ( 8,8, 3, 1,7). here’s the best way to solve it. q5 (a) let u = (1, 2, 3,5,0), v = (0,4, 1,1,2), and w = (7,1, 4, 2,3). Find step by step linear algebra solutions and your answer to the following textbook question: let u = (1, 2, 3, 5, 0), v=(0, 4, 1, 1, 2), and w=(7, 1, 4, 2, 3). find the components of (a) v w. (b) 3(2u v). I tried firstly to find dim of u ∩ ∩ v , by formula dim (u v)=dimu dimv dim (u ∩ ∩ v). dimu comes to be 2, dim v is 3, dimu v comes to be 3, so dim (u ∩ ∩ v) becomes 2. so option 2 and 3 got eliminated. but how to decide if it is option 1 or option4? also is there a fast approach to this problem? what are u, v u, v, to begin with?. Basis v1 = (1,2,3), v2 = (1,0,1), v3 = (1,2,1) to the basis u1 = (1,1,0), u2 = (0,1,1), u3 = (1,1,1). it is convenient to make a two step transition: first from v1,v2,v3 to e1,e2,e3, and then from e1,e2,e3 to u1,u2,u3. let u1 be the transition matrix from v1,v2,v3 to e1,e2,e3 and u2 be the transition matrix from u1,u2,u3 to e1,e2,e3: u1 = 1 1. Find scalars c1,c2,c2, and c3 for which the equation is satisfied, c1 (−1,0,2) c2 (2,2,−2) c3 (iv. 21 (w−5v 2u) v b. your solution’s ready to go! our expert help has broken down your problem into an easy to learn solution you can count on. question: a. let u= (1,2,−3,5,0), v= (0,4,−1,1,2) and w= (7,1,−4,−2,3).

Solved Let U 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 And Chegg Find step by step linear algebra solutions and your answer to the following textbook question: let u = (1, 2, 3, 5, 0), v=(0, 4, 1, 1, 2), and w=(7, 1, 4, 2, 3). find the components of (a) v w. (b) 3(2u v). I tried firstly to find dim of u ∩ ∩ v , by formula dim (u v)=dimu dimv dim (u ∩ ∩ v). dimu comes to be 2, dim v is 3, dimu v comes to be 3, so dim (u ∩ ∩ v) becomes 2. so option 2 and 3 got eliminated. but how to decide if it is option 1 or option4? also is there a fast approach to this problem? what are u, v u, v, to begin with?. Basis v1 = (1,2,3), v2 = (1,0,1), v3 = (1,2,1) to the basis u1 = (1,1,0), u2 = (0,1,1), u3 = (1,1,1). it is convenient to make a two step transition: first from v1,v2,v3 to e1,e2,e3, and then from e1,e2,e3 to u1,u2,u3. let u1 be the transition matrix from v1,v2,v3 to e1,e2,e3 and u2 be the transition matrix from u1,u2,u3 to e1,e2,e3: u1 = 1 1. Find scalars c1,c2,c2, and c3 for which the equation is satisfied, c1 (−1,0,2) c2 (2,2,−2) c3 (iv. 21 (w−5v 2u) v b. your solution’s ready to go! our expert help has broken down your problem into an easy to learn solution you can count on. question: a. let u= (1,2,−3,5,0), v= (0,4,−1,1,2) and w= (7,1,−4,−2,3).

Solved Let U 3 1 0 2 2 And V 1 1 5 4 0 And Chegg Basis v1 = (1,2,3), v2 = (1,0,1), v3 = (1,2,1) to the basis u1 = (1,1,0), u2 = (0,1,1), u3 = (1,1,1). it is convenient to make a two step transition: first from v1,v2,v3 to e1,e2,e3, and then from e1,e2,e3 to u1,u2,u3. let u1 be the transition matrix from v1,v2,v3 to e1,e2,e3 and u2 be the transition matrix from u1,u2,u3 to e1,e2,e3: u1 = 1 1. Find scalars c1,c2,c2, and c3 for which the equation is satisfied, c1 (−1,0,2) c2 (2,2,−2) c3 (iv. 21 (w−5v 2u) v b. your solution’s ready to go! our expert help has broken down your problem into an easy to learn solution you can count on. question: a. let u= (1,2,−3,5,0), v= (0,4,−1,1,2) and w= (7,1,−4,−2,3).

Solved Let U 1 0 2 And V 3 2 4 Compute 2u V Chegg
